What is a Quality Management System?
A quality management system (QMS) offers a comprehensive tool kit to analyze risks, set quality objectives, implement workflows to achieve standards, and audit for optimal performance. It coordinates activities to enhance efficiency and foster continuous improvement across all operations. Discover the benefits of QMS, its principles, and how it’s compliant with ISO 9000 and other standards.
Benefits of QMS
- Improves Regulatory Compliance: Allows you to stay compliant with regulatory standards such as ISO 9001, Title 21 CFR Part 11, NERC, SSOP, HAACP, and more.
- Increases Operational Efficiency: Streamlines processes and reduces errors by automating tasks, leading to more efficient operations.
- Analyzes and Reduces Risk: Identifies the cost of quality management improvements versus the likely impact of reduced financial liability. This includes analysis tools for quantifying the financial risks related to quality exceptions.
- Increases Customer Satisfaction: Shows customers that your products are constantly evaluated for reliability and ease of use. Helps keep promises to customers that determine your ability to gain future business, upsell products, and generate enthusiasm for your goods and services.
- Eliminates Inefficiencies: Create quality products efficiently and eliminate manual paperwork with an electronic quality control system.
- Document Control: Document quality policies and objectives. Includes quality manuals, procedures, and other documents needed for effective planning.
Quality Management Methodologies
- Standardization: This system implements consistent processes, procedures, and frameworks across an organization to manage its operations effectively.
- Total Quality Management: TQM is a management approach that focuses on continuously improving the quality of their products and services and customer satisfaction. In this approach, all employees actively work toward the common goal.
- Six Sigma: This data-driven methodology uses the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) approach to improve process efficiency and eliminate defects by reducing variability.
- Lean Manufacturing: Lean manufacturing eliminates waste and maximizes efficiency. This approach is often combined with Six Sigma as ‘lean Six Sigma.’
ISO 9000, 9001, and Other Standards
The ISO 9000 family of quality management systems is a set of standards designed to help organizations improve product and service delivery by providing documented procedures and workflows.
ISO 9001 is the international standard that specifies requirements for quality management software (QMS). Organizations use the standard to demonstrate the ability to provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
Quality management systems are a set of documented policies, procedures, and responsibilities organized into a structured system of processes to assist an organization in realizing its quality vision goals and objectives. ISO standards led to ISO 9001 for quality management systems. This comprises a set of generic standard requirement standards that govern the quality management systems of certified companies or organizations.
Credited or CB auditors are authorized to award a certificate of compliance with the ISO 9001 standard. This certification must be reviewed annually and renewed every 3 years. One of the foundation requirements of this standard is that its implementation should be placed on a system of dynamic processes rather than a set of static standards.
The ISO 9001 standard includes procedures for the following activities and has required documented procedures:
- Control of documents and records, such as the gathering of customer requirements and the recording of product history
- Control of non-conforming products to prevent defects and rejects from being sent to customers
- Continually improvement through corrective and preventive actions to prevent mistakes from happening again
- Internal audits to show the organization is committed to quality and conformance to the ISO 9001 standard
Maintaining compliance with ISO 9001 standards helps meet customer requirements and expectations, leading to an effective and efficient organization.
Other Certifications and Standards
- API Q1/Q2: Standards specific to the oil and gas industry that are similar in nature to ISO 9001. API W2 has the explicit requirement for contingency planning. Both API Q1/Q2 make the distinction between corrective and preventative action (something ISO 9001 does not)
- ISO 13485: Similar to ISO 9001 but for medical devices. Has a specific requirement for software validation and requires validation reports to verify for the auditor that it will work as intended. Includes requirement for CFR 21 specific electronic signatures
- ISO 50001: Energy management standard for addressing the energy consumption and use of an organization
- ISO 27001: Information security, similar to ISO 9001 but with a change in focus to data security and integrity vs product quality
- ISO 45001: Health and safety, similar to ISO 9001 but with a change in focus to employee safety vs product quality
- ISO 14001: Health and safety, similar to ISO 9001 but with a change in focus to environmental concerns vs product quality
- ISO 17025: Laboratory testing and calibration
- IATF 16949: Automotive quality management standard similar to ISO 9001 with additional requirements
- AS 9100: Aerospace quality management standard similar to ISO 9001 with additional requirements
Quality Management Principles
There are 7 quality management principles that can help guarantee your organization’s success. These fundamental beliefs, rules, and values are accepted as true and known to improve an organization’s quality management processes.
- Customer Focus: Meet customer expectations and the needs of all interested parties
- Leadership: Create conditions in which people are engaged in achieving the organization’s quality goals. Communicate the strategic direction and objectives throughout the organization. Encourage the organization’s commitment to quality.
- Engagement of people: Enhance the capability to create and deliver value through competent, empowered, and engaged employees.
- Process Approach: Focus on key processes, align systems through these processes, optimize resource performance, reduce cross-functional barriers, and uphold consistency, effectiveness, and efficiency.
- Improvement: Maintain an ongoing focus on improvement. Monitor, audit, and review completion and results. Promote and establish improvement objectives at all levels of the organization. Improvement will help identify risks and eliminate root causes.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making: Make decisions based on data analysis and evaluation. Determine and monitor your key data sources. Understand the cause-and-effect relationships. Make decisions and take actions based on evidence.
- Relationship Management: Identify and build relationships with the relevant stakeholders who influence an organization’s performance.
Elements of a Quality Management System
The core elements found and provided by a QMS include:
Continuous Improvement
By harnessing the power of data management, organizations can drive continuous improvement and preventative quality control activities. Ineffective data management practices can lead to inconsistent product quality, operating inefficiencies, compliance risks, poor customer satisfaction, and lower profitability.
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA)
CAPA is a continuous improvement tool that collects and analyzes data to identify and eliminate product quality issues, process inefficiencies, and equipment issues. This helps prevent nonconformance from recurring by eliminating the cause of a nonconformity, while preventative action prevents nonconformance from occurring at all.
CAPA software features offer quality improvement processes to alert you to these potential issues through risk assessments and root cause analysis, which identify the underlying problem with a product or process. By finding out the root cause, you’ll be able to more easily resolve the issue, and actions can be taken to prevent the nonconformance from occurring again.
Audit Management
Total quality management can be achieved through a QMS implementation that focuses on audit management. This includes a preliminary evaluation of your site that details nonconformities. Then a registration audit occurs which includes a readiness audit and a certification audit. From there, a surveillance audit is conducted over time to measure continued conformance to ISO standards and any other additional regulatory programs.
Recertification audits are also common over a three-year registration cycle, called triennial audits. Finally, internal audits can occur at any time at recommended intervals from the QMS.
Risk Management
Risk management processes help quantify, minimize, mitigate, and build contingencies to deal with risks. Risk management within QMS will coordinate and optimize reducing harm to your organization’s earnings potential by identifying and categorizing risk into types, origins, and ownerships.
Manufacturers use risk management to identify hazards associated with their own production process. They also use it for compliance regulations when estimating, monitoring, evaluating, and controlling risks across the product lifecycle.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure modes and effects analysis study the consequences of possible failures, including errors and defects. They aim to decrease manufacturing costs by providing opportunities for preventative and corrective maintenance rather than reactive maintenance.
FMEA processes include defining corrective actions, identifying causes and effects, improving economic production, avoiding defects, preventing failure, reducing product development time and costs, defining and minimizing risks, and improving the quality and reliability over time.
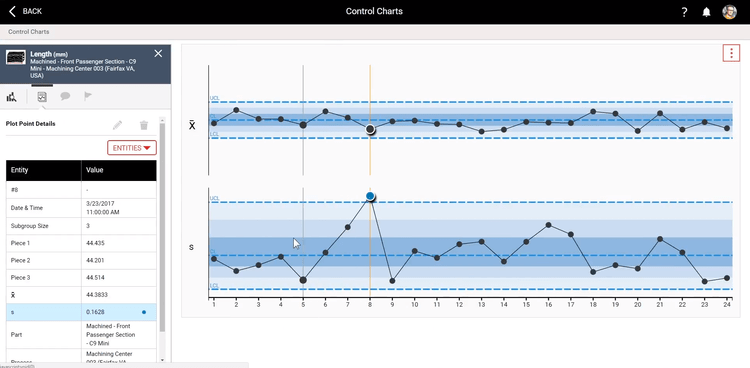
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Statistical process control software collects quality and performance data in real-time for statistical analysis. Manufacturers use SPC software to identify product quality issues and process variations, take corrective action before extensive issues occur, and improve process performance.
The data collected by SPC software is plotted onto user-friendly graphs, including control charts, Pareto charts, and histograms. The data in an easy-to-read format allows you to see when data variations occur and how far they deviate from the expected value.