Top Examples of ERP Systems in 2024
A few examples of the most well-known ERP software include SAP, Oracle NetSuite, Epicor, Acumatica, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software creates a system of business applications designed to streamline and automate your organization’s back office functions, including accounting, forecasting, customer relationship management (CRM), and human resource (HR) operations. Some ERP software offers different functionality based on industry standards or company size.
Top ERP Examples
- SAP Business One - Example of small business ERP
- Oracle Netsuite - Example of cloud ERP
- Acumatica - Example of industry-focused ERP
- Epicor Kinetic - Example of manufacturing ERP
- Dynamics 365 - Example of ERP for Microsoft Office users
- Odoo - Example of open-source ERP
- SYSPRO Example of distribution ERP
ERP System Examples
Here are examples of ERP systems that can help you automate your company processes.
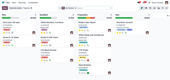
1 SAP Business One
SAP Business One, available on-premise and via the cloud, covers the core functionality a small to mid-size business expects from an ERP: modules for accounting, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), and reporting.
Particularly popular among manufacturers due to its Material Requirement Planning (MRP) features, SAP Business One’s core functionality serves a wide range of industries. The software is customizable to create a more personalized end-user experience.
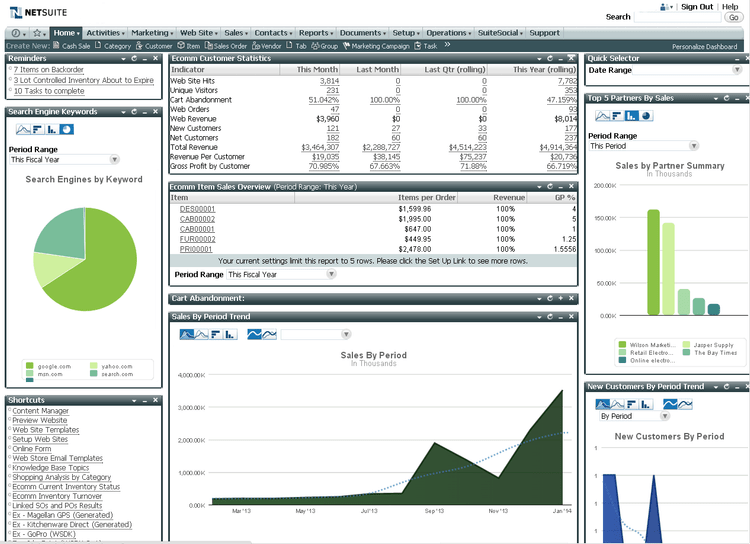
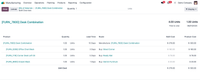
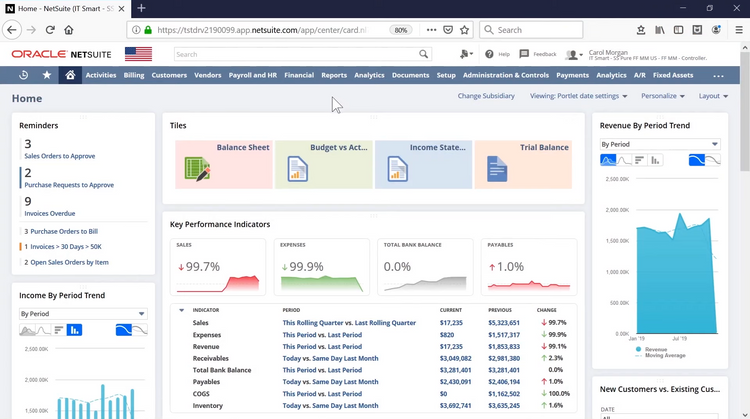
2 Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite is often described as the most deployed ERP in the world. The main modules support finance, sales, HR, and other business operations, including real-time data visibility for more informed decision-making.
While popular with small and mid-market businesses, NetSuite’s modules with supply chain and warehouse management functionality also make it popular among enterprise-level organizations.
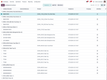
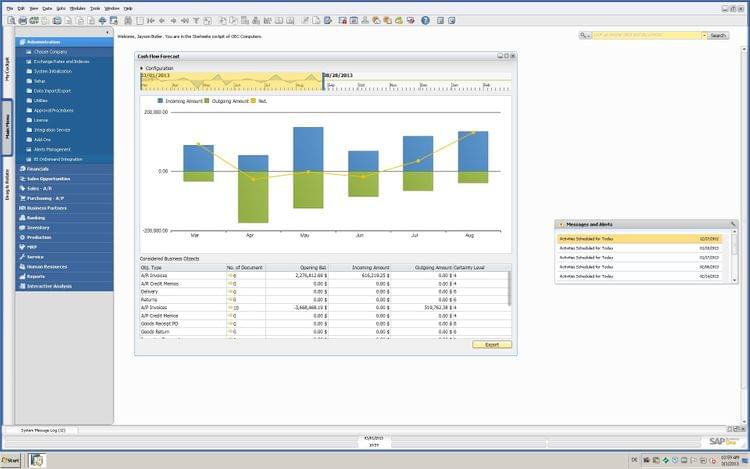
3 Acumatica
Acumatica Cloud ERP, as the name suggests, is a primarily cloud-based ERP platform made for the SMB market. Like other ERP solutions, Acumatica offers business management applications for financial, accounting, inventory management, and more.
There are industry-specific versions of Acumatica, including:
- Construction Edition
- Manufacturing Edition
- Retail-Commerce Edition
- Distribution Edition
Each edition has slightly different functionality to best suit each area, such as the Construction Edition, which includes accounting modules for general contractors, home builders, and land developers. Flexible configuration options make even the base version of this software suitable for use by different industries.
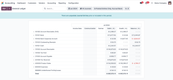
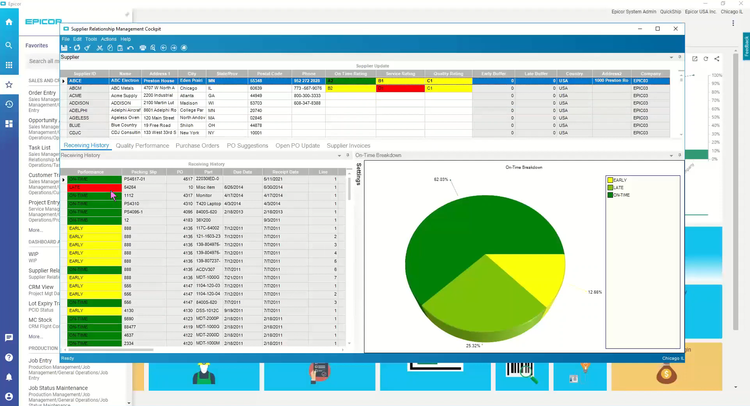
4 Epicor Kinetic
Epicor Kinetic’s integrated ERP has solutions for CRM, manufacturing, supply chain management (SCM), human capital management (HCM), and more. This platform offers scalability for long-term business growth. Epicor notably includes Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) features for keeping organizations compliant with everything from international accounting standards (IAS) to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
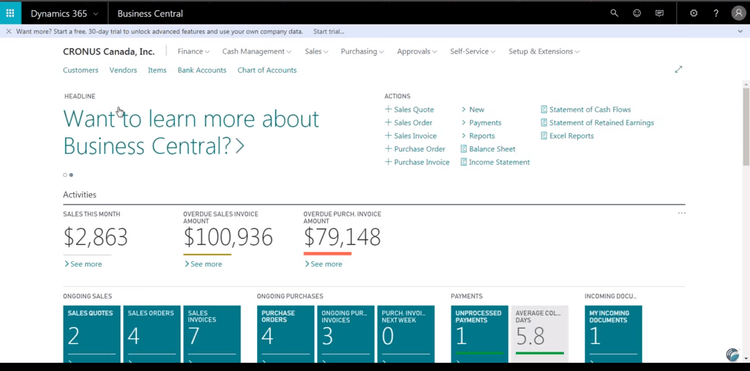
5 Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central
It’s worth noting that while Microsoft Excel is a valuable business tool, it is not an ERP. Instead, Microsoft has Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central. Like other ERPs, it has financial management, reporting features, and project management. Most notable is how Dynamics 365 can operate with other Microsoft software products.
6 Odoo
Odoo is known for its open-source roots and modularity, popular among small to mid-sized companies with high customization needs. Open source ERP describes software with a publicly-available source code. Odoo has an active user base and community-driven development, so it’s always improving and evolving. Additionally, businesses can add modules like point-of-sale, accounting, manufacturing, inventory, and CRM piecemeal to assemble a unique system.
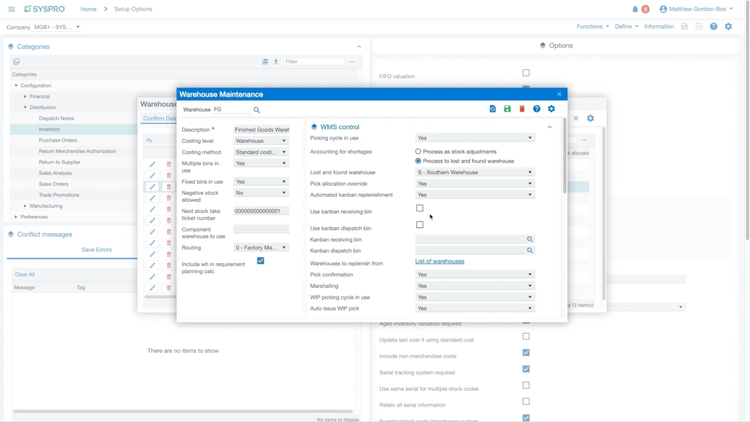
7 SYSPRO
SYSPRO launched in 1978 with a specific focus on the distribution and manufacturing industries. Distributors rely on the program for features like barcode scanning and serial number tracking, making inventory control and warehouse management more efficient. Additionally, SYSPRO integrates with major shipping carriers and supports logistics, including route optimization and freight management. It’s also a good option for manufacturers, especially mixed-mode operations.
What is ERP Software?
ERP stands for “Enterprise Resource Planning,” the consolidated process of gathering and organizing business data through an integrated software suite. ERP software contains a suite of applications that automate business functions like production, sales quoting, accounting, and more.
An ERP creates a single source of information for all different aspects of your business, allowing you to focus on your specific needs from a single system. ERP implementation is designed to serve as many company departments as possible to facilitate better business processes.
Read More: What is ERP and How Do ERP Systems Work?
Who Benefits From Using ERP?
ERP software is not limited to large corporations, as businesses of all sizes can benefit from its expansive functionalities. Startups, often operating from home offices and using basic tools like Excel, can employ ERP as they grow.
- Small businesses, like corner stores, have specific needs met by certain accounting systems.
- Mid-sized companies with 50 to 100 employees can use ERPs to centralize their operations, while small and medium enterprises (SMEs) rely on tailored solutions based on their unique classifications within the economy.
- At the top tier, enterprises with thousands of employees, such as Amazon or Apple, leverage ERP to manage their widespread operations.
This overview sets the stage for a deeper dive into industry-specific ERP software solutions.
Supply Chain Management
An ERP software can help a business integrate its supply chain processes, from procurement to delivery. As a result, the company can reduce inventory levels, decrease order-to-delivery time, and improve customer satisfaction.
Online Retail
Businesses that sell products and services online can use an ERP system to improve their order-to-cash cycle. The ERP software will help automate its order processing, inventory management, and financial reporting. As a result, the company can improve order accuracy, reduce delivery times, and increase customer satisfaction.
Retail
Brick-and-mortar retail stores can implement an ERP system to improve their inventory management and supply chain operations. The ERP software will optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and improve product availability. As a result, the company can improve its supply chain efficiency and reduce costs.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers can implement an ERP system to streamline their manufacturing processes. The ERP software will optimize its production planning, scheduling, and inventory management. As a result, companies can reduce manufacturing lead times, improve product quality, and reduce costs.
Benefits of ERP Software
ERP software offers numerous benefits for businesses. It can significantly reduce costs by centralizing data entry, promoting better planning through real-time insights, streamlining various administrative tasks to enhance productivity, and fostering inter-departmental collaboration by unifying platforms. Moreover, it provides tools to monitor and improve customer satisfaction metrics, ensuring a holistic approach to business improvement.
Better Financial Planning
ERP solutions have modules for forecasting and reporting a wide variety of data. Analytical tools use historical and real-time data to provide the best information for informed decision-making.
Reporting is one of the key features of ERP solutions. The applications can sort data by region, location, profit center, employee, and other customizable ways based on your business’s needs.
Improved Data Security and Accessibility
A common control system allows organizations to ensure key company data can be shared without being compromised. With all departments using the same Cloud-based ERP system, everything can be stored in one shared database that can be accessed anywhere.
Improved Communication
An ERP helps manage different forms of communication so employees can stay in touch with their departments, vendors, or customers.
Electronic data interchange (EDI) compatibility allows the exchange of digitized business documents in a standardized electronic format from one computer to another. This can be used for interdepartmental exchanges, or working with third-party contractors with their own formatting.
Read More: ERP Benefits: Advantages and Disadvantages
Modules of ERP Systems
Diving into the intricacies of ERP systems, one finds a series of specialized modules designed to address businesses’ distinct operational needs. These modules range from Financial Management, which ensures monetary oversight, to Human Resources, which streamlines personnel management. Each module is a pillar, supporting and streamlining its designated business operations.
Financial Management and Accounting
A financial management module is primarily made up of accounting modules that track your business’s overall profit and loss and cash flow. These financial transactions are tracked via a general ledger that shows transactional records and the account structure used to organize these entries.
Procurement
The procurement module, or purchasing module, helps your business source items needed for its operations. A procurement module issues orders for services and products by tracking all key order information in real time, including the vendor, purchase quantities, item or service purchased, delivery timeframes, payment terms, and costs.
Inventory Management
An inventory management module controls inventory by tracking stock levels and prices of all products your company builds, buys, stores, and sells. The solution allows you to view what raw materials you have on hand and where to find them, as well as provide recommendations on when to reorder items.
Supply Chain Management
The supply chain management modules manage the flow of goods and services between locations as efficiently and cost-effectively as possible. This means they provide assistance from the initial acquisition of raw materials to the finished product being delivered to a customer.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The customer relationship management module stores information on all customers and prospects your organization is pursuing. It tracks the relationships and interactions primarily between your sales staff and customers. CRM data is intended to improve business relationships and grow your business, ultimately improving profitability.
Human Resources
A human resource management module manages employee information while automating tasks involving the people in your organization, such as employee scheduling, recruitment, and boosting employee productivity. This detailed module keeps records on all employees and stores documents on them, such as performance reviews, job descriptions, salary information, hours worked, and paid time off.
Read More: ERP Modules: Types, Benefits, and Functions
Industry-Specific ERP Systems
While many of the above ERP examples are made for any type of business, there are many industry-specific options as well. Unlike the more general programs, specialized ERP software provides capabilities tailored to certain business processes. Further, the vendors can better understand support issues or requests for improvement.
One example of industry-specific ERP is within the world of manufacturing. A manufacturing ERP (MRP) software plans production on the shop floor by determining the need for materials and capacity to complete a manufacturing production order. Generic ERP software would likely require integration with third-party software or expensive customization built by the software provider that could require extensive design and test time.
By following an industry’s best practices, these solutions can reduce costs, speed up implementation, and better serve customer requirements to serve the industry’s best practices.
Deployment Methods
From traditional On-Premise ERP systems housed in physical offices to more modern Hosted Cloud ERP solutions accessible via browsers and the adaptable Hybrid ERP that combines the strengths of both, each deployment method offers its own set of advantages and billing structures. As you delve deeper, you’ll discover the nuances of each method, helping you make an informed choice for your organization.
On-Premise ERP
ERP software is in-house software installed in a physical office on local hardware systems. It can also be managed from a dedicated data center. These systems can only be accessed on-site or in-office (literally on the premises).
Software licensing is typically billed upfront in addition to implementation and training costs. The first year of support is usually included, though there may be ongoing costs for annual support and updates. This payment method is more frontloaded, with lower ongoing costs.
Hosted Cloud ERP
Cloud software, or software as a service (SaaS), means a software vendor manages any associated servers, maintenance, and running costs at their own data center. Businesses can access their data and ERP functionality via remote capabilities and/or a web browser.
Usually billed as a subscription-based pricing model. Software costs are often paid monthly or yearly. There are upfront fees for setup and training. This payment method is spread out, with costs evenly distributed throughout ownership.
Read More: On-Premise ERP Software vs. Cloud ERP Software
Hybrid ERP
A combination of on-premises capabilities and cloud-based capabilities that work in unison. Commonly a multi-sourced modular application environment that provides the best of both through a two-tier architecture, meaning all core capabilities (such as manufacturing and financials) are maintained on-premises and other applications (such as CRM and sales) are maintained via the cloud. This combination will also provide a combination of both pricing models–allowing you to pay upfront for on-premise functionality and continue to pay on a subscription basis for cloud functionality.