What is ERP and How Do ERP Systems Work?
Enterprise Resource Planning, or ERP, is a software system that integrates and streamlines core business processes, enabling efficient management and real-time data access for informed decision-making. Enterprise resource planning software, also known as ERP systems, have become indispensable for businesses of all sizes and structures, as they help organizations manage activities such as:
- Accounting
- Procurement
- Project management
- Risk management
- Supply chain operations
What is ERP? A Short Summary
- ERP systems are integrated software solutions that help organizations manage and optimize their operations.
- ERP implementation offers improved efficiency, cost savings, better decision-making, and increased collaboration between departments.
- When selecting an ERP solution, it is important to consider specific needs, industry requirements, scalability, and cost-effectiveness to ensure the system meets goals & objectives.
Understanding ERP: Defining Enterprise Resource Planning

Imagine a world where businesses can seamlessly integrate their operations, access real-time data for informed decision-making, and streamline department processes. This is the power of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, understanding “what is ERP” and leveraging it is crucial for organizations looking to stay ahead of the competition. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of ERP, its evolution, key components, benefits, and future trends, helping you confidently navigate the ERP world.
At its core, an ERP system facilitates the integration and optimization of core business processes, breaking down information silos and providing a single source of truth for decision-makers. By unifying various business functions, such as:
- Finance
- HR
- Procurement
- Supply chain management
ERP software helps organizations gain a holistic view of their operations and identify potential opportunities for growth and improvement.
One of the key advantages of ERP systems is their ability to provide real-time data, allowing leaders and managers to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information. This is particularly important in today’s fast-paced business environment, where organizations must adapt to changing market conditions.
Modern enterprise ERP systems have evolved significantly from their early predecessors, expanding their capabilities to include cloud-based deployment options, mobile device accessibility, and advanced analytics features. With these advancements, ERP systems have become essential for businesses looking to stay competitive in the modern business landscape.
Evolution
The term “ERP” can be traced back to earlier manufacturing resource planning (MRP) and MRP II systems. ERP systems were initially designed to automate back-end operations without customer or public interaction. It primarily focused on managing internal operations rather than customer needs. However, as organizations recognized the benefits of integrating various business processes, ERP systems evolved to encompass a wide range of functions.
Read More: The Difference Between MRP I and MRP II
From the 1990s to the early twenty-first century, the adoption of ERP systems experienced rapid growth as more organizations began to implement these systems to streamline their operations and gain a competitive edge. Early ERP systems were primarily focused on managing inventory, production, and accounting processes. However, as businesses became more complex and global, integrating other functions such as supply chain management, customer relationship management, and human resources management led to the development of more comprehensive ERP solutions.
Today, ERP systems have evolved into integral to modern business management, enabling organizations to access real-time data, optimize processes, and make informed decisions. With the advent of cloud-based ERP solutions, businesses can now benefit from increased scalability, flexibility, and lower upfront costs.
The future of ERP is set to be shaped by emerging technologies such as:
- Artificial intelligence
- Blockchain
- Augmented reality
- The Internet of Things
As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, they will further enhance the capabilities of ERP systems, helping businesses become even more agile, efficient, and responsive to changing market conditions.
Key Components

An ERP system comprises various modules designed to address a specific business need. ERP modules, also known as components, are the building blocks of an ERP system and help organizations manage different aspects of their operations more effectively.
Some of the most common functional areas an ERP system addresses include finance, procurement, manufacturing, supply chain, and human resources.
Finance and Accounting
The finance and accounting modules of an ERP system play a crucial role in handling financial transactions, reporting, and compliance. These modules offer various features, including:
- Accounts receivable and payable
- General ledger
- Expense management
- Financial reporting and analysis
These are the same functions typically found in accounting software. By integrating these financial functions within the ERP system, organizations can streamline their financial processes and ensure accurate and up-to-date financial data.
In addition to handling day-to-day accounting tasks, finance modules in ERP systems also help organizations manage more strategic financial activities, such as budgeting, forecasting, and financial planning. This enables businesses to gain greater visibility into their financial performance and make more informed decisions about resource allocation and investment strategies.
Another important aspect of finance modules in ERP systems is their ability to support regulatory compliance. By maintaining accurate financial records, generating timely and accurate financial reports, and automating compliance-related tasks, finance modules can help organizations stay on top of their regulatory obligations and reduce the risk of financial penalties.
Finally, finance modules in ERP systems can also support better collaboration between different departments and business units. By providing a single source of truth for financial data and enabling real-time access to this information, finance modules can help break down information silos and facilitate more informed decision-making across the organization.
Procurement and Sourcing
Procurement and sourcing modules in ERP systems oversee purchasing, maintaining supplier relationships, and controlling inventory. By automating and streamlining these processes, procurement and sourcing modules can help organizations reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and improve supplier relationships.
One key aspect of procurement and sourcing modules is supplier relationship management, which involves overseeing interactions with suppliers to ensure they provide the most advantageous products and services at the most competitive prices. By centralizing supplier information and providing tools for tracking supplier performance, procurement, and sourcing modules can help organizations identify opportunities for cost savings and more strategic sourcing decisions.
Another important function of procurement and sourcing modules is inventory control, which involves overseeing and regulating a business’s inventory amount. This includes monitoring inventory levels, ordering new inventory, and avoiding overstocking. Procurement and sourcing modules can help organizations optimize their inventory management and reduce carrying costs by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels and automating the reordering process.
In addition to these core functions, procurement and sourcing modules can also support other related activities, such as contract management, supplier risk assessment, and spend analysis. By providing a comprehensive suite of tools for managing the entire procurement lifecycle, procurement, and sourcing modules can help organizations drive greater value from their supplier relationships and improve overall supply chain performance.
Manufacturing and Production
Manufacturing and production modules in ERP systems are designed to assist businesses in optimizing their production planning, scheduling, and resource allocation. These modules enable businesses to:
- Streamline production processes
- Reduce costs
- Boost productivity
- Provide visibility into production processes
- Facilitate the identification and resolution of potential bottlenecks
One of the key advantages of utilizing manufacturing and production modules is the ability to manage production schedules and resources more effectively. By providing tools for planning and scheduling production activities, these modules can help organizations ensure that they make the most efficient use of their resources and minimize the risk of production delays or disruptions.
In addition to optimizing production processes, manufacturing and production modules can also support other related activities, such as quality management, maintenance management, and shop floor control. By providing a comprehensive set of tools for managing all aspects of the manufacturing and production process, these modules can help organizations drive continuous improvement and ensure that their products are produced to the highest quality standards.
However, implementing manufacturing and production modules can present certain challenges, such as the need for investment in new technology and staff training. Organizations should carefully evaluate their specific needs and requirements to overcome these challenges and ensure that the chosen solution is compatible with their existing systems and processes.
Supply Chain and Logistics
ERP systems’ supply chain and logistics modules are critical in streamlining distribution, transportation, and warehouse management. By automating and optimizing these processes, supply chain and logistics modules can help organizations reduce costs, improve customer service, and enhance overall supply chain performance.
One key aspect of supply chain and logistics modules is their ability to provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and transportation activities. By providing this level of visibility, these modules enable organizations to make more informed decisions about inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation planning.
Another important function of supply chain and logistics modules is their support for advanced planning and optimization processes, such as demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and transportation planning. By leveraging sophisticated algorithms and data analysis tools, these modules can help organizations more accurately predict demand, optimize inventory levels, and plan transportation routes to minimize costs and improve customer service.
In addition to these core functions, supply chain and logistics modules can also support other related activities, such as supplier collaboration, trade compliance, and reverse logistics. By providing a comprehensive set of tools for managing the entire supply chain lifecycle, supply chain and logistics modules can help organizations drive greater value from their supply chain operations and improve overall business performance.
Human Resources and Talent Management
Human Resources and Talent Management modules in ERP systems are designed to help organizations manage and develop their workforce. These modules typically include functionality for recruiting, hiring, training, and managing employees and tools for developing and managing talent within the organization.
One of the key benefits of Human Resources modules in ERP systems is their ability to automate administrative tasks, such as employee record-keeping, payroll processing, and benefits administration. By automating these tasks, Human Resources modules can help organizations reduce administrative overhead and allow HR staff to focus on more strategic activities.
In addition to automating administrative tasks, Human Resources modules also provide tools for more effective HR management, such as performance tracking, succession planning, and workforce analytics. Human Resources modules can help organizations make more informed decisions about employee development, retention, and performance management by providing a centralized database for employee information and enabling real-time access to this data.
Finally, Human Resources modules in ERP systems can also support talent management activities, such as talent acquisition, learning and development, and career planning. Human Resources modules can help organizations attract, develop, and retain the best talent to drive business success by providing comprehensive tools for managing the entire talent lifecycle.
Benefits of Implementation
Implementing an ERP system can bring numerous benefits to an organization, including:
- Increased efficiency
- Cost reductions
- Improved decision-making
- Increased collaboration between departments
By integrating various business functions and providing real-time access to data, ERP systems can help organizations optimize their processes, reduce information silos, and make more informed decisions.
One of the key benefits of implementing ERP software is the ability to automate and streamline various business processes, such as procurement, inventory management, and financial reporting. Organizations can reduce manual tasks, minimize errors, and improve overall operational efficiency by automating these processes.
Another important benefit of ERP implementation is the potential for cost savings. ERP systems can help organizations achieve cost savings through:
- Optimizing processes
- Providing better visibility into resource utilization
- Identifying opportunities for cost reduction
- More efficient resource allocation
Finally, ERP systems can also help improve collaboration and communication across organizational departments. By breaking down information silos and providing a single source of truth for data, ERP systems can facilitate better decision-making and ensure that all stakeholders have access to the information they need to perform their jobs effectively. This can improve overall business performance and a more agile, responsive organization.
Deployment Options
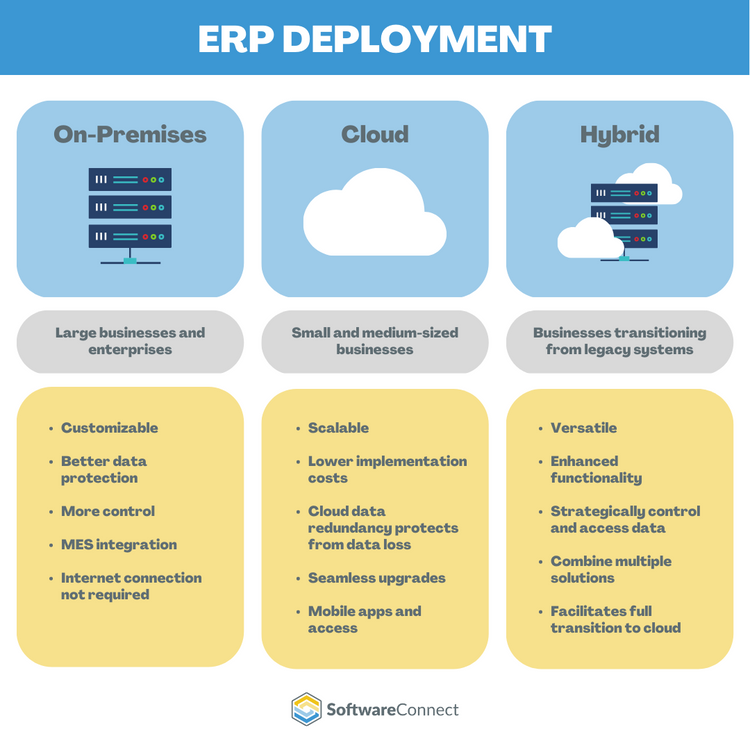
Several deployment options are available for ERP systems, including on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid models. Each option has its advantages and considerations, and organizations should carefully evaluate their specific needs and requirements before selecting a deployment model.
On-premises ERP systems:
- Installed on the organization’s own servers
- Managed by the organization’s IT staff
- Higher upfront costs
- Greater ongoing maintenance responsibilities
- Greater control over the system and its data
Cloud-based ERP systems, or cloud ERP, are hosted on remote servers managed by a third-party provider and typically accessed through a web browser. This deployment model offers lower initial costs, easier scalability, and reduced maintenance responsibilities, making it an attractive option for many organizations, particularly small and medium-sized businesses.
Hybrid ERP systems combine elements of both on-premises and cloud-based deployments, allowing organizations to take advantage of the benefits of both models. For example, an organization might choose to deploy some modules, such as finance and HR, in the cloud while keeping other modules, such as manufacturing and production, on-premises.
When selecting a deployment model for an ERP system, organizations should carefully consider factors such as:
- Cost
- Scalability
- Security
- Integration with existing systems and processes
By evaluating these factors, organizations can make an informed decision about the deployment model that best meets their needs and requirements.
Selecting the Right ERP Solution for Your Business
Selecting the right ERP solution for your business involves evaluating various factors, such as your organization’s specific needs, industry requirements, and future growth plans. You can select an ERP system that best supports your organization’s goals and objectives by carefully considering these factors.
First, assessing your organization’s specific needs and requirements is important. This includes understanding the processes and functions most critical to your business and identifying any gaps or inefficiencies in your current systems. By identifying your organization’s unique needs, you can better evaluate the capabilities and features offered by different ERP solutions and determine which one will best meet your needs.
Next, consider any industry-specific requirements that may apply to your organization. Some industries have unique regulatory or compliance requirements, while others may have specific functional needs that are not addressed by generic ERP solutions. By selecting an ERP system that has been designed with your industry in mind, you can ensure that your organization’s unique needs are met.
Scalability is another important factor to consider when selecting an ERP solution. As your organization grows, your ERP system will need to be able to accommodate increased user counts, transaction volumes, and data storage requirements. By selecting a scalable ERP solution, you can ensure that your system will continue to meet your organization’s needs as it evolves and expands.
Finally, consider the overall cost of the ERP software, including the initial purchase price and ongoing maintenance, support, and upgrade costs. By carefully weighing the costs and benefits of different ERP solutions, you can select the one that will provide the best value for your organization over the long term.
Best Practices for Successful ERP Implementation

Implementing an ERP system can be a complex and challenging process, but with careful planning and adherence to best practices, organizations can increase the likelihood of a successful implementation. Some of the key best practices for ERP implementation include:
- Thorough planning
- Stakeholder buy-in
- Employee training
- Ongoing support
Thorough planning is essential for a successful ERP implementation. This includes developing a detailed project plan, setting realistic timelines, and allocating appropriate resources to the project. By carefully planning and managing the implementation process, organizations can minimize the risk of delays, cost overruns, and other implementation challenges.
Stakeholder buy-in is another critical factor for a successful ERP implementation. This involves securing support from key decision-makers within the organization and ensuring that all affected departments and employees understand the new system’s benefits and are committed to its success. Organizations can increase the likelihood of a smooth and successful implementation by fostering a sense of ownership and commitment among stakeholders.
Employee training is also essential for a successful ERP implementation. This includes providing comprehensive training on the new system for all affected employees and ongoing support and resources to help them adapt to the new system. By investing in employee training and support, organizations can ensure that their employees are well-equipped to use the new system effectively and maximize its benefits.
Finally, ongoing support is crucial for a successful ERP implementation. This includes providing regular updates and improvements to the system and addressing any issues or concerns that may arise during the implementation process. By providing ongoing support and resources, organizations can help ensure that their ERP system continues to deliver value and meet the organization’s needs over the long term.
Measuring Performance and ROI
Measuring an ERP system’s performance and return on investment (ROI) is crucial for validating the investment made and monitoring success and progress over time. To effectively measure ERP performance and ROI, organizations should begin by setting clear goals and objectives for the implementation, such as improving efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing collaboration between departments.
Once goals and objectives have been established, organizations should track key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor progress and measure success. KPIs should align with the organization’s goals and objectives and provide a clear and quantifiable measure of performance. Examples of KPIs might include improvements in order processing time, reductions in inventory carrying costs, or increases in on-time delivery rates.
In addition to tracking KPIs, organizations should also monitor the success of the ERP implementation itself. This includes:
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the implementation process
- Assessing the level of user adoption
- Measuring the overall satisfaction of stakeholders with the new system
By regularly monitoring the success of the implementation, organizations can identify and address any issues or challenges that may arise and ensure that the ERP system continues to deliver value.
Finally, organizations should periodically reassess their ERP performance and ROI to ensure that the system meets their needs and delivers the expected benefits. This may involve adjusting KPIs, revising goals and objectives, or seeking additional improvements and enhancements to the system. By continually evaluating and improving the performance of their ERP system, organizations can maximize their return on investment and ensure that their ERP system remains a valuable asset for the organization.
The Future of ERP: Emerging Trends and Technologies
The future of ERP is shaped by emerging trends and technologies that promise to transform how organizations manage their business processes and make data-driven decisions. Some of the most significant emerging technologies influencing the current ERP landscape include artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
AI and machine learning technologies have the potential to revolutionize ERP systems by automating complex tasks, analyzing large volumes of data, and providing real-time insights and recommendations for decision-making. By incorporating AI-driven analytics and automation into ERP systems, organizations can further streamline their processes, reduce manual tasks, and improve overall efficiency.
Blockchain technology, which enables secure and transparent data sharing across a distributed network, has the potential to significantly enhance supply chain management, financial transactions, and data integrity within ERP systems. By leveraging blockchain technology, organizations can improve their ERP systems’ security, transparency, and efficiency, unlocking new possibilities for collaboration and innovation.
Augmented reality (AR) and IoT technologies can also play a significant role in the future of ERP, particularly in areas such as manufacturing, logistics, and warehousing. By integrating AR and IoT devices with ERP systems, organizations can gain real-time visibility into their operations, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall productivity.
As these emerging technologies continue to evolve and mature, they will help shape the future of ERP, enabling organizations to become more agile, efficient, and responsive to changing market conditions. By staying abreast of these trends and technologies, businesses can ensure that their ERP systems remain valuable for driving growth and success in the modern business landscape.
Choosing an ERP Vendor: Factors to Consider
When selecting an ERP vendor, it is essential to take into account factors such as:
- Industry expertise
- Customization options
- Support services
- Overall cost
By carefully evaluating these factors, organizations can decide on the best ERP vendor to meet their needs and requirements.
Industry expertise refers to the vendor’s knowledge and experience in the specific industry in which the ERP system will be implemented. This includes understanding the industry’s unique requirements and challenges and the best practices for deploying an ERP system in that industry. By selecting a vendor with industry expertise, organizations can ensure that their ERP system is tailored to their specific needs and that it will be able to address the unique challenges of their industry.
Customization options are another important factor to consider when selecting an ERP vendor. ERP vendors typically offer a range of customization options, including customizing the user interface, adding new features, and integrating with other systems. Understanding the customization options available and how they can be used to meet the organization’s specific requirements is essential.
Support services are a critical factor to consider when selecting an ERP vendor. ERP vendors typically offer various support services, such as training, technical support, and consulting services. It is essential to be aware of the available support services and how they can be used to ensure the successful implementation and use of the ERP system.
Finally, the overall cost of an ERP system should be considered when selecting an ERP vendor. This includes the initial purchase price and ongoing maintenance, support, and upgrade costs. By carefully weighing the costs and benefits of different ERP vendors, organizations can select the one that will provide the best value for their organization over the long term.
Summary
In conclusion, ERP systems have come a long way since their inception, evolving from simple inventory management tools to comprehensive business management solutions that integrate and optimize a wide range of business functions. By understanding the key components, benefits, deployment options, and future trends of ERP systems, organizations can make informed decisions about the right ERP solution for their needs and ensure a successful implementation. As technology continues to advance and reshape the world of ERP, businesses that stay abreast of these developments will be well-positioned to thrive in the competitive landscape of the modern enterprise.
FAQ
What is ERP in simple terms?
ERP stands for enterprise resource planning and is a type of software system that automates and manages core business processes such as finance, HR, manufacturing, supply chain operations, and more to optimize performance.
It helps organizations streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. ERP systems are designed to integrate all aspects of a business, from customer relationship management (CRM) to inventory management and financials. They provide a single source of data that users can access.
What’s the difference between CRM and ERP?
CRM systems focus on customer satisfaction and loyalty, while ERP systems streamline and optimize core business processes.
CRM systems support front-office business functions, whereas ERP systems connect back-office functions.
Is SAP an ERP system?
SAP is a market leader in enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and offers a variety of solutions to manage business processes and relationships. It serves customers in over 180 countries and provides on-premises, cloud, and hybrid deployment models, focusing on cloud computing.
SAP’s solutions are designed to help businesses streamline their operations, reduce costs, and increase efficiency. The company’s suite of products includes ERP, analytics, customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain management.
What is the main purpose of an ERP system?
The main purpose of an ERP system is to integrate and streamline core business processes, enabling efficient management and real-time data access for informed decision-making.
What are the main benefits of implementing ERP software?
Implementing ERP software improves efficiency, cost savings, better decision-making, and enhanced collaboration, allowing organizations to realize maximum value.
