Understanding Dropshipping and How To Get Started
What Is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where your eCommerce business sells items through a third-party supplier. Instead of a traditional retail model, you purchase inventory from a supplier when a customer buys that product on your site. The supplier then ships the item directly to that customer.
How Dropshipping Works
Dropshipping offers a low-risk business model to online retailers, improving time to market for orders. eCommerce stores that utilize this method also pay no upfront costs or storage expenses for inventory.
However, there are risks to dropshipping. Relying on a third party’s inventory infrastructure opens your dropshipping operation up to delayed shipments, damaged products, and customer dissatisfaction.
Before diving into the actual process behind dropshipping, let’s examine the relationship between your store and its suppliers.
Manufacturer vs. Distributor vs. Wholesaler
Suppliers can play any of the following roles in commerce:
- A manufacturer makes finished products or raw materials.
- A distributor markets and sells these products to a wholesaler.
- A wholesaler sells large quantities of products at low prices to retailers.
Your role as a retailer is to market and sell goods to consumers for an established price. In a traditional business model, you would purchase inventory from a wholesaler, store that inventory, and sell it in a brick-and-mortar or an online store. Dropshipping follows an alternate process:
- Your customer places an order and pays the retail price you set on your eCommerce site.
- Your store sends the order to your dropshipping supplier. You pay the supplier the wholesale price and collect the profit margins as revenue.
- Your supplier processes the order and ships the product directly to the customer.
Dropshipping vs. Direct-to-Consumer Model Effective order management allows you to sell across multiple channels to reach a broader customer base. Online businesses can use dropshipping alongside traditional retail or business-to-consumer (BTC) methods.
Dropshipping follows this trajectory:
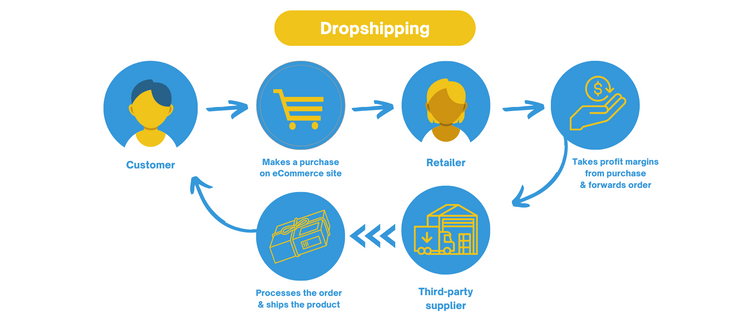
The customer purchases an item on an eCommerce site. The retailer pays the supplier’s wholesale price, takes the profit margins remaining from their retail price, and forwards the order to the supplier. The supplier handles order fulfillment and ships the product to the customer.
The direct-to-consumer model follows this trajectory:
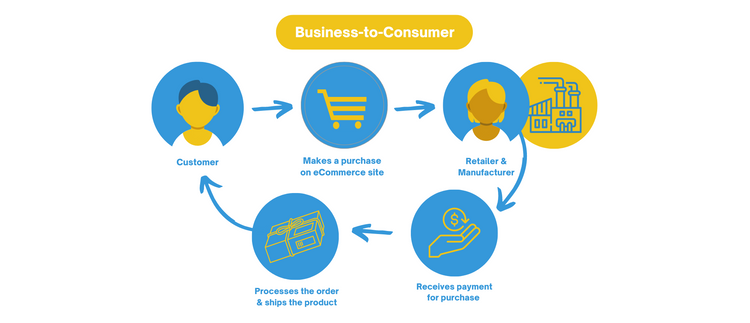
The customer purchases an item on an eCommerce site. The retailer then outsources the product assembly to a manufacturer, then ships the finished item directly to the consumer. The BTC model bypasses distributors and wholesalers entirely.
Steps to Starting a Dropshipping Business
Now that you understand the process behind dropshipping, you can integrate this low-risk business model into your sales channels. Take a four-pronged approach to sourcing products and suppliers through this beginner’s guide:
1. Decide on Your Products
Conduct market research to find trending or niche products. One strategy could be to search for commodities with more devoted followings.
Examples might include:
- Cosmetics
- Custom t-shirts
- Pet care
- Vehicle customization
- Jewelry
- Gaming headsets
- Women’s fashion
Take advantage of search and buying trends to identify popular topics and purchases. For instance, Google Trends shows drops and surges in web searches, while Amazon Top Sellers and AliExpress Dropshipping Center provide vital insights into consumer demand.
2. Research the Competition
Once you’ve landed on a solid niche, do a quick Google search to pinpoint your top 10 competitors. Take note of recurring products across competitors and potential discrepancies between their offerings and consumer demand.
Audit the competition’s social media accounts to see how often they communicate with their customers. Pay attention to the competitor’s tone and the overall consumer sentiment toward the company. Then, identify ways to communicate faster, more effectively, or more persuasively.
Finally, subscribe to their newsletters and marketing emails. Over time, you’ll acquire a feel for their brand identity, new products, and content that can help you optimize your own.
3. Select Your Suppliers
Next, analyze potential suppliers to find partners that provide quality products and fast shipping times. You can search AliExpress, Alibaba, and Shopify dropshipping directories for sellers with ratings of 95% or higher with at least one year of activity on the site.
Determine your top five sellers and contact them for shipping times and minimum order quantities. After narrowing it down to two to three sellers, place an order with each supplier to inspect the quality and overall shipping experience.
4. Determine Pricing
The final step is to determine the retail price for your products. Consider your supplier’s wholesale price, shipping costs, and taxes. Your markup should cover these expenses and maintain your targeted profit margin. Check the manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP) and research competitor pricing to ensure you aren’t aiming too low or high.
Additionally, consider how dropshipping will affect your accounting processes. You can expect to manage a high volume of supplier invoices and taxes across different regions. Dropshipping through multiple channels can also impact your bookkeeping.
Amazon dropshipping will require tracking additional advertising, merchant, service fees, and refunds through their marketplace. At the same time, you’ll l have to record expenses incurred through your separate eCommerce site.
Best Dropshipping Platforms
Dropshipping can require a hefty upfront investment in time and energy, but you can ease your workload with the right platform.
-
EDI Solutions
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) software allows trading partners to coordinate more efficiently through automated purchase orders, invoices, and other transactional documents. TrueCommerce automates communications with your suppliers for rapid order processing and fulfillment. EDI systems are ideal for larger retailers and e-tailers looking to expand to a wider range of products. -
Inventory Management Software
Inventory control solutions keep track of all information surrounding the items your company buys and sells. For example, [Fishbowl] can predict inventory requirements based on sales trends and integrates seamlessly with Amazon, Shopify, QuickBooks, and more. -
eCommerce Platforms
eCommerce solutions are ideal for startup businesses and small retailers looking to build their own virtual storefronts. BigCommerce is an affordable option, offering unlimited staff accounts and no transaction fees. Popular BigCommerce dropshipping extensions include Dropified, Syncee, and Wholesale2B.
Establishing Sales Channels
Your eCommerce store plays a primary role in advertising and generating sales through whichever channel you choose. While some of these options include bidding sites and social media stores, Amazon and eCommerce stores remain the most popular avenues:
Selling on Your eCommerce Site
Your eCommerce site can gain legitimacy through a descriptive domain name, high-quality product images, and authentic nsumer reviews. Your website also offers total control over your brand without third-party fees from Facebook Marketplace or Amazon.
Shopify remains one of the most popular eCommerce platforms, boosted by dropshipping extensions like Automizely, Oberlo, and Spocket.
Helpful features for beginner dropshippers include:
- Intuitive website editors
- Flexible point-of-sale systems
- Seamless checkout
- Real-time shipping quotes
These commerce solutions also allow integration with marketplaces like Amazon and eBay.
Selling on Amazon
Three obvious advantages of dropshipping through Amazon are more visitors, fewer marketing costs, and a higher sales volume. However, to dropship on Amazon, you must identify as the seller of record (SoR) who sets the price, records the purchase as revenue, and assumes responsibility for sales tax.
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) shares similarities with dropshipping: you send products to Amazon fulfillment centers where their workers pick, pack, and ship them on your behalf. Dropshippers also benefit from the fact that Amazon manages customer service and offers Prime Shipping.
To qualify for FBA, you must:
- Have an Amazon seller account
- Ship a minimum of five products a day
- Pay fees for storage, overage, refund administration, etc.
- Provide large quantities of the product upfront to the fulfillment center
Benefits
Dropshipping offers advantages for both the sellers making customer-facing transactions and the suppliers fulfilling those orders. Some of these benefits of dropshipping include:
Advantages for Sellers
Low startup and overhead costs
Entrepreneurs looking to start businesses save on expenses associated with production, industrial warehouse loans, and employee salaries.
Avoid the need for supply chain or inventory management
eCommerce beginners avoid the pitfalls of supply chain interruptions and inventory storage expenses by dropshipping products instead.
Focus efforts on branding, marketing, and customer experience
Less time spent on inventory management means retailers have the space to optimize their marketing strategies and build better customer support.
Flexibility and scalability
Because the dropshipping business model allows you to run operations from anywhere with an Internet connection, your eCommerce startup can scale to meet increased demand without many restrictions.
Advantages for Suppliers
Improved quality management
Suppliers can channel their time and energy into improving product quality, with fewer resources required for marketing efforts.
Improved distribution management
Suppliers can also focus on optimizing the shipment process, with the onus of advertising and customer support on the retailer.
Challenges
Dropshipping poses unique challenges to sellers, and there are several factors to consider. Cons of dropshipping include:
Low profit margins
The average profit margin for dropshippers is 10%. You may even have to pay your supplier additional fees for picking, packing, and shipping each customer order.
High competition, lack of unique/exclusive products
Because the barrier to entry is low, the dropshipping field is quite competitive. Also, many competitors will offer the same products from the same suppliers, driving competition even higher.
No control over supply chain or product quality
Dropshipping is ideal for many startups because your store relies on a third party’s inventory infrastructure. However, not having a hand in production or inventory management means you’re at the mercy of your vendors and the supply chain.
For example, if a product arrives damaged or long after its intended delivery date, you’re responsible for refunding the customer and paying return shipping fees. Moreover, you’ll need to closely monitor your supplier’s inventory and request pre-purchases if shortages are on the horizon.
Harder to build brand loyalty
Because you’re responsible for order fulfillment, not production, items will not carry your logo. As a result, customers are more likely to build a relationship and brand sentiment towards your supplier or distributor.
Dropshipping remains a popular and lucrative model if you can manage risk effectively and find trustworthy suppliers.
FAQs
Is dropshipping legal?
Yes, dropshipping is a legitimate fulfillment method permitted by Shopify, Amazon, and other eCommerce leaders. However, you must ensure your suppliers are trustworthy and do not violate copyright laws. Retailers should draft dropshipping agreement contracts with each supplier to establish wholesale prices, delivery standards, and return policies.
Do I need an LLC to start dropshipping?
All dropshipping stores should obtain a business license to cover liability and taxes. According to the IRS, an LLC is a US business structure establishing your company as a liability separate from your personal properties.
Though it differs from state to state, most cities require a business license for your company to operate. (Disclaimer: Software Advice conveys general information only and does not provide legal advice or opinions.)
What is dropshipping vs. retail arbitrage?
Retail arbitrage involves a reseller purchasing stock from a retailer and then listing products on a marketplace like Amazon or eBay. The reseller physically holds this inventory until its purchase.
This differs from the dropshipping model, where the retailer has no stock on hand.
Can you do dropshipping on Amazon? On eBay?
Amazon and eBay allow dropshipping through their marketplaces, but you must follow their policies. You are ultimately responsible for listing fees, fulfillment issues, and customer support.
What is dropshipping on Shopify?
Shopify is an eCommerce platform for online stores and point-of-sale systems. Their dropshipping apps directly connect you to hundreds of suppliers, allowing you to compare and select products with positive user feedback, high sales volumes, and competitive wholesale pricing. You can then import these selections directly into your Shopify store.
