Developing a Successful ERP Reporting Strategy
A well-defined ERP reporting strategy is a roadmap for organizations to utilize the data stored within their ERP system effectively. It outlines the goals and objectives of reporting, identifies the key metrics and KPIs (key performance indicators) that need to be tracked, and establishes the processes and procedures for generating reports. By clearly understanding what needs to be reported and how it should be done, businesses can ensure that their reports provide meaningful insights that drive decision-making.
Short Summary
- When developing an ERP reporting strategy, you’ll first want to define the scope of reporting. This involves identifying the specific areas of the business that need to be monitored and measured through reports.
- An important element is how you establish data governance practices. This refers to the set of policies, procedures, and controls put in place to ensure data accuracy, integrity, security, and compliance.
- It is essential to consider the frequency and timing of reporting. Different stakeholders within an organization may have varying reporting needs and timelines.
Key Elements
Developing a successful ERP reporting strategy requires careful consideration of key elements that ensure accurate and valuable insights for business owners, IT professionals, and ERP users.
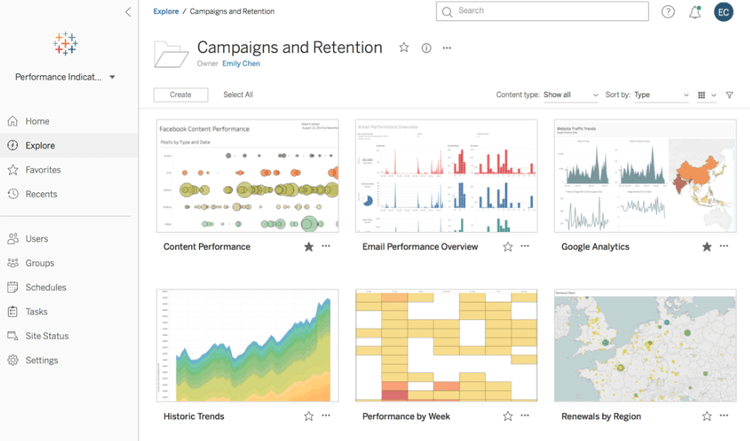
Data Analysis and Requirements Gathering
The first step in developing an ERP reporting strategy is to thoroughly analyze the data that needs to be included in the reports. This involves identifying the key metrics, KPIs, and performance indicators relevant to the organization’s goals and objectives.
Engaging with different stakeholders within the organization is important to gather these requirements. This can include department heads, managers, executives, and end-users who rely on ERP reports for decision-making purposes. By involving these individuals in the process, you can better understand their specific reporting needs and ensure that the reports provide them with actionable insights.
During this phase, it is also crucial to consider the frequency at which data should be updated in the reports. Some organizations may require real-time or near-real-time data updates, while others may find daily or weekly updates sufficient. Understanding these requirements will help determine how data should be collected and integrated into the reporting system.
Report Design and Structure
Once the data analysis and requirements gathering phase are complete, it is time to design an intuitive and user-friendly report layout. The goal here is to present information in an easily understandable and visually appealing way.
When designing ERP reports, the target audience must be kept in mind. Different stakeholders may have varying levels of technical expertise and familiarity with ERP systems. Therefore, it is essential to balance providing comprehensive information and avoiding overwhelming users with complex data.
You can incorporate relevant visualizations in several ways, such as:
- Charts
- Graphs
- Dashboards Visual representations of data can help users quickly identify trends, patterns, or anomalies, enabling them to make informed decisions more efficiently. Additionally, organizing the report into sections or tabs can help users navigate through the information easily.
Data Integration and Validation
Data integration and validation are critical aspects of an ERP reporting strategy as they ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented in the reports. Integrating data from various ERP modules, such as finance, sales, inventory, and HR, allows for a comprehensive view of the organization’s operations.
Establishing robust data integration processes and workflows is important for seamless data integration. This may involve implementing extract, transform, load (ETL) tools or utilizing APIs to connect different systems and automate data transfer. Doing so can eliminate manual data entry errors and minimize the risk of inconsistent or incomplete data in your reports.
Furthermore, implementing data validation processes is essential to maintain data integrity. This involves regular checks on incoming data to identify discrepancies or anomalies. By validating the accuracy and completeness of the data before it is included in reports, you can ensure that decision-makers are basing their actions on reliable information.
Security and Access Controls
Protecting sensitive business information is crucial when developing an ERP reporting strategy. Implementing strong security measures and access controls ensures that only authorized individuals can access and manipulate ERP reports. Security measures include:
- Defining user roles and permission: This ensures different stakeholders within the organization are only granted access to their level of information. For example, executives may need access to high-level financial reports, while department managers may only need access to specific operational metrics.
- Authentication methods: Methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA) add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification forms before accessing ERP reports.
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit helps prevent unauthorized access or tampering.
- Conducting audits: Audits help identify and address vulnerabilities in the ERP reporting system. By proactively mitigating security risks, organizations can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their reports.
Best Implementation Practices
Implementing an effective ERP reporting strategy is crucial for businesses to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions. By following best practices, organizations can ensure that their reporting processes are efficient, accurate, and aligned with their overall business objectives. Here are four key best practices to consider when implementing an ERP reporting strategy:
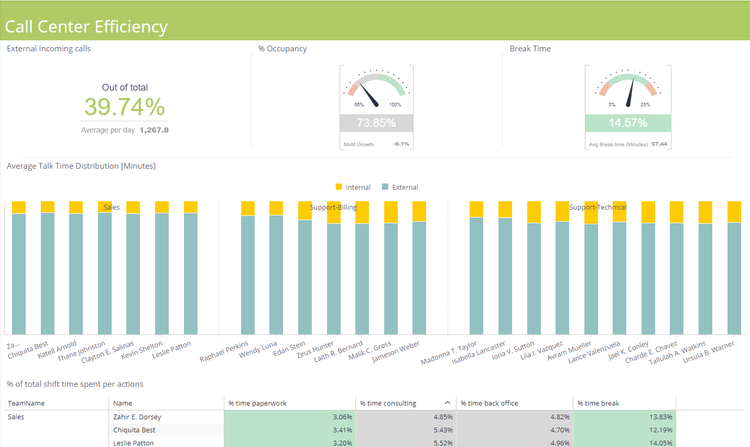
Establish Clear Objectives and KPIs
Before diving into implementing an ERP reporting strategy, it is essential to establish clear objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs). These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure they align with the organization’s overall goals.
By defining clear objectives and KPIs for reporting, businesses can focus on what matters and accurately measure their progress. For example, if a company aims to improve its supply chain efficiency, a relevant objective could be to reduce lead times by 20% within six months. This objective can then be translated into specific KPIs such as average lead time per order or on-time delivery rate.
Aligning reporting objectives with overall business objectives ensures that the reports generated provide meaningful insights and contribute to strategic decision-making.
Regularly Review and Update Reporting Processes
Review and update the reporting processes regularly to maintain the effectiveness of an ERP reporting strategy. Conducting periodic audits allows businesses to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
Organizations should evaluate their reports’ accuracy, relevance, timeliness, and usability during these audits. They should also assess whether the current reporting tools and systems meet their evolving needs. By staying updated with industry trends and emerging technologies in reporting, businesses can leverage new capabilities to enhance their reporting processes.
For example, advancements in data visualization tools can help present complex data in a more intuitive manner. Adopting such tools can improve user experience and enable stakeholders to understand and interpret reports more efficiently.
By regularly reviewing and updating reporting processes, businesses can ensure that their ERP reporting strategy remains aligned with their changing requirements and continues to deliver valuable insights.
Provide Adequate Training and Support
Even the most sophisticated ERP reporting system is only as effective as the users who interact with it. Organizations must provide adequate training and support to their users to maximize the benefits of an ERP reporting strategy. Training should focus on:
- Generating reports
- Interpreting and utilizing the information effectively
- Understanding key metrics
- Analyzing trends
- Drawing actionable insights from the reports
Additionally, ongoing support is essential to address any challenges or questions that arise during day-to-day operations. This can include providing access to user manuals, conducting regular training sessions, or establishing a dedicated helpdesk for reporting-related queries.
By investing in comprehensive training and support, businesses empower their users to leverage the full potential of their ERP reporting system, leading to better decision-making at all levels of the organization.
Foster Collaboration between IT and Business Teams
Successful implementation of an ERP reporting strategy requires collaboration between IT teams responsible for maintaining the reporting infrastructure and business teams relying on the reports for decision-making.
IT and business stakeholders should establish open communication and feedback channels to ensure reporting requirements are clearly understood. Regular meetings or workshops can facilitate discussions around report customization, data accuracy, or any other relevant topics.
It is crucial to involve both IT and business teams in the decision-making process for reporting enhancements. By soliciting input from end-users who rely on reports daily, organizations can identify pain points or areas where improvements are needed. This collaborative approach ensures that the implemented ERP reporting strategy meets the needs of all stakeholders involved.
Furthermore, fostering collaboration between IT and business teams promotes a sense of ownership over the reporting process. When both parties feel invested in its success, they are more likely to contribute actively to its continuous improvement.
Utilizing Technology
In today’s digital age, technology is crucial in supporting an ERP reporting strategy. With the advancements in software and tools, businesses can now leverage technology to streamline their reporting processes and gain valuable insights from their ERP systems.
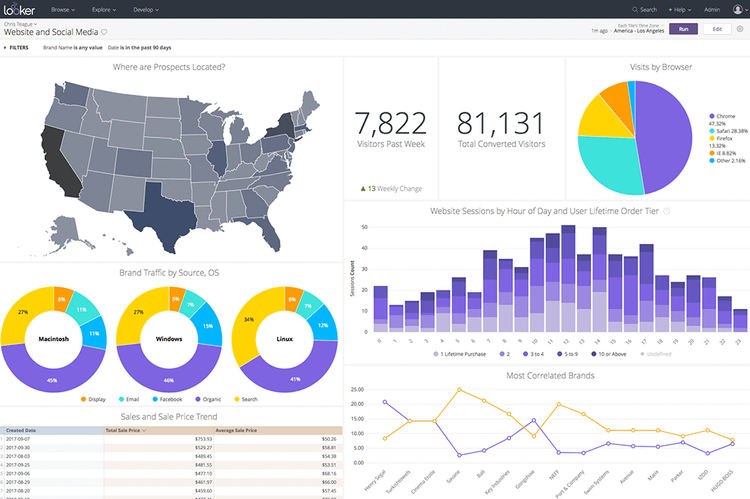
Utilizing Advanced Reporting Tools and Software
One of the primary ways technology supports an ERP reporting strategy is by using advanced reporting tools and software. These tools allow businesses to extract data from their ERP systems and generate comprehensive reports highlighting key metrics and trends. By using these tools, businesses can analyze their data more effectively, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions based on accurate information.
Advanced reporting tools also offer features such as customizable dashboards, real-time data updates, and interactive visualizations. This allows users to easily navigate through complex datasets, visualize trends and patterns, and better understand their business operations. With these capabilities, businesses can quickly identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in their processes and take proactive measures to address them.
Integrating ERP Systems with Business Intelligence Platforms
Another way technology supports an ERP reporting strategy is by integrating ERP systems with business intelligence (BI) platforms. BI platforms are designed to consolidate data from various sources, including ERPs, into a single unified view. This integration enables businesses to access all relevant data in one place and perform advanced analytics on it.
By integrating ERPs with BI platforms, businesses can create comprehensive reports that combine financial data with other operational metrics. For example, they can analyze sales figures alongside inventory levels to identify potential stockouts or optimize pricing strategies. This holistic view of data allows businesses to make data-driven decisions aligning with their goals and objectives.
Read More: What is Business Intelligence?
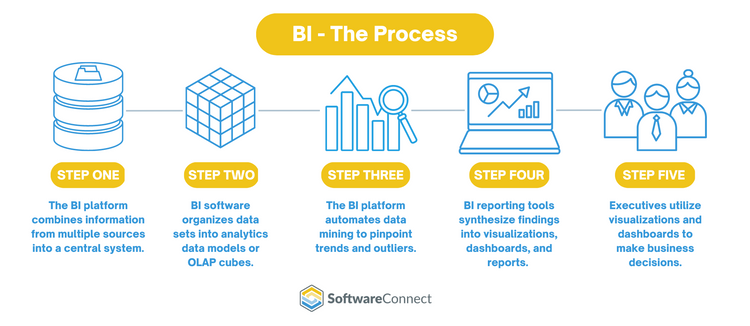
Automating Data Extraction and Report Generation Processes
Lastly, technology plays a vital role in automating data extraction and report generation processes for an ERP reporting strategy. Manual data extraction and report generation can be time-consuming and prone to errors. However, with the help of technology, businesses can automate these processes, saving time and ensuring accuracy.
Automated data extraction tools can connect directly to ERP systems and extract relevant data on a scheduled basis. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and ensures that reports are always up-to-date. Additionally, automated report generation tools can generate reports based on predefined templates or user-defined criteria, further reducing the effort required to create comprehensive reports.
Conclusion
A clear ERP reporting strategy is vital for effective business data management and analysis. Such a strategy offers:
- Enhanced Visibility: Allows stakeholders to gain real-time insights into operations like sales, inventory, and financials, pinpointing trends or issues to enhance performance.
- Data Accuracy & Consistency: Standardized processes and technology solutions minimize human errors, fostering trust in data-derived insights.
- Collaboration & Accountability: Clear report-related roles promote team cohesion, cross-functional communication, and data-driven decisions for all staff through tools like self-service analytics.
- Agility: With adaptable technology, businesses can modify reporting processes per changing needs, facilitating timely decision-making in shifting market conditions.
A strategic approach to ERP reporting ensures businesses harness their ERP system’s full potential, enabling decision-makers to navigate today’s intricate business environment effectively.
