Integrating ERP and BI: Benefits and Key Differences
Enterprise resource planning software streamlines many back-office tasks from accounting to human resources. Yet, an ERP isn’t always the best at collecting and organizing real-time data. It’s business intelligence or BI tools that expertly gather and analyze key data to find actionable insights. Integrating BI and ERP is important for businesses, as combining their functions can have several benefits, including predictive analytics, enhanced reporting, and improved insights.
What is ERP?
An ERP is an integrated suite of business applications that covers workplace functions like financials, sales, and other back-office operations. The variety of features connect different areas of your business together so you can do all your work from one central platform.
ERP software helps businesses in many ways by combining various modules into one platform. It acts as a central hub of real-time visibility into operations, facilitating continuous improvement and holistic process optimization. ERP’s reporting capabilities enhance decision-making by allowing data analysis from various angles when paired with BI’s ability to gather data. Moreover, it simplifies data security management and promotes collaboration by consolidating different forms of data and communication.
Some top ERP systems that utilize BI tools include:
What is BI?
Business Intelligence, or BI, refers to tools that gather and analyze data to give businesses more informed decision-making abilities. These tools help managers make data-informed decisions when trying to improve business strategies. Other main features are focused on data: discovery, mining, integration, visualization, and analysis. All are designed to help improve decision-making at the highest level.
There are five key steps to follow with BI:
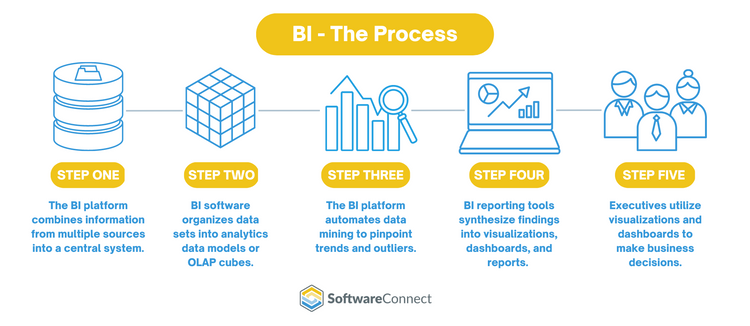
The most crucial elements of BI tools are Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) and Big Data. OLAP is a way to analyze different types of business data from a variety of critical viewpoints. Big Data refers to an increased volume of complex data sets from a multitude of sources. Together, these features store large quantities of business data and then perform multidimensional analysis on it. Ideally, the data is pulled from the central hub created by an ERP system, which includes data from departments like accounting, human resources, and CRM.
Role of BI Tools in ERP
When paired with an ERP, BI tools provide real-time data gathering and sharing. This allows for more actionable insights based on which KPIs are performing well or failing. A report by Fortune Business Insights found the Business Intelligence Market Size is projected to reach $54.27 Billion by 2030. There are standalone BI tools, but as we’ve seen, they work best when paired with ERP software.
Integration Benefits
Integrating BI tools within an ERP system can provide businesses with many benefits, including:
- Data Analysis and Consolidation: The ERP acts as a central hub so different departments can all share and see how other areas are performing. In turn, the BI tools then analyze all the data collectively in real time to determine areas of improvement.
- Reporting: BI tools enhance reporting by incorporating a larger dataset and condensing it down to viewable charts and graphs, all while speeding up the process.
- Increased Decision-Making Speed: According to a survey by Aberdeen Group, 69% of data analysts noted decision-making windows were shrinking. As such, they needed faster BI tools to keep up with increasing time crunches.
- Predictive Tools: BI offers predictive modeling and analysis, allowing companies to plan according to future financial projections. ERPs, on the other hand, offer historical data for past performance, so combining them allows for both.
With businesses relying more than ever on real-time, strategic decision-making, it’s critical to integrate BI tools with an ERP to provide more complex data for analysis.
Key Differences between ERP and BI
The main difference between an ERP and a BI tool is the scope. A full ERP includes functionality for a whole range of business processes, while a BI is focused solely on collecting and analyzing data. Without an ERP to act as a framework, the ability of the BI to gather data from various business departments is limited.
| ERP | BI | |
| Functionality | Supports core business processes, such as order management, inventory management, accounting, payroll, and HR | Supports data analysis, visualization, and reporting |
| Data Sources | Primarily relies on internal data generated by an organization's operational processes. | Connect to multiple data repositories, including ERP systems, databases, spreadsheets, and external data sources |
| Users | Used by various departments across an organization, including finance teams, procurement, manufacturing, and HR | Typically used by analysts, data scientists, and decision-makers |
| Processing | ERP is an online transaction processing (OLTP) system that records transactions as they occur. | BI is an online analytical processing (OLAP) system, meaning it offers multidimensional analytical capabilities like dashboards and advanced reporting. |
| Purpose | Designed to manage and optimize operational processes and data within an organization. | Designed for data analysis and reporting |
However, there are still times when standalone solutions are more appropriate. It will depend on the business scope and the total budget. Getting both an ERP and a BI can increase overall software costs, so it may be better to start with one or the other.
Future Trends in ERP Business Intelligence
Three of the top trends in ERP with BI are:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning Integration: ERP systems are increasingly incorporating AI and machine learning to provide predictive analytics, automated insights, and smarter decision support. Cloud-Based ERP BI Solutions: The shift towards cloud-based ERP BI solutions continues to grow, offering businesses scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency.
- User-Friendly Dashboards: ERP BI tools are focused on improving data visualization techniques and creating user-friendly dashboards to make data insights more accessible and actionable for non-technical users.
