AI in ERP: Examples and Top Software
With generative AI reshaping how we work, ERP vendors are labeling everything from old workflow rules to basic ChatGPT wrappers as AI. This guide cuts through all the noise to show you the ERP systems actually driving AI innovation today.
ERP AI Today
How Does AI Factor into ERP?
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software is a suite of business applications integrating financials, sales, and operations. While it already automates repetitive processes, AI adds reasoning. It can infer patterns and relationships between thousands of data points.
Most companies don’t build or train their own AI models. Instead, they:
- Rely on AI integration delivered by ERP vendors
- Use prebuilt models embedded in their ERP system
- Improve outputs by supplying better context data (like ERP records)
- Rarely, fine-tune a model for niche workflows
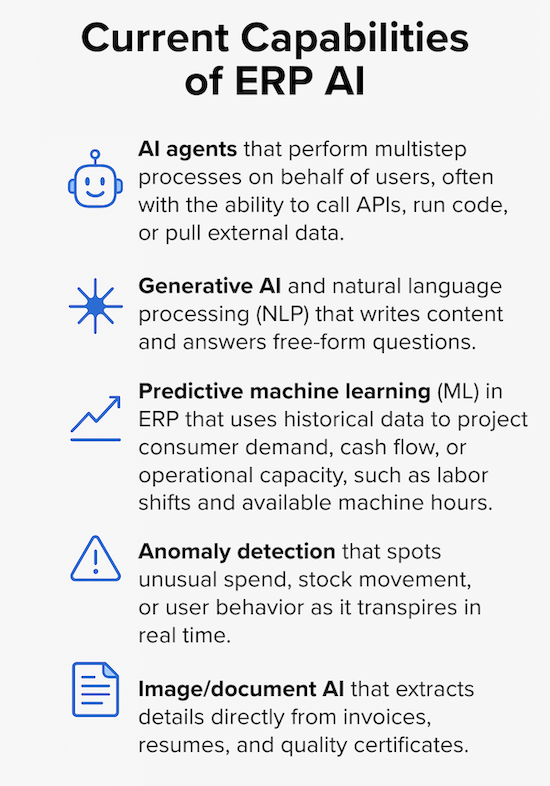
Current Capabilities of ERP AI
Artificial intelligence in ERP systems so far has typically manifested as:
- AI agents that perform multistep processes on behalf of users, often with the ability to call APIs, run code, or pull external data.
- Generative AI and natural language processing (NLP) that writes content and answers free‑form questions; can also perform AI summarization.
- Predictive machine learning in ERP that uses trained ML algorithms to project consumer demand, cash flow, or operational capacity, such as labor shifts and available machine hours.
- Anomaly detection that spots unusual spend, stock movement, or user behavior as it transpires in real time.
- Image / document AI that extracts details directly from invoices, resumes, and quality certificates.
Why This Tech Is Still Worth Watching
An IBM survey of 2,000 CEOs shows only 25 % of AI initiatives deliver a return on investment. However, artificial intelligence tools in ERP systems aren’t all hype:
- ERP systems provide clean, structured data, ideal for enriching context windows in AI-driven tools.
- Vendors keep pushing new use‑cases: for example, SAP plans 400 embedded AI scenarios by year‑end 2025.
- Investment and GPU spending remain high, with promising proof of concepts.
- Companies with strict data governance see an immediate productivity boost, giving users a clear reason to keep systems organized.
Industry watchers consistently name Microsoft Dynamics 365, SAP S/4HANA with Joule AI, Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP with AI Agent Studio, and Infor CloudSuite as top innovators for their deeply embedded AI in ERP systems.
AI in ERP Examples
Proven Use Cases
The earliest examples of AI in the enterprise market are everywhere now: think first-tier customer support chatbots or auto-drafted email responses. However, ERP tools continue to develop to provide even deeper value:
AI Agents
Agentic AI handles multi-phase tasks on your behalf. It triggers intelligent workflow automation and doesn’t require detailed instructions at every stage, saving you from running batch jobs or hopping between tabs.
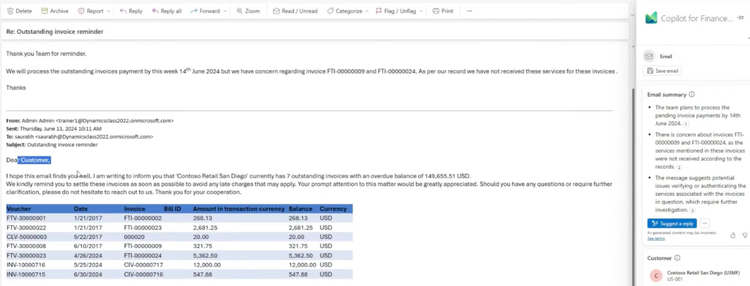
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance – Collections Coordinator Copilot
Microsoft allows you to build AI-driven assistants called Copilots inside products like Dynamics 365; this is a very similar process to creating a custom GPT in ChatGPT. In addition to custom copilots, you can use preloaded agents like the Collections Copilot right out of the box.
In the Collections Coordinator workspace, an LLM:
- Summarizes a customer’s overdue invoices
- Writes a personalized dunning email
- Marks an invoice “promised to pay” or “disputed” via the Copilot for Finance Outlook add‑in
The status instantly syncs to AR ledgers and helps reduce time spent chasing overdue payments.
Generative AI in ERP
GenAI converts structured data to human language and vice versa. It also answers ad‑hoc questions and devises marketing content.
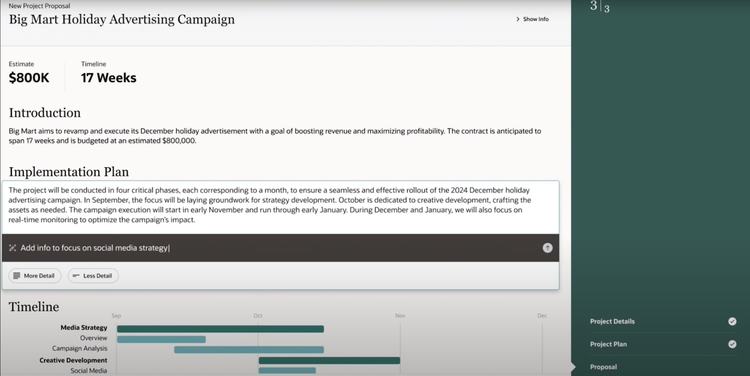
Oracle Cloud ERP – Project Planning AI
A project manager can click “Create Project Plan” inside the proposal editor. The AI assistant pulls two similar historical campaigns, merges their tasks, and recalculates resource costs, all through a natural language interface. If margins dip below target, it automatically suggests lower-cost resources and refreshes the entire WBS in seconds.
You can refine the output with prompts like “add info to focus on social media strategy.” From there, Oracle’s generative assistant rewrites project details like implementation plans using performance stats, channel-specific language, and campaign data.
Machine Learning
Machine learning models adjust using trends in past data, which helps ERP systems evolve from static rules to intelligent classification and forecasting.
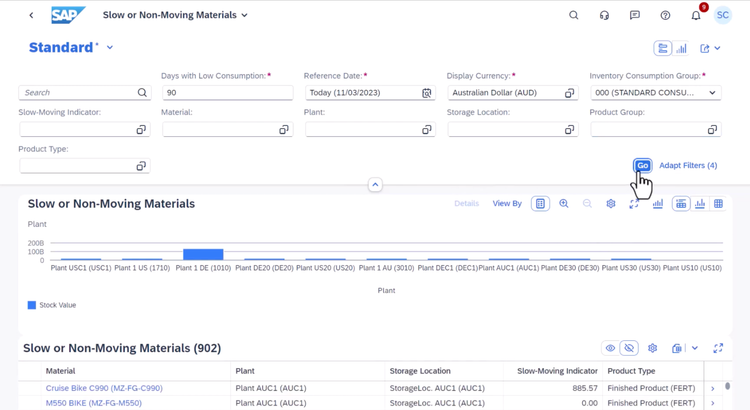
SAP S/4HANA - Inventory Optimization
S/4HANA’s built-in ML feature pinpoints non-moving or slow-moving inventory across all warehouses. By evaluating historical movement patterns, SAP classifies each SKU and predicts which ones are likely to remain unsold. Planners can then surface items flagged with a high slow-movement indicator and their dollar values. From there, they can start a clearance promo or investigate warehouse practices tied to quality control lapses.
Additionally, this enterprise-grade ERP continuously assesses vendor performance in the replenishment workspace and adjusts lead times. It corrects outdated values that might have been set years ago as static master data, ensuring your inventory planning and production schedules reflect reality.
Anomaly Detection & Variance Insight
Anomaly detection measures each transaction’s likelihood of error or fraud before it reaches downstream reports. Beyond just flagging the problem, AI tools also explain the root causes in natural language.
Dynamics 365 Fraud Protection
Real‑time machine‑learning models monitor eCommerce checkouts, bank transfers, and expense claims for suspicious activity. The system calculates risk scores and blocks any anomalies based on dynamic thresholds. It then includes contextual reasoning for each flag, like “payment pattern doesn’t match user history.” This helps your finance team act faster without digging through extensive logs.
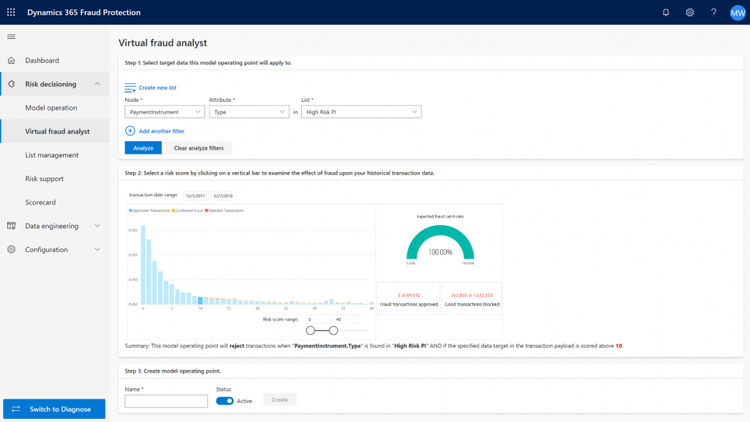
Image and Document Recognition
Image and document AI lifts structured fields such as dates, totals, and lot numbers from PDFs, scans, or photos. This helps manage repetitive transaction processing, like invoice matching.
This is more advanced than traditional optical character recognition. OCR converts images into machine-readable text; it doesn’t know what the text means and often struggles with inconsistent formatting or unstructured documents.
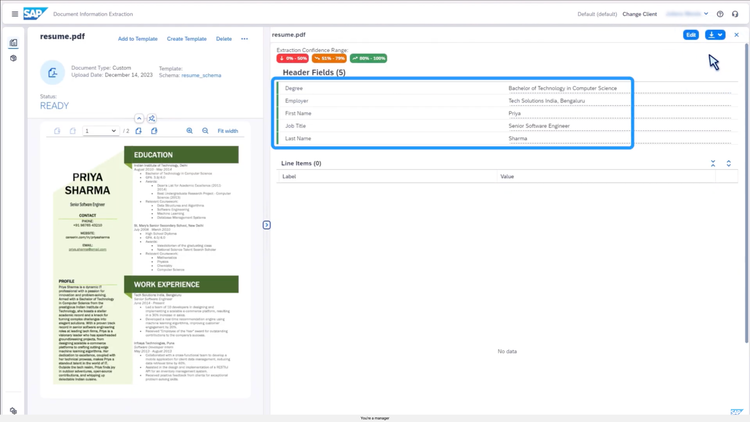
SAP S/4HANA Cloud – Document Information Extraction
You can define extraction keys using plain-language prompts. For example, type “extract applicant name, university, and years of experience” to parse data from a resume. Once configured, simply upload documents like purchase orders, delivery notes, and quality certificates into the interface.
SAP S/4HANA automatically extracts the relevant fields and maps them into your ERP records. It supports over 40 languages and complex records like Chinese birth certifications or multilingual compliance forms.
Best ERP Systems With AI Capabilities
Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft is a major partner of OpenAI, investing $10 billion in 2023 as a key financial backer. It began embedding Azure OpenAI in 2023; today, every part of its ERP and CRM system includes its Copilot AI assistant.
- AI agents: Collections coordinator, sales email generator, purchase order change impact analysis.
- GenAI: Natural‑language query in Dataverse; build workflows based on what you describe using Power Automate.
- Anomaly detection: Fraud protection for payments and ticketing; predictive cash flow ML models.
- Image AI: Reads invoices and receipts to lift totals and due dates.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud with Joule AI
Joule launched in late 2023, and by the end of 2025, it’s expected to support over 400 AI use cases across the ERP. Joule is built into SAP modules across finance, procurement, and supply chain. AI in SAP ERP includes:
- AI agents: Joule chat assistant across Finance, Materials Management, and Sales and Distribution.
- GenAI: Code generation inside SAP Build for low‑code extensions.
- Predictive ML: Runs MRP simulations to forecast inventory and supplier lead times.
- Image AI: Extracts data from invoices, certificates of analysis, and resumes.
Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP
Oracle’s AI stack runs on OCI, using its in-house LLMs and vector database support. A vector database allows users to search by meaning rather than exact keywords, making AI in ERP more context-aware. AI capabilities are available across all major modules, from ERP to supply chain management (SCM). AI in Oracle ERP inclues:
- AI agents: Project plan generator, supplier risk assistant, autonomous close checklist.
- GenAI: Narrative summaries and contract clause generation in Fusion Procurement.
- Predictive ML: Forecast demand in financials; predict cash flow in supply chain planning.
- Anomaly detection: Expense fraud scoring, duplicate expense detection, purchasing pattern outliers.
Infor CloudSuite
Infor integrates AI across its CloudSuite ERP solutions for manufacturing and distribution. It leverages Infor AI (formerly Coleman AI) capabilities.
- AI agents: Infor’s Digital Assistant; helps perform tasks like purchase order creation, answering queries.
- GenAI: Generates, summarizes, contextualizes compliance reports & internal communications
- Predictive ML: Supports demand forecasting, preventive maintenance scheduling, inventory optimization
- Intelligent OCR: Intelligent Document Processing combines OCR and machine learning to extract document data
Benefits of AI in ERP
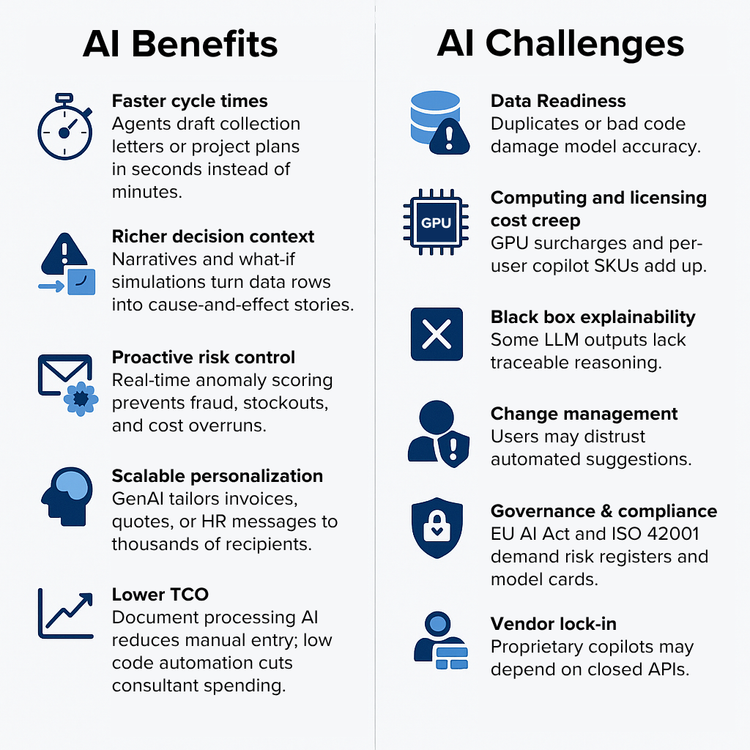
When leveraged properly, artificial intelligence can accelerate digital transformation for your company:
- Faster cycle times: AI agents craft collection letters or project plans, trimming days‑long workflows to minutes.
- Deeper decision context: What-if simulations and narratives transform raw data rows into cause‑and‑effect stories.
- Proactive risk control: Live anomaly scoring prevents fraud, cost overruns, and stockouts.
- Scalable personalization: GenAI personalizes thousands of recipients’ quotes, invoices, or HR messages.
- Lower total cost of ownership: Document processing AI reduces manual entry, while AI‑authored low‑code automation cuts consultant spending.
- Skill‑set amplification: Natural‑language UX lets non‑technical users query live ERP data.
- Continuous improvement: ML models retrain on each transaction, boosting forecast accuracy over time.
AI Challenges
However, AI in ERP also comes with a number of caveats. Most ERP users won’t have to deal with these issues directly, but when things go wrong, they’re the ones who feel the impact as it ripples through your business.
- Data readiness: Duplicates or bad code damage model accuracy; even the best AI features can fail to deliver if implementation challenges like poor data mapping aren’t addressed.
- Computing & licensing cost creep: GPU surcharges and separate licensing fees for each user accessing an AI assistant can add up.
- Black box explainability: Some LLM outputs lack traceable reasoning.
- Change management: Users may distrust automated suggestions; AI adoption often requires a cultural shift and training programs to help users understand the tools.
- Governance & compliance: Regulations like the EU AI Act and ISO 42001 mandate risk registers and model cards, creating more compliance overhead.
- Vendor lock‑in: Proprietary copilots may depend on closed APIs and ecosystem-specific models, making switching vendors or integrating third-party AI tools difficult.
- Bias & data drift: Historic training data may reinforce outdated patterns and skew forecasts, unless actively retrained and audited.
What’s Coming Next in ERP AI
Areas We Expect AI to Affect
Think of the following sectors as the next wave, not today’s feature list. Vendors are prototyping these capabilities, teasing them in roadmaps, or testing with early adopters. Expect these ideas to surface in commercial ERP releases over the next 12–24 months.
Logistics and Supply Chain (Prototype Stage)
Vendors like SAP and Oracle are experimenting with automated supply chain agents that continuously scrape news feeds, social media, and government alerts to assess supplier risk and propose actions.
For example, maybe it detects a tier‑1 supplier’s factory shutdown. This prompts it to check your open purchase orders and lead time buffers. From there, it automatically creates change orders to qualified alternates—all without human input.
Why it matters: Reaction time drops from days to minutes. This brings down your scramble costs, premium freight, and line stoppages.
Manufacturing and Engineering (In Development)
You feed a generative design assistant a CAD model. It identifies raw materials and secondary operations, then suggests a draft bill of materials and preliminary routing steps based on CAD geometry and past configurations.
Why it matters: AI reduces lead time on new product information and manual engineering effort and standardizes production guidelines.
Construction Project Management (Pilot Stage)
Using live BIM quantities and supply chain data, a generative AI schedule optimizer:
- Rewrites WBS tasks
- Re‑levels crews
- Proposes real-time contract-clause adjustments for review when timelines shift
Why it matters: By keeping Gantt schedules synchronized with field realities, you can mitigate labor bottlenecks and prevent expensive change‑order cascades.
Wholesale & Distribution (Roadmap Feature)
NetSuite and Blue Yonder have teased dynamic pricing tools that pull:
- Nightly inventory aging curves
- Competitor web-scrape data
- Margin objectives
They then post optimized list prices to your eCommerce and CRM channels.
Why it matters: Without relying on spreadsheets, you can protect margins and quietly discount any slow-moving inventory.
Warehouse Operations (In Testing)
AI runs thousands of virtual simulations inside a digital‑twin warehouse. This way, it learns optimal slotting, pick paths, and labor allocation as product mix and order profiles change.
Why it matters: AI outperforms static rule‑based optimizers, shifts automatically with peak‑season surges, and reduces travel time in your warehouse.
Accounting / Finance (Early Pilots Emerging)
An LLM reviews scanned invoices, POs, and free‑text freight memos. It identifies any mismatches and auto‑codes legitimate freight variances to the correct expense account. Finally, it routes exceptions for approval. Sage Intacct and Oracle Fusion ERP are piloting invoice triage tools.
Why it matters: This eliminates manual GL reclassification, speeds up three‑way match resolution, and results in stronger audit compliance.

2025 AI ERP Trends to Watch
MCP Protocol – Multi‑Agent Coordination Protocol
A vendor‑neutral framework that lets finance, supply chain, and HR agents communicate goals (e.g., reduce past‑due invoices by 5 %). Agents subscribe to each other’s intents, work out conflicts, and execute ERP actions. It’s more or less a smart messaging system that helps different modules collaborate without your input.
A2A Protocol – Agent‑to‑Agent Workflows
A lighter‑weight spec focused on direct, two-way conversations between AI agents. For example, a collections agent can ask a cash‑forecasting agent if delaying a payment will hurt cash flow and receive an immediate, structured reply. Oracle and Microsoft have both showcased early A2A interactions at spring 2025 events.
Hyperautomation
Combines AI agents and robotic process automation (RPA) bots to automate end‑to‑end processes, like sending a quote, processing an order, and getting paid. The ERP becomes a control center, calling in outside tools for tasks like ID checks, tax compliance, and shipping, without relying on manual steps.
AI‑Driven Customization
Copilots can now build custom screens or workflows without needing to hire developers. Just give the assistant a prompt in plain language, like “create a return form with barcode scanning.” The system then writes the code in the ERP’s native language, whether that’s AL code for Business Central or ABAP Cloud for SAP S/4HANA. From there, it builds a responsive front-end, like a web form with barcode input fields, for you to test and edit.
Explainable AI (XAI)
New dashboards expose the why behind each AI recommendation. They show sample rows, confidence scores, weighted features, or even the raw prompt sent to the LLM. This is vital for meeting compliance rules like SOX to prevent corporate fraud, FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for tamper-proof electronic records, and the EU AI Act for AI risk-based regulation.
Reasoning Models at the Edge
Some small LLMs run directly on handheld scanners or maintenance tablets; no internet connection is needed. This means workers on the factory floor can look up BOMs, follow checklists, and access troubleshooting help even without Wi-Fi.
All of this is still early, but moving quickly—expect pilots in 2025 releases and mainstream adoption by 2026‑2027.
The AI Supply Chain Behind Your ERP
Knowing who’s behind your ERP’s AI helps you understand what you’re really paying for, and if it’s the best option.
Leading AI Players
| Company | Flagship Model | What It’s Known For |
|---|---|---|
| OpenAI | ChatGPT / GPT‑4o | First mover; still the reference standard. |
| Anthropic | Claude 3 | Long context; excels at reading huge documentss. |
| Gemini 1.5 | Tightest tie‑in to Google Cloud & Workspace. | |
| Meta | Llama 3 (open source) | Free to download; can run fully on‑premises. |
| DeepSeek | DeepSeek‑MoE | Mix‑of‑Experts model; fast and cheap. |
| X (formerly Twitter) | Grok | Baked into the X platform; less polished elsewhere. |
| Rising challengers | Mistral, Alibaba (Qwen) | Strong scores on open leaderboards at lower cost. |
Note: Microsoft doesn’t build its own model; it resells OpenAI inside Azure.
Major Hyperscalers
| Cloud | Nickname | Why You’d Pick It |
|---|---|---|
| AWS | “Everybody’s default” | Widest region footprint; Bedrock can swap models on the fly. |
| Azure | “OpenAI inside” | Instant GPT‑4o access; ideal for Microsoft stacks. |
| Google Cloud | “Gemini home turf” | T.PUs + deep Google Workspace hooks. |
| Oracle Cloud | “Value player” | Cheaper GPU hours;favored by Oracle ERP users. |
Public LLM Leaderboards
These can let you track where your vendor’s model actually ranks.
- LMArena: Head‑to‑head human voting on model quality
- Hugging Face Leaderboards: Raw benchmark scores (no human votes, just test sets)
Hardware Economics
Hyperscalers and SaaS vendors treat “NVIDIA + CUDA” as the default AI substrate, letting NVIDIA set the price. NVIDIA combined potent GPUs with easy‑to‑use CUDA software and secured most of the world’s high‑end GPU supply before competitors could react.
| GPU Generation | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| A100 | Workhorse of early ChatGPT deployments. |
| H100 | ~3× faster; now the most common cloud GPU. |
| H200 | Larger RAM → bigger context windows & lower cost per answer. |
| B100 (2025) | Promised ~2× speed gain—should drop token prices if supply meets demand. |

Evaluating ERP Vendors for AI – Key Questions
Many vendors overhype AI; ask these questions before purchasing an ERP.
Core Capabilities
- Does the vendor have proven AI expertise, or are they repackaging rules-based automation with new branding?
- Can the AI figure out where the right info is on a document, even if it’s a format it hasn’t seen before? Or does it rely on static templates?
- Is a first‑class agent framework (Copilot Studio, Joule Automations) available?
Data Privacy & Security
- Where does the LLM run, and who can see your prompts?
- Are your AI-generated data summaries locked down and only stored in approved geographic locations?
Transparency
- Can you access confidence scores, prompt logs, or validation traces?
- Is there an audit API for SOX and FDA records?
Licensing & Lifecycle
- Is AI bundled or a usage‑based add‑on?
- How often are models refreshed, and can old versions be pinned?
- How will recent mergers and acquisitions affect the vendor’s AI roadmap, model support, or data policies?
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is AI in ERP?
AI-enabled ERP systems use artificial intelligence to assess large volumes of data, providing insights and recommendations across multiple departments. For example:
- In finance and operations, it powers cash flow forecasting, scenario planning, and demand forecasting.
- In inventory management systems, it projects stock levels and automates reordering.
- In human capital management, it helps with resume rescreening and workforce planning.
How does AI improve manufacturing?
AI helps manufacturers run smarter through intelligent manufacturing capabilities:
- Predictive maintenance powered by ML technologies to forecast downtime
- Recommending BOMs and routings through generative design
- Flagging scrap spikes using real-time anomaly detection
- Streamlining report generation by compiling production data
What types of AI technologies are used in ERP systems?
Some common types of AI used in ERP include:
- Machine learning and predictive analytics
- Natural language tools (Natural language processing, speech recognition, chatbots, and virtual assistants)
- Generative AI and large language models
- Automation technologies (Robotic process automation, anomaly detection, process mining)
- Visual AI (Image recognition and computer vision)
What are the best practices for using AI in ERP systems?
Even if you’re not building AI models yourself, using AI features in ERP still requires smart oversight:
- Data governance: Know where your data comes from, who owns it, and how it’s used.
- Data privacy standards: When using AI to forecast demand or track employee data, comply with GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations.
- Ethical AI deployment: Make sure AI-driven decisions are explainable; ask ERP vendors to disclose what AI models are trained on and whether you can audit decisions.