The Best EHR Software
Compare the best EHR software based on pricing and features like clinical documentation and collaborative EMR tools. Our top picks cover everything from solo practices to large healthcare organizations.
- Effectively cuts down on manual work
- Offers revenue cycle management tools
- Integrates with practice management solutions
- Compliance with ICD10 and SNOMED standards
- Online appointments and medical marketing
- Collaboration features for healthcare teams
- ViewPoint tool offers strong reporting and analytics
- Scalable, user-based pricing model
- Includes 18 fully integrated modules for different industries
Electronic health records software, also known as electronic medical records software, helps you streamline clinical workflows. Our guide covers the top solutions for your practice, whether you’re a start-up or a well-established multi-specialty clinic. We ranked our top picks based on our advanced review methodology.
- athenaOne: Best Overall
- Hippocrate: Most Affordable Option
- Multiview: Best ERP Option
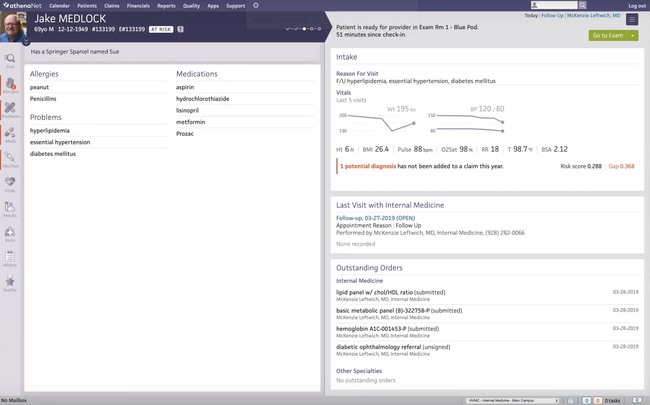
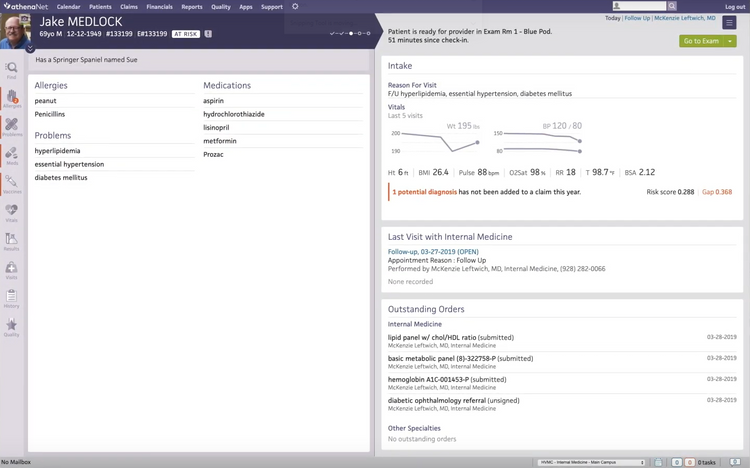
athenaOne - Best Overall
athenaOne features a clinical documentation and encounter workflow engine that streamlines everything from pre-visit prep to post-visit billing. Your clinicians and staff can start by completing tasks before the patient ever arrives, like reviewing charts. You can even customize intake forms to fit your specialty, from orthopedics to cardiology.
During the visit, this medical charting software helps keep face time front and center. With embedded, voice-driven dictations and customizable macros, providers can chart naturally without being glued to a screen. What’s more, your physicians can access patient records, check schedules, and handle charting right from their mobile device. For practices focused on value-based care, preventive care tasks and coding gaps–like flu shots or HCC RAF prompts–pop up directly in the workflow.
Overall, athenaOne is a solid choice for start-up practices, urgent care centers, specialty practices, and federally qualified health centers. While some have noted it can lag when pulling up records, it’s still quite efficient at cutting down on manual work and automating encounters, for small clinics to large healthcare institutions.
Hippocrate - Most Affordable Option
Hippocrate offers a forever free platform for solo practices with one doctor and a small practice plan starting at $25/user/month for two to 15 doctors. It includes a collaborative EMR tool that lets your physicians connect not just with their own team but other providers as well. Whether discussing a tricky case or referring a patient to a specialist, your physicians won’t need to rely on a separate messaging tool.
This EHR software includes a solid set of built-in features:
- Secure messaging supporting HIPAA-compliant, encrypted chats between healthcare professionals
- A referral workflow that lets you send imaging, charts, and labs along with the patient
- Cross-specialty communication for rural or telemedicine-based care
- Audit trails to track all activities for compliance
- Integration with patient records, so all conversations and referrals stay documented
While large practices will need to reach out for a custom pricing quote, Hippocrate is refreshingly cost-effective. Just keep in mind: the free solo plan comes with ads. If you’d rather keep things ad-free, the small practice plan is the way to go.
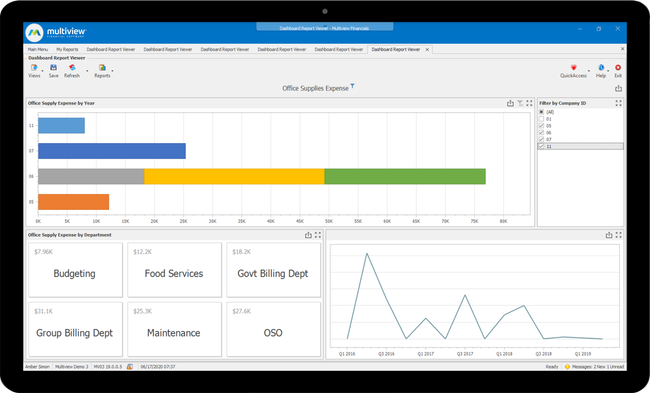
Multiview - Best ERP Option
If you’re already using an EHR software like Epic, Cerner, or Meditech, you’re halfway there. But when it comes to tying patient care to financial outcomes, you’ll need a system like Multiview. This healthcare-focused ERP integrates with EHR or EMR software to help connect the dots between clinical data and financial strategy.
It starts by pulling revenue and patient-level billing directly from your EHR into Multiview’s data warehouse. From there, you can create high-level financial dashboards and drill all the way down to patient-specific transactions. You can even track patterns across locations and departments and analyze performance by service line or payer type.
Plus, with built-in auto-reconciliation, Multiview runs daily checks between your EMR and accounting records. It flags discrepancies with automatic alerts, so nothing slips through the cracks. Your team can catch and resolve mismatches before they snowball into bigger problems, and it provides an automated trail of reconciled transactions for any future audits.
If you’re looking for an EHR software that can also handle all your financial, budgeting, and forecasting needs–you won’t find that in one product. But you can pair your existing EHR with Multiview to gain the level of control your care team and CFO actually need. While pricing requires a custom quote, it’s a solid fit for mid-sized to large healthcare organizations.
What is Electronic Medical Records (EHR) Software?
Electronic health records software (EHR software), also known as electronic medical records software (EMR software), creates electronic data sets of patient information, such as charts of medical and treatment histories, diagnoses, medications, immunizations, allergies, lab results, and more. This information helps streamline provider workflow and is often used by doctors, physicians, and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about a patient’s care.
Electronic medical records is the original term, which covered the clinical functions of the software, which included drug/allergy interaction and documentation of encounters. Today, electronic health records is the more commonly used term that refers to any software used by healthcare physicians to track aspects of patient care. This can encompass medical practice management software features such as medical patient scheduling and medical billing.
EHR software can be used by hospitals, laboratories, specialist offices, medical imaging facilities, pharmacies, emergency facilities, and school and workplace clinics. The EMR data gathered by EHR software is designed to be easily transferred between different healthcare providers’ offices, so all information on patient care is available to those who need it. These businesses use EHR software for productivity and financial improvements, to improve the quality of care offered, and to improve the job satisfaction of employees responsible for recording the data.
Key Features
- Patient Scheduling: Create and view custom schedules for providers across multiple locations. Color code timeslots for easy identification of what. Send out automatic appointment reminders via email or text in order to reduce no-shows.
- Patient Workflows: Improve the workflow of your medical practice and avoid bottlenecks. Track charts as they flow through the office–from chart preparation to registration, to the nurse, the billing department, and the physician, etc.
- Task Management: Streamline tasks into an electronic to-do list. Provide a single point of view for all your daily work activities, including encounters, reviewing lab results, signing prescriptions, tracking orders for needed office supplies, and more.
- Templates: A customizable complete note to mark the clinical encounter that meets documentation standards with minimal extra typing. Templates are meant to fit your specialty, workflow & preferences and optimize your charting process. Create templates for medical charting, SOAP notes, patient intake forms, flowcharts and lab orders.
- e-Prescribing: Digitally prescribe and maintain records of controlled substances in a HIPAA-compliant manner. Create and sign prescriptions before sending them to the patient’s preferred pharmacy.
- Reporting: Create reports based on real-time clinical and financial data. Get insight into key areas for improvement or where focus is needed in your medical practice.
- Revenue Cycle Management (RCM): Helps automate and streamline claims management, payment processing, and the overall revenue process. Used by healthcare organizations to improve cash flow by tracking all patient care from the initial phone call, appointment scheduling, co-pay, and final payment on the remaining balance.
- Patient Encounters and Charting: View patient histories like medications, allergies, existing problems, and immunizations. Receive prompts for questions related to medical and psychosocial concerns and note responses accordingly. Ensure documentation is thorough so as not to affect claims reimbursement.
- Patient Portal: A custom landing page for patients to log in and view/create appointments, receive prescriptions, speak with doctors via telemedicine conference or secure emails/messages, pay bills, and more.
Primary Benefits
EHRs let healthcare providers exchange information securely via electronic methods, which helps your medical practice provide higher-quality care while enhancing the type of services your organization can offer patients. This means patients will continue to use your organization for all their healthcare needs. Benefits not offered by EMR solutions can usually be found via integrations with other systems, such as HIPAA-compliant accounting software.
Some of the top benefits of electronic medical records software include:
Provide Up-To-Date Information About Patients When Needed
Integrated electronic health record systems improve care coordination by connecting all providers with the same accurate information regarding a patient’s health. With the number of specialists available today, many patients see multiple doctors and practitioners depending on their needs. Alternatively, patients have more resources at their fingertips to see multiple providers for second opinions or to find someone more favorable to their insurance plan. Healthcare providers’ easier access to their patient’s health records reduces medical errors.
Patients also have the ability to view their health records online via patient portals. These web-based systems let patients log in from their home computer or their mobile device via iOS or Android smartphones. This lets patients easily adjust certain details about themselves, such as contact information, current medications, allergies, and more. They can easily see when their next appointment is, pay bills, find a nearby pharmacy that can fill their prescriptions, and more.
Diagnose Patients and Reduce Medical Errors More Effectively
How does electronic health records software diagnose a patient? EHRs improve a healthcare facility’s risk management by considering all aspects of a patient’s condition. Diagnostic information can be used in decision-making when all relevant health information is in one place. This includes lab results and previous medical conditions and surgeries a patient may have had.
A smart EHR software will not be a simple ledger of information but rather a computer system that calculates when potential problems may occur. For example, if the EHR system has a list of a patient’s current medications or allergies, it can give an alert if the patient is prescribed something that may conflict. Likewise, if a patient goes into the emergency room for any reason, healthcare decisions can be adjusted appropriately when they are in situations where a patient is unresponsive.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Electronic medical records software was originally created to streamline the gathering and recording of the necessary information. An electronic system will be more efficient than paper records by allowing for a centralized location for charts while providing quick access to pertinent patient information. In a life-or-death scenario, quick access to a patient’s medical history means everything.
In addition to quick access to patient records, communication is also improved. Some may feel that the health industry is rather disjointed; you go to your general practitioner for a lingering health concern, who recommends you to a specialist who prescribes you medicine, which you have to get filled at a nearby pharmacy and get billed to your insurance company. EHR solutions will let all of these channels speak with one another easily, so the patient experiences little to no interruption in their care. Offices can easily schedule appointments, and physicians and insurance personnel will get to see everything they need to about the appointment.
Merit-Based Incentive Payment Systems (MIPS)
Medicare and other merit-based incentive payment systems continue to encourage healthcare organizations to use EHR systems in their organizations. The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act of 2009 can be responsible for creating a critical national goal for all hospitals to implement an EHR software. The concept of meaningful use means using EHR technology in a certified manner, which will help:
- Reduce health disparities
- Engage patients in their health
- Improve care coordination
- Improve public health
- Ensure privacy
EMR Software vs EHR Software
What is the difference between electronic medical records (EMR software) and electronic health records (EHR software)? One may believe it’s a matter of personal preference of using the term “medical” or “health”, but the terms have evolved to mean two different things. For the sake of simplicity, you are usually fine with assuming that EMR software and EHR software are the same things.
EMR is the older term that contains the standard medical and clinical data gathered in one provider’s office. The concept of electronically recording this medical data came in the 1960s; it became a reality when the first EMR system was developed in 1972 by the Regenstreif Institute. As most new technology is, the first EMR’s were high-priced and not widely used except by large hospitals.
With the rise of the Internet in the 1990s and the prevalence of computers being more readily available in the workspace, healthcare IT budgets started to increase faster than ever before. Today, medical records are increasingly paperless and accessible via computer systems or even online.
In the name change from electronic medical records to electronic health records is the meaning behind that middle word. The “H” for health implies a bigger meaning than the “M” in medical. Many felt that EMR was a tool only to be used by doctors. Today, EHR systems can also be used by patients, insurance companies, and the government. “Medical” is also a more limited word, implying that the software only stores medical records. In reality, EHR software options store info on patients’ mental health and can be used by non-traditional medical offices, such as chiropractors and ophthalmologists.
Emerging Trends
- Telemedicine software provides remote clinical care by connecting patients and doctors in real time via videoconferencing and the Internet. Part of the telehealth movement, this software provides an effective and convenient method of providing healthcare to those who cannot easily access a healthcare facility, such as the elderly, the sick, or people who live in rural areas.
- Artificial Intelligence and Voice Recognition can help healthcare providers make diagnoses or recognize historical trends about a patient’s condition. Similar to using a voice-activated tool such as Alexa or Google Home, a voice-activated EHR solution can let a doctor ask for details about a patient’s recent blood tests, for example. The system would indicate whether they’re in a healthy range.
- A 2025 report by Definitive Healthcare found that 89% of the nation’s largest hospitals use six EHR vendors: Epic, Cerner, Meditech, CPSI and its subsidiaries, Harris and its subsidiaries, and MEDHOST supply certified EHR technology.
Pricing Guide
EHR software costs can range from $3,000 to over $1,000,000/year based on your desired features and practice size:
Small Practices: $3,000–$10,000/year
- Ideal for solo or small practices with 1-3 providers
- Examples: Practice Fusion, SimplePractice, Hippocrate
Mid-Sized Practices: $10,000–$40,000/year
- Best for growing clinics with 4-10 providers needing more automation, support, and integrations
- Examples: CharmHealth, AdvancedMD, DrChrono
Large Practices EHR: $40,000–$150,000/year
- Designed for larger practices with 11-50 providers and complex workflows.
- Examples: athenaOne, eClinicalWorks, Greenway Health
Enterprise-Level Organizations: $150,000–$1,000,000+/year
- Best for hospitals and multi-location health systems with over 50 providers needing compliance tools, scalability, and advanced features
- Examples: Epic, Cerner, Meditech
Remember to factor in licensing fees alongside implementation, training, support, and any add-ons, such as e-prescribing or telehealth tools.