Bookkeeping vs. Accounting
Bookkeeping records financial data, and accounting interprets it. This guide will explain the differences and similarities between bookkeeping and accounting and help you choose the right financial professional.
What is Bookkeeping?
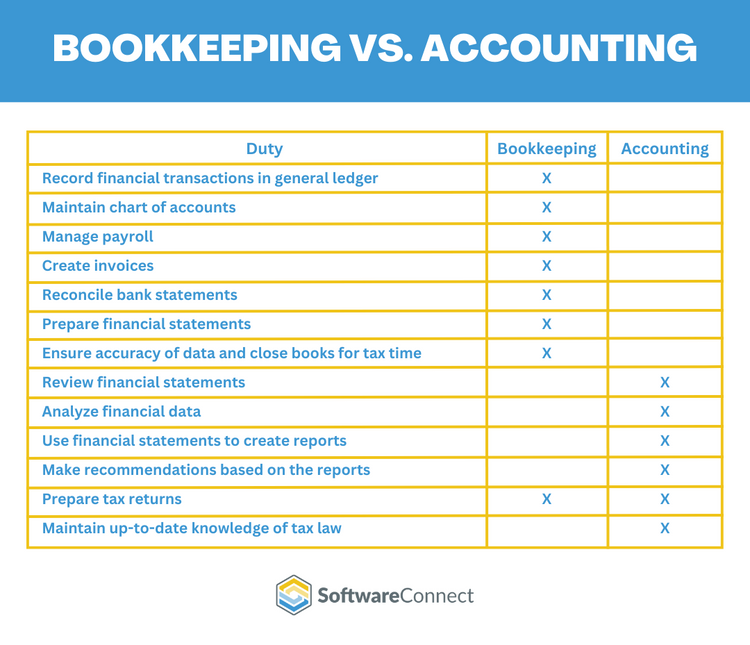
Bookkeeping is the recording and organization of financial data. Some of the primary duties of a bookkeeper include recording financial transactions in the general ledger, maintaining a chart of accounts, managing payroll, and creating invoices. They also likely will need to prepare financial statements and reconcile bank statements.
Becoming a bookkeeper does not require any formal education, but it does require knowledge of finances and accounting. There are optional licenses available for bookkeepers through accreditors like the American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers (AIPB) and the National Association of Certified Public Bookkeepers (NACPB).
What is Accounting?
Accounting is compiling and interpreting financial data to help companies make informed business decisions. Duties of an accountant include:
- Review financial statements
- Analyze financial data
- Use financial statements to create reports
- Make recommendations based on the reports
- Prepare tax returns
- Maintain up-to-date knowledge of tax law
Many accountants use accounting software like QuickBooks to automate accounting tasks and ensure the accuracy of financial data.
Accountants typically have a bachelor’s degree in accounting and are also registered Certified Public Accountants (CPA). To use the title of CPA, an accountant must pass the CPA exam. Other certifications that accountants might have include Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) and Certified Internal Auditor (CIA).
| Credential | Certification Requirements | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Accountant | 4 year bachelor’s degree in accounting | The minimum credential needed to practice accounting |
| CPA | Meet state requirements, pass Uniform CPA exam, and meet continuing education requirements | Maintain knowledge of standard accounting practices and tax laws |
| CFA | 4 years of relevant work experience and must pass a 3-part exam | Knowledge of ethical financial practices, portfolio management, and investment analysis |
| CIA | 2 years of relevant work experience and must pass exams | Security monitoring and financial risk assessment |
How Are Accounting and Bookkeeping Similar and Different?
Though many confuse the two roles, bookkeepers and accountants have distinct differences. Bookkeepers focus on day-to-day financial recording, while accountants give a big-picture view of a company’s finances.
While accounting can include bookkeeping tasks like recording daily transactions into the general ledger, bookkeeping does not include accounting responsibilities such as analyzing your company’s financial health. Both bookkeepers and accountants can prepare tax returns, but only accountants can perform routine financial audits. Internally conducted audits ensure that financial records are accurately and ethically recorded according to industry standards. Finally, unlike bookkeepers, accountants with CPA certification can represent your company if the IRS audits you.
Does My Company Need a Bookkeeper or Accountant?
When your taxes are too complex, your business is growing, or you don’t have enough time to manage your accounting tasks, you should hire a professional. Based on your organization’s needs and budget, you can decide whether you need a bookkeeper or an accountant.
A bookkeeper is typically a lower-cost solution for handling day-to-day tasks such as payroll and fund allocation. On the other hand, an accountant makes projections and handles overall financial strategy and decisions.
In larger companies, it can be necessary to have both a bookkeeper and an accountant. However, employing one of the two may only be required for smaller or simpler operations. For example, you may not need the services of a bookkeeper if your accountant uses software that automates bookkeeping processes.
