7 Benefits of ERP Systems for Your Business
With a modern enterprise resource planning or ERP systems, businesses can enjoy a wide range of benefits like streamlined operations, enhanced collaboration, and real-time adaptability to changing needs. At Software Connect, we personally use and review ERP solutions to better understand these top benefits.
Article Summary:
- ERP systems provide a range of benefits, from improved efficiency and enhanced collaboration to better decision-making.
- The full range of benefits depends on the selected software and the business itself.
- Customization and modular design allow for even more benefits.
The main 7 benefits of an ERP system include:
- Improved efficiency
- Enhanced collaboration and innovation
- Better decision-making
- Scalability and flexibility
- Increased risk management
- Lower operating costs
- Maximize Profits
What is ERP?
ERP software is designed to manage various operations within an organization efficiently. They comprise a suite of tools that facilitate the optimization of business processes, such as:
- Supply chain management
- Accounting functions
- Human resources (HR)
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Risk management
By centralizing data, ERP systems eliminate the issue of scattered information across different applications and spreadsheets throughout the organization, reducing the prevalence of duplicate data in various formats. This streamlined approach to data management leads to improved efficiency, better decision-making, and, ultimately, a more competitive business.
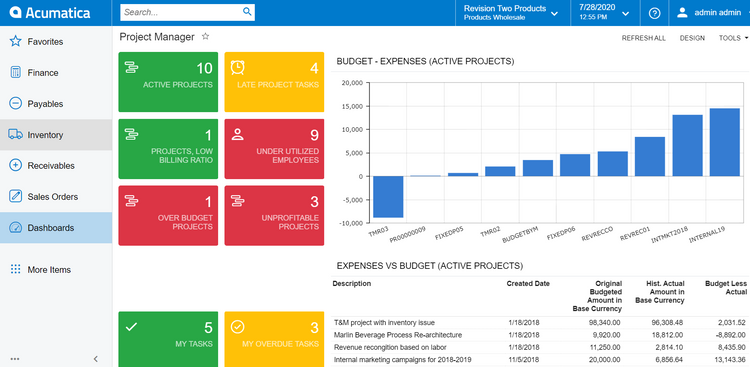
Read More: See top examples of ERP systems to get a better idea of what ERP is.
7 Main Benefits of ERP Software
ERP systems offer numerous advantages that can transform how businesses operate, ultimately leading to increased profitability and growth. These 7 main benefits stem from the system’s ability to improve efficiency, enhance collaboration, and facilitate better decision-making by providing real-time data, analytics, and reporting tools.
1 Improved Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of ERP systems is their ability to optimize efficiency by automating tasks. By replacing repetitive manual activities with automated workflows, businesses can save valuable time and resources, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities. Some benefits of automation include:
- Real-time insights into business performance
- Faster data processing
- Reduced errors from manual data entry
- Improved communication with automatic reminders
- Scalability for future growth
- A single, consistent source of financials and other records
For example, report generation is a task that can be highly automated through an ERP. Since all the numbers are available in one central database, new reports on company finances or sales performance can be created with a click of a button. The data can be presented in traditional report formats or more visual formats, like graphs or charts, to be as clear as possible.
Another way to improve efficiency with an ERP is through instant access to real-time data. Modern ERP systems can leverage new technologies such as AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) to intelligently suggest actions and streamline operations across the organization.
2 Enhanced Collaboration and Innovation
Another key benefit of ERP systems is the ability to enhance organizational collaboration. ERP systems help organizations by:
- Consolidating data from all departments into a single source
- Making it simpler to share accurate and up-to-date information with everyone in the company
- Improving coordination and communication between departments
Suppliers, for instance, can use ERP to monitor inventory levels and plan ahead, optimizing supply chain operations. In addition, departments can enjoy enhanced collaboration with fewer errors in data and communication, ensuring a seamless flow of information and a more agile business.
With improved sharing capabilities, ERP systems enable better collaboration between locations and remote teams. Cloud-based deployments allow for mobile access anywhere, further streamlining communication.
3 Better Decision-Making
ERP software is crucial in facilitating better decision-making within a business. These systems provide real-time data, analytics, and reporting tools, enabling managers and executives to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
A single unified reporting system within an ERP suite offers the advantage of:
- Producing precise, current data without the need for IT specialist involvement
- Accessing accurate and up-to-date data so businesses can enhance overall performance and competitiveness
- Increasing data security assists with regulatory compliance and may decrease auditing costs.
And new technologies, like AI, machine learning, and IoT, are being added to ERP systems to further improve predictive analytics. Real-time data analysis offers businesses enhanced decision support.
4 Scalability and Flexibility
As businesses grow and evolve, their needs change and their systems must adapt accordingly. ERP systems offer scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to easily adjust and expand in line with changing needs and requirements.
The modular nature of ERP systems enables companies to select and incorporate only the most suitable components and exclude what is not necessary, making it easy to add new features to an ERP platform.
5 Mitigate Risk
An ERP system helps businesses reduce operational inefficiencies, improve collaboration across departments, and enhance overall productivity by centralizing all critical information in one place. However, an ERP system also plays a vital role in mitigating business risks beyond these operational benefits. This is accomplished by:
- Having accurate information available
- Safeguarding financial management
- Improving data security
ERP systems are also backed by increased data security. With an unfortunate rise in cybersecurity threats over the years, ensuring your business follows data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA is critical. Both on-premise and cloud-based ERP deployments keep data contained and connected to reduce risk and meet compliance.
6 Lower Operating Costs
The final key benefit of all ERP systems is the ability to lower operating costs. Reducing manual tasks, increasing real-time visibility, and promoting higher efficiency all leads to a better bottom line. And since an ERP is a collection of different applications, it reduces the need for multiple software subscriptions or implementations.
The total cost of ownership of an ERP depends on several factors. The first to consider is the scope of the software, or what functionality is required. The more modules there are, the higher the costs will be. Another factor is the total number of concurrent users. Not everyone needs access, so limiting licenses can save money.
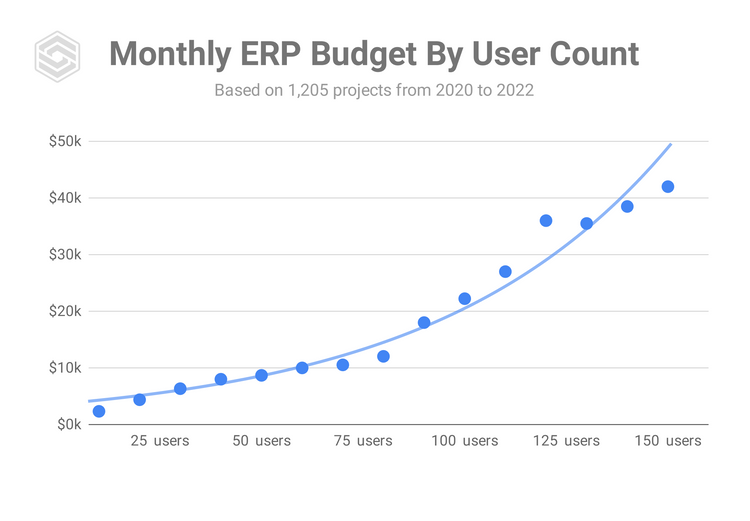
Implementing an ERP system may seem costly at first, but the long-term savings are undeniable.
7 Maximize Profits
An ERP system can increase company profits from 6-11%. With the correct use of ERP finance modules, businesses can significantly reduce transactional expenses and unveil concealed costs. Moreover, by implementing an ERP, staff can redirect their focus from mundane tasks to activities that directly boost revenue. Some tools that can be used to maximize profits include:
- Budgeting and planning
- Accurate financial reporting
- Optimized cash flow management
- Demand and sales forecasting
- Effective production planning
- Inventory optimization and efficient procurement
These tools and modules work together to ensure businesses operate efficiently, helping them stay below budget. Accurate sales forecasts also help companies make better-informed decisions, allowing adjustments to inventory levels and future purchases to avoid costly overstock.
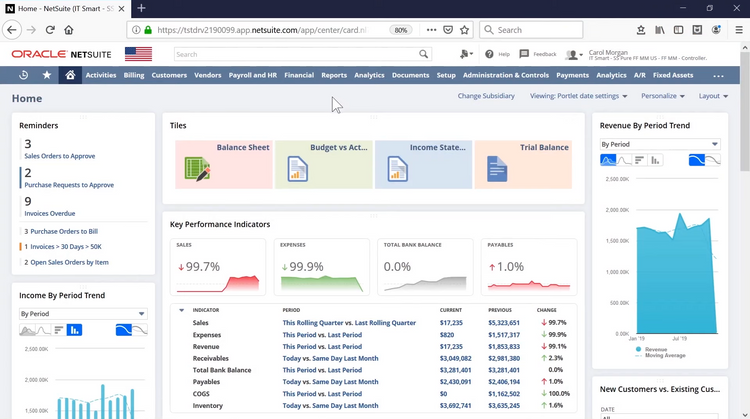
Who is an ERP Good for?
ERP systems empower businesses to stay agile and competitive in today’s fast-paced market by optimizing processes and providing a single source of truth for all business data. This can provide benefits to employees in several departments as well as customers:
For the Accounting Department
- The CFO: A report writer with data visualization tools to share financials with investors.
- The Controller: A cash management application to plan liquidity and optimize interest-earning positions.
- The Billing Clerk: Automatic overdue invoice reminders based on configurable business logic.
- The Budgeting Analyst: Integration of budgeting and accounting to allow for up-to-date variance reporting.
For the Sales Department
- The Sales Ace: Mobile apps that provide the ability to check stock levels before promising items to customers.
- The Sales Manager: Forecasting tools that use past data to create more accurate predictions about future sales.
- Sales Support: Document conversion capabilities that easily turn quotes into orders and orders into invoices.
For the Supply Chain Team
- The Buyer: Vendor comparison analytics to gauge factors like average lead time when selecting suppliers.
- The Shipping Tech: Integration of order software with major shipping providers for better tracking and cost management.
- The Purchasing Manager: Granular approvals control to ensure requisitions receive the right oversight.
- The Inventory Clerk: Cycle count features to check stock counts more efficiently with statistical sampling.
- The Warehouse Supervisor: RFID functionality to track the precise location of every inventory item in the warehouse.
For the Production Team
- The Quality Director: Statistical process controls to track improvements on minimizing defect rates.
- The Plant Manager: Machine scheduling management tools to minimize downtime and reduce cycle times.
- The Engineer: A bill of materials to communicate materials and assembly instructions to the production floor.
- The Equipment Manager: Computerized maintenance management software to track which machines are due for repair.
- The Machine Operator: Integrate change order management to make sure that work orders and production instructions are always up-to-date.
What are the Benefits of ERP for Customers?
ERP systems can improve customer service. To start, streamlining workflows leads to overall better products and services for customers. And CRM modules lead to better communication by automatically sending emails to customers after they’ve placed an order. Businesses can also use ERP to personalize services through increased transparency in past customer interactions.
Cloud vs. On-Premise ERP
When choosing an ERP system, one of the most important choices is deciding between cloud vs. on-premise. In short, the main difference is that cloud systems are hosted on a third-party data center, while on-premise systems are locally installed on company servers. Because of several advantages, most modern ERP systems are cloud-based.
Cloud Advantages
Businesses looking to avoid high upfront costs, slow deployment, and complex management may want to invest in a cloud ERP. The primary benefits include:
- Lower initial investments due to monthly subscription pricing
- Streamlined deployment and implementation
- Data is available anywhere with an internet connection
- Adaptable solutions reduce IT resource requirements
- Scalable for growing businesses and supports remote work
Future ERP Benefits
The 7 primary benefits of ERP are just the start of what this type of software has to offer modern businesses. New technology advances in AI and machine learning are automating even more routine tasks to cut down on manual labor. Evolving algorithms mean more refined predictive analytics to enhance decision-making at the highest level.
Another trend to watch in ERP will be the increased incorporation of features to help organizations track and report on their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives, aligning with the growing focus on sustainability. Combined with cloud deployment, which offers scalability, cost savings, and easier accessibility, more businesses are using ERP to adapt to future work conditions today.
