The History and Evolution of ERP Systems: The Past and Future
Enterprise resource planning (ERP software) has a long and storied past, stretching from manufacturer’s ledger books in the 1940s to the integrated suite of business applications we know today.
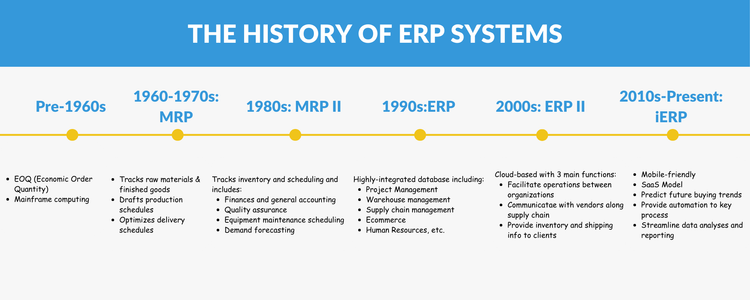
The history of ERP unfolds as follows:
- Pre-1960s: Traditional paper and pencil methods; bill of materials processed by mainframe computers in the 1940s and 50s.
- 1960s-1970s: Development of inventory control systems and the introduction of MRP.
- 1980s: Rise of MRP II.
- 1990s: Complete integration of business processes leading to the early forms of ERP.
- 2000s: Introduction of ERP II, incorporating CRM and Business Intelligence into operations.
- 2010s-Present: iERP integrates AI, machine learning, and IoT to harness real-time data.
History of ERP
ERP history begins with humble scheduling methods predating the computer. Manufacturers utilized the economic order quantity (EOQ) model, a paper-based scheduling system, to track their business operations. Slide rules acted as mechanical analog computers to help calculate inventory levels and the required raw materials needed for finished goods.
The 1940s and 50s saw the introduction and evolution of mainframe computers. In response to the mass output of WWII, large manufacturers began generating computerized bills of materials to draft purchasing and production plans.
1960-1970s: Inventory Control & MRP I
Early inventory control (IC) systems monitored raw material and finished goods quotas against customer demands. Whether manufacturers tracked these metrics through time-consuming pencil-and-paper methods or expensive mainframe computing, the question remained: how do we better coordinate our procurement, production, and delivery efforts?
Enter MRP I (material requirements planning), first developed in the early 1960s by IBM and JI Case, a construction machinery and tractor manufacturer. This system offered the coordination manufacturers desired through its three main functions:
- Track the availability of raw materials and finished goods in inventory
- Draft production schedules to meet demand
- Optimize delivery schedules for finished goods
However, early MRP software required immense processing power, an option only available to enterprise-level manufacturers.
1980s: MRP II
MRP II, a term popularized by Oliver Wight, ascended as the more advanced version of MRP in the 80s. In addition to inventory management and production scheduling, this system included new functionalities:
- Finances and general accounting
- Quality assurance
- Equipment maintenance scheduling
- Customer demand forecasting
At last, manufacturers were nearing a complete picture of the various processes in play to make efficient, high-quality production possible. Today, MRP I is a historical and academic term. Any MRP software on the market today is, in effect, an MRP II system.
1990s: ERP
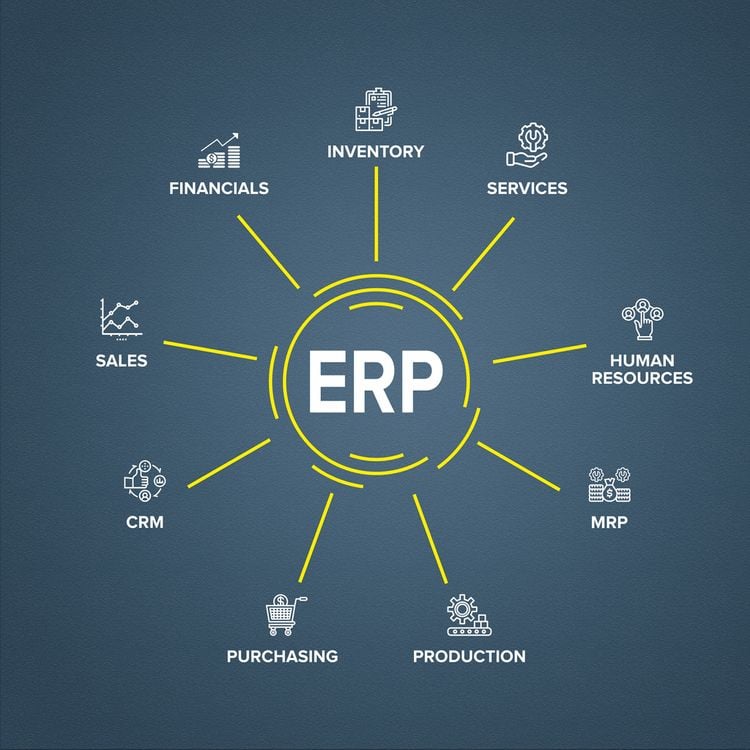
ERP introduced full integration of not just manufacturing processes but the company as a whole. ERP software functions through one database, incorporating metrics from all departments to create a single, definitive source of data.
ERP solutions segment data into distinct modules to support different business processes. Some basic ERP modules include:
- MRP
- Project management
- Warehouse management
- Supply chain management
- eCommerce
- Human resources
ERP software systems operated in on-premise locations until NetSuite established Cloud ERP in 1998, making data accessible anywhere with an internet connection. Thanks to the cloud and the data storage costs, ERP software changed the world by making data more accessible to small businesses.
2000s: ERP II
With the rapid technological developments of the early aughts, ERP software solutions could send and receive information from external organizations, vendors, and clients. The term ERP II arose in 2000 to describe these new advancements.
ERP implementation now resulted in three main functionalities:
- Facilitate operations between different organizations
- Communicate with vendors and partners throughout the supply chain
- Provide transparency to clients about inventory and shipping info
Customer relationship management (CRM) and business intelligence (BI) add-ons allowed manufacturers to nurture customer relationships and evaluate internal and external data to inform business functions at every level.
2010s-Present: Extended ERP
Extended ERP (aka iERP) as we know it today utilizes artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) to deliver real-time data. Offered mainly as a SaaS (software as a service) model based in the cloud, these systems predict future buying trends, provide automation to crucial business processes, and streamline reporting through web-based apps readily available even on mobile devices.
The Future of ERP
ERP software solutions are constantly growing with the latest business and technological trends. As organizations in all industries increasingly turn to ERP to help conduct their business processes, ERP vendors will continue evolving with the demands of today’s economic landscape. ERPs are also are beginning to implement direct machine integration which can connect to factory equipment or product tracking scanners.
ERP systems primarily focus on integrating finance, HR, and manufacturing into a unified system. However, with the boom of AI in recent years, ERP systems now offer features that can compile immense amounts of data, generate in-depth reporting, and discover insights into business performance. AI in ERP can range from voice command UI, and AI virtual agents to complex machine learning algorithms.
An example of AI in action is through the Epicor ERP. They introduced an AI-based voice command user interface that allows users to access data, run reports, and assist in making business decisions.
Key Takeaways
- As the cloud reduces data storage costs, ERP software can collect more granular data for thorough analysis and reporting.
- ERP will continue to fortify data security and consistency in the cloud through data access management, role-based permissions, protected IoT devices, and more safety protocols.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning will enable ERP software to make accurate demand forecasts, develop marketing opportunities, and identify potential flaws in your production planning.
- The Internet of Things, allows the ERP system to collect real-time data, alerting you to upcoming machine maintenance and ways to increase production output.
Important ERP Vendors
Baan
Now owned by Infor Global Solutions, Baan or Baan ERP formed in 1978 in Barneveld, Netherlands. This consulting company provided financial and administrative services. Baan developed Baan 4GL and Tools, database application development platforms that rose to prominence in the 90s.
Epicor Software Corporation
Epicor, founded in 1972 in Austin, Texas, officially launched financial and accounting software for businesses in 1984. They would market this technology alongside IBM in a campaign called The Platinum Series. Epicor would develop products for the manufacturing, distribution, retail, and service industries.
JD Edwards World Solution Company JD Edwards was founded in 1977 in Denver, Colorado and acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2005. With the introduction of JD Edwards WorldSoftware, popularly known as World, this company helped develop the trademark consistent interface of ERP across all modules.
Microsoft
Tech giant Microsoft would acquire four popular business applications in the mid-90s, integrating them into their Business Solutions Division. In 2006, they remarketed each program to fit the newly-launched Dynamics brand, and 2007 marked their transition to a web-hosted application with Dynamics CRM Online
Oracle Corporation
Now the third-largest software vendor after Microsoft and IBM, Oracle was first formed in 1977 as Software Development Laboratories. The US Air Force was the first to use its commercial relationship database program released in 1979 as Oracle.
SAP
Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing (SAP) is a German enterprise software company founded in 1972. They became renowned for SAP R/3 software in 1992, helping to rocket the company to its current status as the world’s leading ERP software vendor.
Why are ERP solutions so important?
Having an ERP system in place allows businesses in every industry to track and manage their data, promote efficient workflows, and connect teams across the globe.
-
Make more accurate financial decisions. ERP provides real-time insight into budgeting and forecasting, accounts payable and receivable, sales and billing, and more financial data.
-
Foster cross-department collaboration. Your team can communicate instantaneously from anywhere in the world. ERP allows your workforce to collaborate on content creation and other initiatives in actual time.
-
Improve data security. ERP provides data security by storing your documentation, payroll details, communications, and supplier lists in one location. Audit tools and user access management solutions add an additional layer of security to your information.
-
Streamline workflows. Employees can seamlessly share and access a single, definitive source of information, regardless of their office location and department. Your workforce can quickly access data related to numerous modules, from customer relationship management to human resources.
-
Speed up and monitor internal processes. Continuously optimize and make your workflows more transparent. ERP allows you to take a holistic approach to your business, pinpointing potential issues and ways to improve your procedures.
Looking for the Best ERP? Check out our picks for best ERP software or talk to an advisor for customized help.
FAQ
I’m not in the manufacturing industry. Should I still implement an ERP system for my company?
While MRP systems exist to optimize the manufacturing process, ERP solutions streamline workflows in construction, healthcare, nonprofit, real estate, hospitality, education, retail and yes — manufacturing. ERP variants are specialized for each industry for companies ranging from small businesses to enterprise-level organizations.
When Was ERP Invented?
ERP’s foundational system, known as MRP, emerged in the early 1960s. MRP was designed to assist businesses in balancing production with demand.
Who Invented ERP Software?
The MRP system, viewed as the first version of ERP, was a collaborative development between IBM and JI Case, a producer of construction machinery and tractors. Joseph Orlicky, an engineer at IBM, laid down the fundamental principles of MRP in 1964.
What Was the First ERP System?
The MRP system was the precursor to modern ERP. Initially labeled as MRP I, it was primarily concerned with inventory tracking and coordinating production and delivery timetables. As it evolved into ERP, the system expanded to include functions such as accounting, human resources, and customer relationship management.
What are the differences between ERP and MRP systems?
Although ERP can trace its origins back to MRP solutions, these two systems are different in a few key ways:
- ERP is customized to fit any industry; MPR is utilized mainly in manufacturing
- ERP includes modules for accounting, budgeting, human resources, inventory management, and supply chain management; MRP tracks inventory control, production & maintenance scheduling, demand forecasting, shipping logistics, and shop floor control
- ERP can be integrated with other system; MRP is meant to operate as standalone software
- ERP involves slower, more time-consuming implementation; MRP involves faster, more affordable implementation
Find out more about the differences between ERP and MRP systems.
