What Is Inventory Shrinkage? Formula, Examples, & Prevention
Inventory shrinkage occurs when actual inventory levels are lower than your accounting records. A loss of inventory ultimately translates to a loss in profit, diminishing your bottom line. By calculating your shrinkage percentage rate, you can pinpoint the reasons behind your inventory loss and take steps to address the root causes.
Top Five Causes
Shrinkage includes both internal and external sources, including accounting errors, theft, or product damage:
-
Administrative errors
Many businesses incur inventory discrepancies through human error. This occurs when employees incorrectly total the amount of inventory in their warehouse or on the retail floor. -
Damaged or lost items
Faulty packaging, water damage, and expired goods present another form of retail shrinkage. This category renders products unsellable and creates a disconnect between your recorded and physical inventory levels. -
Wholesaler fraud
This occurs when vendors invoice your retail business for a certain amount of items but do not ship the entire quantity. You can reduce this shrinkage risk by counting orders as soon as they arrive at the loading dock. -
Shoplifting
Concealing and leaving with store items isn’t the only form of shoplifting — price tag swapping, or tampering with item labels or SKU numbers to pay a lower upfront cost, is also a pivotal contributor to inventory shrink. -
Employee theft
Although this includes straightforward merchandise theft, shrinkage can occur through cash drawer skimming, “sweethearting” (providing free or discounted items to family and friends), and fraudulent returns.
Shrinkage Sources by Industry
Shrinkage rates fluctuate widely from industry to industry. Stores in the consumer staple sector encounter a higher degree of wastage or spoilage, as perishable goods expire. Stores in the consumer discretionary sector experience increased instances of internal and external theft.
Fashion Industry Shrinkage - Consumer Discretionary Sector
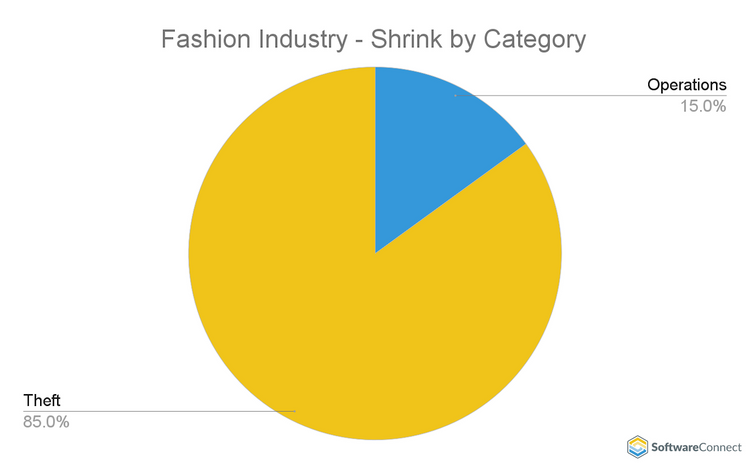
| CATEGORY | SHRINK SOURCE |
|---|---|
| Shoplifting | 32% |
| Employee Theft | 48% |
| Vendor Theft | 5% |
| THEFT | 85% |
| OPERATIONS | 15% |
Grocery Industry Shrinkage - Consumer Staple Sector
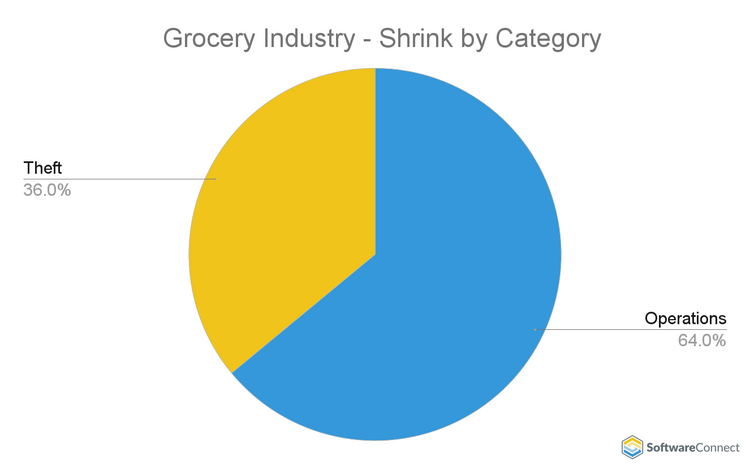
| CATEGORY | SHRINK SOURCE |
|---|---|
| Shoplifting | 13% |
| Employee Theft | 20% |
| Vendor Theft | 3% |
| THEFT | 36% |
| OPERATIONS | 64% |
Types of Inventory Shrinkage
Restaurants and Hospitality
- Over-portioning: Staff may use more ingredients than needed, with leads to higher food costs.
- Spoilage: Perishable goods like food and beverages may expire due to improper storage or inventory mismanagement.
- Comped Meals: This includes meals provided for free or at a discount to employees or for customer satisfaction. This can reduce inventory without corresponding revenue.
- Theft: Employees or customers may steal food, beverages, or supplies.
- Broken or Damaged Items: Kitchen equipment, plates, and glasses may break.
Manufacturer
- Production Errors: Miscalculations or errors during production can result in defective goods that can’t be sold.
- Waste: Some materials must be scrapped during production, which can lead to shrinkage.
- Obsolescence: Products become dead inventory if they’re obsolete before they’re used or sold.
- Administrative Errors: Misplacing inventory during storage or shipping, miscounting, and inaccurate data entry can also lead to shrinkage.
Vendor
- Product Mislabeling: Vendors may incorrectly label products, creating a disconnect between what you ordered and what you received.
- Short Deliveries: Vendors may ship fewer items than ordered, either by mistake or due to fraud.
- Overcharges or Fraudulent Claims: Shrinkage can occur if vendors inflate costs or bills for products never delivered.
- Damaged Items in Transit: Goods may be damaged during transport from vendor to customer.
- Theft: Suppliers or delivery personnel may steal goods while handling shipments.
Retail
- Shoplifting: Customers steal merchandise from the retailer.
- Employee Theft: Employees steal items or mismanage inventory.
- Administrative Errors: These can occur due to incorrect pricing, mislabeling, and scanning errors at checkout.
- Return Fraud: Customers may return used or damaged goods for a refund, leading to a loss in inventory.
- Damaged Goods: Items on display or products being transported through the store could be damaged.
How to Calculate
The best way to calculate shrinkage rate value is to subtract the total value of your current inventory from the total value of inventory you’re supposed to have.
Recorded Inventory Value - Physical Inventory Value
= Inventory Shrinkage Value
To calculate the shrinkage rate percentage, divide your inventory shrinkage value by your recorded inventory value, then multiply by 100.
(Inventory Shrinkage Value / Recorded Inventory Value) x 100
= Inventory Shrinkage Rate Percentage
Examples
The total value of your recorded inventory stands at $200,000. But after conducting a physical count, you determine that the total value of your physical inventory is actually $190,000:
$200,000 (Recorded Inventory Value) -
$190,000 (Physical Inventory Value) =
$10,000 (Inventory Shrinkage Value)
Divide your inventory shrinkage value by the total value of your recorded inventory, then multiply by 100.
($10,000 / $200,000) x 100 = 5%
Your inventory shrinkage rate is 5%. According to the 2023 National Retail Security Survey, the average shrink rate for retailers across industries in 2022 was 1.6%. An acceptable rate lies between 1% and 2%, so you’ll want to take measures to reduce your shrinkage rate.
The good news is by monitoring this percentage over time, you can pinpoint the causes of inventory shrinkage. For example, if your shrink rate spikes sharply over a short period, you can likely attribute this to a clerical error. Conduct an inventory audit and amend your records accordingly.
On the other hand, a steady and elevated shrink rate could indicate internal or external theft. Therefore, it’s worth revisiting your stock check/receiving processes, employee screening procedures, and overall security measures.
Journal Entry
In accounting, you’ll want to record retail shrink in your inventory to reflect the fact that there was a loss in value. Conversely, debit your shrinkage expenses account to indicate the increase in expenditures for your business.
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage Expenses | $10,000 | |
| Inventory | $10,000 | |
| Total | $10,000 | $10,000 |
When deducting inventory shrinkage losses for tax purposes, your accounting department should reduce this amount by the total you received for your insurance claim reimbursement. Then, you can take one of two routes according to IRS guidelines:
- Deducting the loss separately using IRS Form 4684
- Deduct the loss from your cost of goods sold (COGS) account
Loss Prevention Methods
Your company can proactively reduce missing inventory by installing security cameras in critical areas to double checking during inventory counts.
Double-check systems
Improve your inventory accuracy by implementing daily or weekly stock checks and receiving counts. Ensure that your team alternates counting duties to deter mistakes or even dishonest employees from reporting false inventory records. Double-checking ensures that two workers conduct inventory counts simultaneously, then compare numbers to guarantee accurate results.
Cycle counting
Rather than shutting down your facility’s operations to do a massive inventory count, cycle counting allows you to tally a portion of your high-dollar items in a particular location and specific day. Cycle counting requires you to work in regular intervals, moving from one subset of products to another to keep accurate inventory records.
Employee screening and education
From the very beginning, close screening of potential candidates reduces potential inventory theft. Run credit, background, and criminal checks before hiring, and reach out to applicants’ references to identify any red flags.
Instruct employees on best practices to avoid spoilage, such as stocking new products behind those with upcoming expiration dates. Train your team on smart shelving practices and proper handling and storage to help curtail damaged goods.
Finally, pay employees fairly and strive for good morale in your retail environment to promote solidarity and trust between the company and your team. Give workers the tools they need to expedite the payment process and create line item records for every item sold through point of sale (POS) system software.
Vendor fraud prevention
Frequently audit your wholesalers by reviewing your master files and comparing your suppliers’ invoices against purchase orders and goods receipts. Assign multiple employees to vet vendor invoices to prevent a worker from duplicating invoices or soliciting payment from fake vendor accounts.
Unique identifiers for products Assign SKUs, QR codes, or barcodes to each of your items to promote accurate recording and tracking of your inventory. Some inventory management systems include barcode scanner apps, allowing warehouse workers to scan products using mobile devices. Monitor items as they move from receiving to sales and determine which items are routinely misplaced or stolen.
Enhanced security measures Some simple, inexpensive ways to deter theft include strategically displaying high-dollar items behind locked cases or in the back of your retail shop. Anti-theft sensors or ink security tags attached to products lower the chances of an opportunistic grab-and-dash.
Simple signage lets consumers know about CCTV cameras, and employees can frequently check in with customers to deter shoplifting even further. Installing security cameras in employee-only areas, such as stockrooms and break rooms, can also decrease internal theft.
Consider shopping around for commercial-grade security systems If you own a large retailer. Businesses experiencing a particularly high theft rate can also hire a team of security guards to patrol parking lots and entrances.
Automation
Inventory management software lowers the probability of incorrect data entry and other critical mistakes as products transfer from the stock room to the sales floor. Conduct inventory loss analysis at a forensic level with increased transparency in movement histories and stock counts. Plus, ensure you always have the right amount of stock without spoilage from over-ordering.
Further Reading
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good inventory shrinkage ratio?
Is inventory shrinkage a KPI?
Is inventory shrinkage considered an expense?
What facotrs promote shrinkage?
How do I calculate inventory shrinkage?
You can calculate shrinkage value and rate using the following formulas:
Inventory shrinkage value formula
Recorded Inventory Value - Actual Inventory Value = Inventory Shrinkage Value
Inventory shrinkage rate formula
(Inventory Shrinkage Value / Recorded Inventory Value) x 100
= Inventory Shrinkage Rate Percentage
