The Best Big Data Analytics Tools
Get the best software for your business. Compare product reviews, pricing below.
Big data is where the data volume, acquisition velocity, or data representation requires the use of significant scaling for efficient processing. Big data generally means you’re working with larger volumes, a higher velocity, and a great variety. Can you harness the data that is out there to deliver the value proposition for your business?
Find out if big data analytics tools are right for your operation:
What Are Big Data Analytics Tools?
Big data analytics tools let end-users analyze huge volumes of transactional data and other sources that may be left otherwise untapped by conventional business intelligence programs. This is accomplished through data processing, data modeling, data mining, online analytics processing, ultimately helping to create insights, visualizations, dashboards, and reports your business can act upon.
Big data itself is a concept that facilitates the handling of a large volume of data sets. These datasets will be used to serve the business they belong to by helping set goals for the operations. Whether in the cloud or on-premise, these analytics platforms provide the self-service tools you need to dig deeper into your organization.
Big data analytics tools are used by any organization that outgrows simple databases or other data handling architectures. A good example of a simple database is data that can be expressed or handled well in a traditional spreadsheet program such as Excel. Big data tools include non-relational databases (NoSQL), relational parallel processing databases, and big data frameworks/ecosystems.
Features of Big Data Analytics Tools
- Data processing: Collects and organizes raw data preparation for eventual use by reformating it into similar and usable data sources. Includes data modeling and data mining.
- Online analytics processing (OLAP): OLAP’s perform a multidimensional analysis of business data. They allow companies to conduct complex calculations, evaluate trends, and work with data modeling.
- Predictive analytics: Uses historical data sources to predict what will happen in the future. Examples in everyday business include identifying customers to upgrade/remove services and focusing marketing campaigns on the right targets
- Statistical analytics: Analyzes data that is made up of numbers for the purpose of analyzing risk or future decision-making
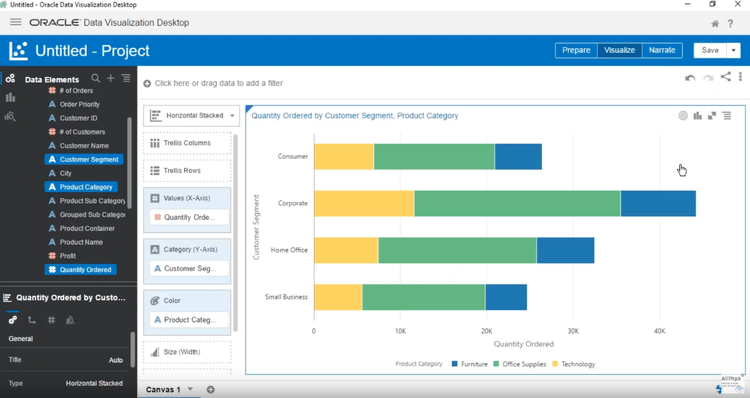
- Data Visualizations: Patterns, trends, and correlations that place data into a visual context to help people understand. Creates a visual means of enabling rapid consumption of key business data, primarily in the forms of charts, graphs, and plots.
- Dashboards: A visualization tool that displays the current status of metrics and KPIs for your business, based on your preferences (what numbers to show, what metrics to display, etc.)
- Reporting: Create reports that let you view trends pertaining to company financials, sales, marketing, human capital management, and more.
Benefits of Big Data Analytics Tools
Big data analytics tools can be of use to any business with a large volume of data that lacks the capability to sift through and understand what it means for their business. Some of the top benefits of big data tools include:
New Product Ideas
Knowing how your customer’s feel about your products and services, or how satisfied they may feel if you created a new product can help your company sustain customers while continuing to add more consistently. This process is called NPD, or new product development.
Some new product development steps include the process of idea generation, idea screening, and idea development/testing. From there, an organization must conduct market testing, work through implementation processes, and determine a price for the product.
Benefits of using big data in new product development include:
- Creating products that consumers can connect with or relate to
- Increase the value of the product
- Minimize risks in the development process
- Forecast the performance of the products
Identify More Efficient Ways of Doing Business
Storing a lot of data can be costly. Some big data storage and processing frameworks such as Hadoop can assist you in storing a great deal of data (more on that below). There is also predictive analytics which data scientists can use to predict the success of new products.
Predictive analytics can let users suggest that the business continues on the path their on or pivot to a more efficient method of doing things. These suggestions are usually based on historical sales, but can also be based on internal capacity, online conversion rates for related products, sales forecasts, and an analysis of other new product launches.
Make Faster and Better Decisions
An efficient big data analytics tool will provide you with the increased speed needed to analyze sources of data and ultimately make decisions based on what you’ve learned from this data.
For example, your business may want to gather metrics that will improve customer loyalty and satisfaction, with the end goal of keeping current customers active and not moving to another product/service. Big data analytics software can help you decide what sort of personalization experience to give your customers, such as recommended or personalized product and service suggestions based on their historical use, their previous purchases, the frequency they purchase these products/services, etc.
This is just one of the many examples of putting real-time data to work, which can help increase customer engagement. Customer service can be a very important deciding factor for many to choose to continue business with your company, and data analytics help improve your efficiency at providing this service.
Big Data Analytics and Machine Learning
Machine learning is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models with computer systems to perform tasks without using instructions, but instead relying on patterns and inference. @:Daniel Faggella, CEO at Emerj
Machine learning is a form of AI that lets a system learn from data. One famous example is IBM Watson, which is a computer system capable of answering questions posed in natural language.
In big data analytics, machine learning is the processor while big data is the data that’s being fed into the processor or analytical system. Machine learning will then help learn or improve upon its predictions using the data fed into it. In short, machine learning provides extensive calculations done over datasets which creates a learning model. As data file sizes continue to grow, there is larger importance on implementing a distributed computing method with big data analytics solutions.
A great example of the use of big data with machine learning is when it comes to preventative maintenance in a manufacturing plant. Big data can be gathered from the machinery sensors that can help the machine test specific models. If the temperature of a machine seems off, perhaps a replacement part is needed. A maintenance team can also be alerted to address the situation at the earliest available moment.
Business Intelligence Software vs Big Data Analytics Tools
Some may consider business intelligence systems and big data analytics tools to be relatively the same thing. They may argue that BI tools and big data analytics software are merely synonyms of one another. While they do provide very similar types of functionalities, the systems can provide a different set of results.
Business Intelligence Software
Business intelligence (BI) is more of an umbrella term that includes big data, data analytics, reporting tools, data visualization, and other tools and systems that make use of historical data. BI tools vendors are always looking for ways to improve their solutions to give the end-user all that they need to learn about their data and make better decisions.
Big Data Analytics Tools
Big data analytics tools can mean different things to different people. To some, it’s a business intelligence software that deals with a larger volume of data. To others, it is a specific type of approach to analytics or focuses on a specific area such as marketing or customer insights. What most can agree on is that big data is found within the overall practice of business intelligence.
What’s The Difference?
Business intelligence software encompasses all types of data analytics and reporting tools that help a business make better decisions. Big data analytics tools help determine the relationship between different sets of data and ultimately create insights. Big data analytics tools will typically be used to process larger volumes of or more complex sets of data. Most BI tools will be sold in various tiers that allow for add-os for “big data capabilities”.
Data Storage and Processing Frameworks
As Big Data defines a data set that is large and complex, businesses will equally need a large and complex framework they can rely on to store their data (data warehouse) and handle batch processing (data management).
One example of a framework is Apache Hadoop, an open-source software project that enables the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of servers. These data sets include information from corporate systems (ERP and CRM software), external data, social media data, and more. It’s designed to scale up from a single server to thousands of machines, with a very high degree of fault tolerance.
Hadoop is both a framework and an ecosystem application rather than a database, which lets you store and process a large volume of data. It can also handle the complexity of handling volume, velocity, and a variety of data.
Integrating Hadoop into your BI architecture has the following benefits:
- Low-cost data storage
- Highly scalable
- Structured, semi-structured and unstructured data
- Batch oriented query processing

