The Best Financial Services Software
Financial services software helps retail banks, credit unions, and private equity firms improve customer service, automate accounting, and drive growth. We reviewed the top options for functionalities like multi-site support and financial planning.

- Hundreds of third-party add-ons available
- Feature sets for multiple industries
- Highly customizable
- Combined ERP and CRM
- Similar interface to MS Word and Outlook
- Integrations with Microsoft applications
- Multidimensional reporting capabilities
- Scalability for multi-entity support and user growth
- Simple and responsive user interface
In this guide, we’ve reviewed top platforms for different functionalities, like financial planning and regulatory compliance.
- NetSuite: Best for Financial Planning
- Dynamics 365 Business Central: Best CRM
- Sage Intacct: Best for Compliance and Security
- FlexiFinancials: Best for Bank Accounting
- XLedger: Best for Private Equity Firms
- Multiview: Another Good Option
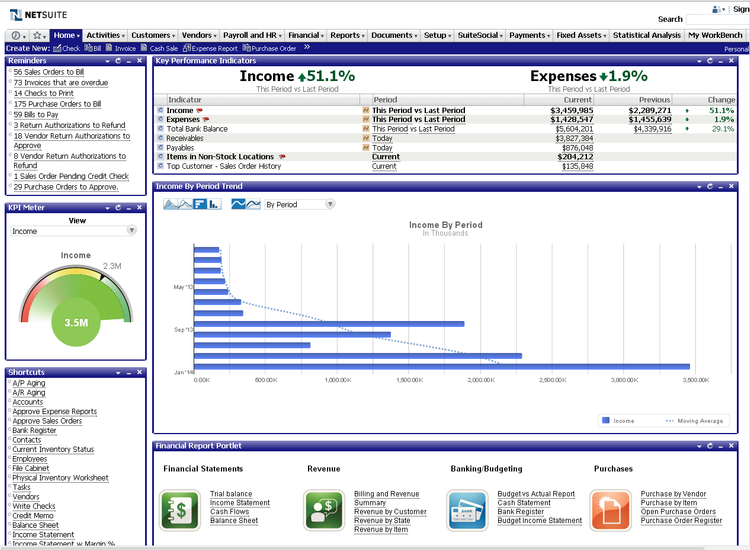
NetSuite - Best for Financial Planning
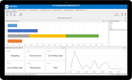
NetSuite’s budgeting and forecasting module allows you to create “what-if” scenarios for more accurate financial projections. Compare your current forecast with actual real time data to make adjustments according to updated estimates. These can be different dimensions, like projected revenue, capital expenditures, or location. This helps multi-site retail banks and credit unions create complex models to meet fluctuating market demands.
Additionally, you can create detailed revenue and sales plans to help align your corporate objectives. Collaborate with your finance, service, and sales departments to ensure goals are met. Throughout the year, track performance and KPIs on interactive dashboards against the plan to make informed adjustments. This helps your institution drive revenue and financial growth.
NetSuite is best for midsize banks with multiple entities. The starter accounting package costs around $1,299/month plus $99/user/month. While it may exclude smaller operations, it’s well-suited to driving growth for financial service companies.
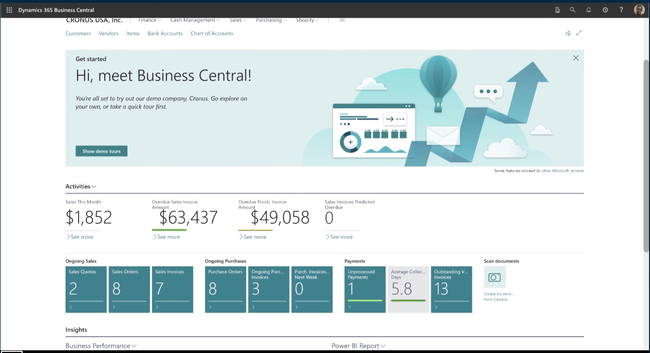
Dynamics 365 Business Central - Best CRM
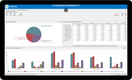
Dynamics 365 Business Central’s built-in CRM boosts marketing and sales performance. The module includes interaction tracking and AI renewal opportunity guidance to help sales teams better communicate with clients. Also, detailed customer data dashboards can help personalize service.
The module is also great for companies that use Outlook because of its native integration with the platform. Now salespeople can view all necessary information while communicating with clients from one screen. Data can include contracts, invoices, and sales history. This helps drive efficiency and reduce errors from manually searching data.
Business Central’s CRM is a good option for small to midsize financial service organizations. Its Essentials plan starts at $70/user/month, making it more affordable for small teams. However, its CRM does lack some advanced functionality, as other options like Salesforce let you extract more granular insights.
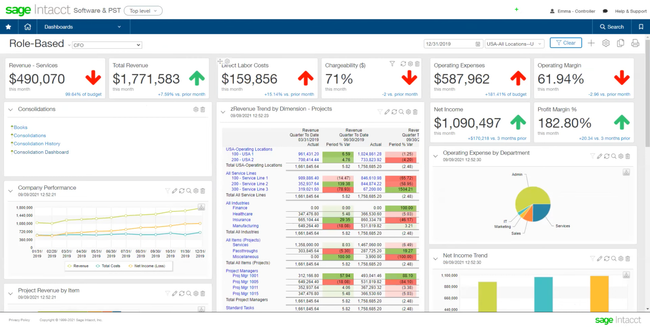
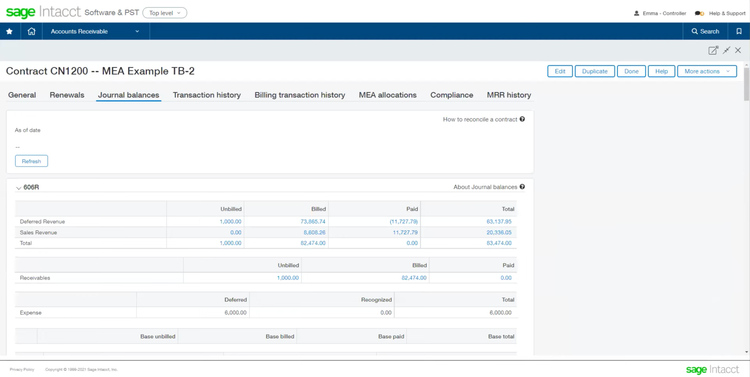
Sage Intacct - Best for Compliance and Security
Sage Intacct can help your business comply with a number of regulatory requirements. These include:
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) compliance: Provides detailed audit trails for every change made to financial data for accountability and transparency.
- IFRS and GAAP reporting: The system includes prebuilt GAAP statements and supports reporting for multinational companies.
- GDPR and data security: Offers secure data storage with encryptions to safeguard sensitive customer information. Set permissions to manage data access.
You can also help your company protect against fraud with the system’s general ledger outlier detection tool. It uses machine learning to spot unusual activity or unexpected transactions that deviate from normal patterns. This is especially important for the financial services industry, which is prone to internal fraud due to its high-value nature and history of insider trading.
Sage Intacct is best for small to midsize financial service companies looking to stay compliant with several regulations. However, one downside is that you’ll need to integrate with Salesforce for CRM functionality. If you’re looking for an all-in-one solution, Netsuite or Dynamics 365 Business Central are good alternatives.
FlexiFinancials - Best for Bank Accounting
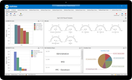
FlexiFinancials’ strong general ledger helps large businesses manage complex accounting processes. It consolidates transactions for multiple companies, letting you set flexible intercompany rules. You can also automate your reconciliation processes for account aging, debits, credits, and clearing. These functionalities help organize your books and streamline the financial close.
Flexi integrates with nearly any core banking system, including Fiserv, Finastra, and Nymbus, to combine its accounting functionality with your existing platform. Unfortunately, it does not list its prices publicly, so you must request a custom quote.
XLedger - Best for Private Equity Firms
[Xledger](/reviews/xledger/] is a cloud-based financial ERP designed to streamline back-office operations for professional services and private equity firms. It is built around a robust accounting core that supports general ledger, AP/AR, cash management, and reporting.
Xledger offers a platform that simplifies multi-company consolidation, a must-have for private equity firms managing a portfolio of companies and SPVs (Special Purpose Vehicles). The multi-entity automation engine significantly reduces the manual work of bank reconciliations, intercompany transactions, and eliminations. So instead of wrangling spreadsheets and manual roll-ups every month, teams can create consolidated financial statements with drill-downs to the entity-level for more granular reporting.
Xledger is best suited for growing private equity firms that manage multiple subsidiaries and need a scalable, consolidated accounting system. Its cloud architecture and automation tools make it easy to handle complex business structures, and with quote-based pricing, the system is tailored to match the specific size and requirements of each firm.
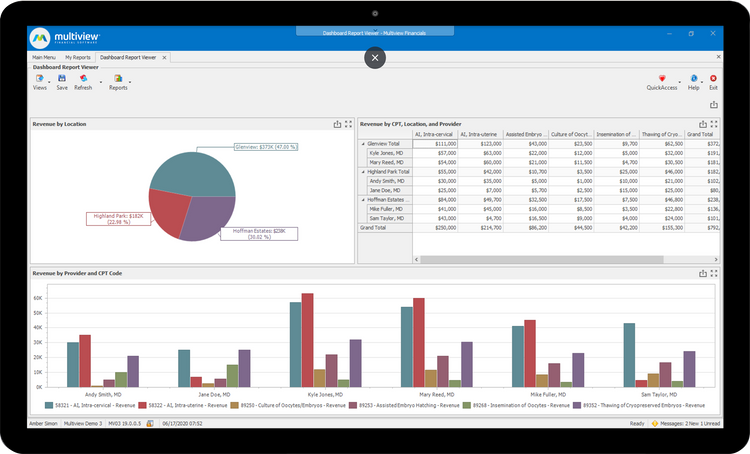
Multiview - Another Good Option
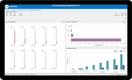
Multiview ERP includes an effective business intelligence module for company-wide performance evaluation. Its user-friendly interface is easy to navigate, allowing you to generate pre-built reports with minimal clicks. It uses real time data from the connected ERP, so you are always reviewing current figures. This lets you extract insights fast without needing to build complex models or consult with IT.
The module also displays charts, graphs, and infographics of data across all departments. Build dashboards to monitor KPIs from all entities, letting you view consolidated data or location-specific performance. Click into each graph to see specific trends and make better-informed decisions to drive growth.
Because Multiview supports large data volumes, it is best for mid to large-size businesses. The system is an all-in-one ERP suite with 18 integrated modules for various capabilities like accounting and document management.
What is Financial Services Software?
Financial services software manages the daily operations of banks, savings institutions, credit unions, private equity, and credit card companies. Also known as banking software, these solutions enable wealth management in corporate, retail, and private banking, which all rely on online technologies to provide digital banking services, payment capabilities, and analytical insight for regulatory compliance. Any organization providing financial services such as checking accounts, savings accounts, investments, or credit/loans can benefit from using financial services software.
- Retail banks use financial services software to primarily record and manage customer transactions in relation to their accounts by linking with internet banking features, ATMs, and payment networks in order to ensure the customer is able to access their financial information both in-person and through mobile banking apps.
- Investment banks, which require connection to financial markets such as security exchanges, focus more on providing analytics on investment financial performance and tools to assist in secure, compliant equity trading.
- Private equity firms use financial services software to manage deal pipelines, consolidate finances across multiple companies, monitor portfolio performance, and streamline investor reporting for transparency and compliance.
In addition to these standard financial management capabilities, financial software vendors also offer a variety of ancillary products and/or integrations with other software solutions to provide all the functionality your business needs to facilitate a complete digital transformation. Examples include fraud risk management, credit background check, credit management, loan origination and servicing, and banking investment intelligence.
Key Features
- Account and Transaction Processing: Manages scanning and verifying checks, processes bank teller actions such as a cash count or item list, handles bank cash management, check management, credit card transaction processing, money order management, the management of corporate clients’ cash payments, and micro account management systems.
- Customer Self-Service Portal: Includes online payment processing for eCommerce, bill pay, remote deposit, transaction history tracking, and more.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Provides financial advisors with contact and task management information, workflow automation, financial document imaging, and customer onboarding.
- Marketing Automation: Manages digital marketing and content marketing efforts for your financial institution. Helps reach customers through personalized messages regarding retirement savings, college funds, credit card debt, home-buying, and more. Based on credit info, age, and demographics, the system sends appropriate messages to customers and prospects.
- Business Intelligence Systems: Gather and sorts big data from lenders, creates engaging visuals to analyze and report findings.
Primary Benefits
All financial services software is designed to aid both businesses and consumers in improving their financial operations. Since the financial services sector handles a variety of tasks for consumers, such as retail banking, ACH transfers, mobile payments, lending and borrowing, and more, providers require a strong software tool with benefits specific to the financial tech (FinTech) industry.
Stay Ahead of Regulatory Compliance
Maintaining regulatory compliance is a top concern for most financial services organizations. Financial institutions are better off avoiding the negative financial ramifications that could occur by not staying on top of them. Examples of regulatory compliance requirements for banking institutions include:
- Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review (CCAR)
- Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA)
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB)
- Office of the Comptroller of Currency (OCC)
Financial services software aims to protect your financial organization from facing government fines and forfeitures. In doing so, you can safely handle your client’s financial assets with care. As a software buyer, any solutions you are considering will need to be compliant with these regulations.
Improve Customer Service
Using customer relationship management (CRM) features can help ensure client details are readily accessible. Any sent mail, phone conversation details, or face-to-face meeting details can be stored in the system–letting your staff more easily educate themselves on a customer’s banking history. Taking advantage of a contact history tool can better help identify past issues a customer has had, or help you better understand common issues and complaints certain customers experience.
As your financial institution begins to grow, customers become more of a number, and there is a loss of personal connection. This can be circumvented by diligent note-taking within CRM software so your company can still provide a meaningful customer experience as much as possible. On the commercial side, financial software with automated blockchain can record all online transactions so all relevant information is shared between proper parties, whether they are traditional customers or vendors.
Enhance Reviews with eDiscovery Capabilities
Financial service organizations use software for eDiscovery purposes–meaning the software can aid in collecting, processing, and analyzing raw data. Many organizations are sending banks and credit unions electronically stored information in response to internal, due diligence, or litigation requests.
A financial services eDiscovery software feature helps financial institutions prioritize the reviews of emails, databases, text documents, trade data, and internal spreadsheets. The quick collection of historical and real-time data allows organizations to streamline their litigation support.
Increase Productivity
Using web-based financial services software can give your staff access from anywhere via a web-browser of even a mobile device. If your financial organization has multiple branches, this can be useful for gathering real-time data from other areas such as the corporate office or a holding company. In a web-based environment, loan servicing and administration can be streamlined by accessing key credit file data from the corporate office files.
A web-based option will limit any concerns your financial organization may have over version control–allowing your bank to be more productive and quicker to respond to consumer inquiries.
ERP Options
A financial services software will primarily focus on providing your customers with the financial tools they desire, managing your customers’ financial assets, or both. Like all businesses, a financial services company still needs a way to automate their back-office processes and strengthen their own financial transactions.
An ERP package for a financial services institution will combine the requirements for maintaining government regulations, managing your financial operations, and providing transparency–all while being integrated into the company’s sales order management, enterprise performance management, human resources, and customer relationship management (CRM). Usually, these core features provide financial visibility into receivables and payables, along with sales forecasts, which allows them to stay fluid and facilitate proper communication with staff and stakeholders.
Relevant to the financial services industry, a capable ERP system should include a client database, financial dashboards complete with reporting and analytics, budgeting and forecasting, and payment management. Most importantly, these features can adjust how your customers view your relationship together by putting into perspective your real financial data.