ERP Modules Explained
The most popular ERP modules include financial management, procurement, inventory management, supply chain management, CRM, and human resources.
The best ERP systems will include various modules chosen to meet your business’s specific needs. These applications connect all areas of your business processes in real time by enabling collaboration and eliminating the need to re-enter data into other disparate systems.

What are the Basic Modules of an ERP System?
An ERP module is a software component that meets a particular need of an operation or department within an organization. The specific business function that ERP modules provide is based on data collected by or inputted into the system. All ERP software, such as SAP and Oracle, is made up of ERP system modules that meet the needs of financials, warehousing, supply chain, and more.
One major benefit of ERP is the ability to pick and choose the ERP modules desired for your business. Some ERP systems may offer a more rigid set of required modules or included as part of a specific package. Other software solutions may allow you to craft your own. Similar to choosing the interior features of a new car, the body of the car can be thought of as the core ERP software, while the seat fabric, electronics, tires, and legroom can be thought of as the modules.
Why are ERP Modules Important?
An enterprise resource planning system is the heart of any organization. This is because ERP software allows a business to add functionality while keeping the same foundation in place. Smaller businesses may outgrow their existing business software—meaning they have to go through a lengthy ERP implementation. However, existing ERP users can upgrade or downgrade their system as their requirements change over time.
Because the ERP market constantly changes and adds new programs and features, having a scalable and flexible system will have an incredibly positive impact on your business.
Types of ERP Modules
Because ERP is widespread in all types of businesses and because of its modular nature, no two ERP systems are alike. Every module can be integrated into a system to work in tandem with another module—likely filling a specific role or business need that your business has.
No single ERP module is more important than another, but a handful tends to be more commonly implemented when a business is adding ERP software to its operations. A qualified ERP vendor will be able to determine which modules will work best for your management system.
Here are these popular ERP modules explained:
Financial Management and Accounting
A financial management module is primarily made up of accounting modules that track the overall profit and loss of your business as well as the overall cash flow. These financial transactions are tracked via a general ledger that shows transactional records and the account structure used to organize these entries.
Entries from other accounting modules will flow into the general ledger and include both an accounts payable module and accounts receivable module. Accounts payable functionality will include tasks such as invoice processing, payables approvals, and executing payments. Accounts receivable will automate the cash flow and funds owed to your business for goods or services provided.
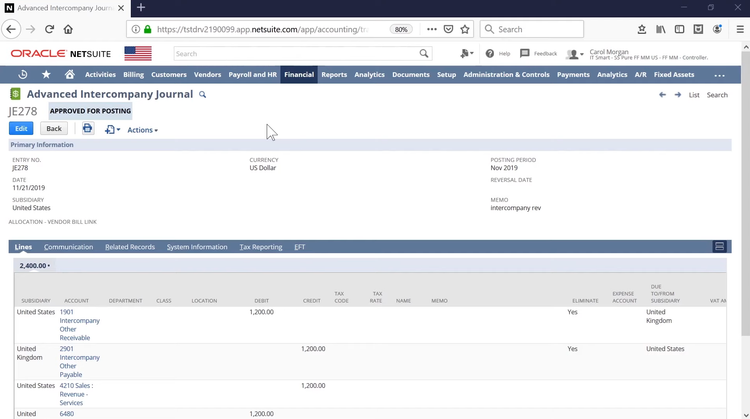
Procurement
The procurement module, or purchasing module, helps your business source items needed for its operations. A procurement module issues orders for services and products by tracking all key order information in real time, including the vendor, purchase quantities, item or service purchased, delivery timeframes, payment terms, and costs. The procurement modules in an ERP serve to maintain efficient operations by ensuring necessary materials are available at the desired quality, quantity, timing, and cost.
Procurement software creates what is known as a purchase order, a financial document issued to vendors when buying suppliers or services. A purchase order can usually be created automatically when stock levels are running low and go hand in hand with an inventory management module. These documents enable procurement teams to place orders, specify requirements, and designate delivery dates, streamlining the procurement process. Automation of purchase requisitions and orders allows for significant time and cost savings, enabling personnel to dedicate their efforts to more strategic initiatives.
The procurement process also helps manage quotes and is part of a more complex supplier relationship management process. This process ultimately tracks approved vendors and ties those suppliers to particular items. Other benefits include centralizing communication, monitoring supplier performance, facilitating vendor audits, integrating with accounts payable and receivable, and ensuring compliance while reducing risks.
Inventory Management
An inventory management module provides inventory control by tracking stock levels and prices of all products your company builds, buys, stores, and sells. The solution allows you to view what raw materials you have on hand and where to find them and provide recommendations on when to reorder items.
Items in an inventory management software module are tracked via unique serial numbers (SKUs) or barcodes. These identifiers allow personnel to trace their current location anywhere in the store or warehouse for efficient receiving and picking. The module can also sync with eCommerce and POS systems for multi-channel inventory management.
Inventory control modules also monitor inventory costs and integrate with the procurement module for purchase order management. Part of inventory tracking is the financials that go with it, as you want to keep sufficient inventory stock without tying up too much cash into inventory. By forecasting supply and demand and setting stock minimums and maximums, you can weigh trends with your products to increase inventory turnover and prevent stockouts and delays.
Supply Chain Management
The supply chain management modules manage the flow of goods and services between locations as efficiently and cost-effectively as possible. This means they provide assistance from the initial acquisition of raw materials to the finished product being delivered to a customer.
Primarily used by manufacturers, logistics providers, distributors, suppliers, and retailers, supply chain management software modules help plan, control, and execute the required manufacturing and/or distribution of finished goods. This helps maximize cost reduction opportunities in getting products from the vendor to the customer.
Supply chain management can include various modules such as procurement, inventory control, manufacturing, order management, and warehouse management. These tools can help automate requisitions, service/product orders, vendor data, contract management, sales forecasting, demand planning, and managing yards, dock, and labor.
One major trend in ERP is the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to provide advanced quality control in supply chain operations. First, IoT sensors can monitor the quality and condition of goods throughout the supply chain, ensuring that products meet predetermined quality standards. Then, AI algorithms can analyze data to identify patterns in potential quality issues, enabling proactive measures and a more efficient supply chain.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The customer relationship management module stores information on all customers and prospects your organization is pursuing in one central repository. It tracks the relationships and interactions primarily between your sales staff and customers. CRM data is intended to improve business relationships and grow your business, ultimately improving profitability.
Examples of tools provided via CRM software modules include contact management, communication tracking, opportunity/lead tracking, order history, issue ticketing, quote creation, and sales agent productivity. All customers can be monitored from the initial marketing stage through a quote/sales process and ultimately through customer service. This advanced tracking can lead to improved resolution time for customer support, better forecasting through purchase pattern monitoring, and higher client retention.
Human Resources
A human resource management module logs employee information while automating tasks involving the people in your organization, such as employee scheduling, recruitment, and boosting employee productivity. This detailed module keeps records of all employees and stores documents such as performance reviews, job descriptions, salary information, hours worked, and paid time off.
Because HR software provides better employee record-keeping for the sake of increasing employee performance, it helps your organization achieve its goals by allowing managers to better allocate employee time and resources to become a more productive and profitable business.
Human resource capabilities share many similarities with CRM and can be thought of as a CRM for employee data. Given the large amount of information stored on every employee across the organization, there is a lot of room for error regarding duplicate or inaccurate data that organizations may input, making HR modules essential.
Other ERP Modules
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Streamline the manufacturing process through production planning, scheduling, and inventory control. Calculate material requirements, coordinate personnel and machine workloads, and optimally plan purchasing to meet customer demand.
- Order Management: Streamlines order entry and order processing by helping merchants capture, track, and fulfill orders across multiple sales channels. Connects inventory and sales orders, creates shipping schedules, tracks fulfillment, and creates reports.
- Warehouse Management: Coordinates inventory and actions throughout a warehouse or distribution center to optimize inventory picking and shipping. This allows distributors to control workflow, stock, labor, and bills and coordinate with shipping yards and docks.
- eCommerce: Provides the capability to create a web store with a shopping cart, shipping options, and payment processing. Can directly update inventory and calculate sales tax required to fulfill orders.
- Professional Services Automation (PSA): Assists with project and resource management for service-based companies by collecting and applying time and expense data to customer billing. Can also store contract data, coordinate communication between team members and clients, and estimate project expenses and revenue.
- Marketing Automation: Manages marketing processes and multifunctional campaigns across multiple channels. Target customers with automated messages across email, web ads, social media, and text campaigns. Measure tasks and workflows to increase operational efficiency and grow revenue faster.
- ERP Analytics: Analyzes data generated by the ERP system to extract valuable insights and drive strategic decision-making. It involves collecting, organizing, and interpreting data from different modules within the ERP system to identify patterns, trends, and correlations.
FAQs
There are some commonly asked questions when it comes to ERP modules:
What is ERP, and How Do ERP Systems Work?
ERP is an acronym that stands for “Enterprise Resource Management”, the consolidated process of gathering and organizing business data through an integrated software suite. ERP software contains applications that automate business functions like production, sales quoting, accounting, and more.
In layman’s terms, ERP facilitates your company’s operations across every department. ERP solutions improve how you handle business resources, whether it’s raw materials for manufacturing or staffing hours for human resources.
Learn more: What is ERP and How Do ERP Systems Work?
What ERP Modules Are Required?
Business requirements will determine which ERP modules a company requires. An ERP system would require at least two modules. Otherwise, it would be a single-application product. Most businesses will start with a financial module to run their accounting and pair that with an operational module such as inventory management, order management, or something else related to the supply chain.
What is the Cost of an ERP Module?
The cost of each ERP module highly depends on which vendor you purchase through, your business’s needs and size, and your desired deployment method. Core ERP packages usually include financials and inventory modules, while others may add extra costs. The cost of monthly ERP subscriptions ranges from $1,700 to $10,000. In many cases, ERPs are bundled by industry, such as Manufacturing ERPs, and include several modules, including MRP and order management.
Learn more: How Much Does ERP Cost?
What ERP Modules Exist Outside of Functional Modules?
When the phrasing “ERP modules” is used, most are referring to ERP functional modules. This refers to any module that provides a function for your business, including financials, human resources, engineering/production, sales, purchasing, and more.
There are other types of ERP modules that are non-functional, such as:
- Technical modules
- Application suites
Technical modules work as an operating system for your functional modules. This includes application programming interfaces (APIs), security safeguards, networking and interfaces, and management information systems.
Application suites are the overall connection and relationship your ERP software holds with other information systems within your organization. This ERP framework provides the interactions required for your ERP to speak with other systems, including:
- Supply chain management (SCM) software
- Customer relationship management (CRM) software
- Product lifecycle management (PLM) software
- Supplier relationship management (SRM) software
