Why ERP Systems are Important for Your Business
Why Is ERP Important?
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions, an integrated suite of business applications, allow organizations to streamline and optimize their business processes, such as financial, sales, and operations, leading to more accurate and efficient business operations. ERP software makes business functions more agile by implementing software on a modular basis to handle current needs immediately and plan for future needs later.
Read More: What is ERP and How Do ERP Systems Work?
Why You Should Implement an ERP System
Whether you’re a small business owner just starting out, or a capable enterprise looking to fine-tune your processes, your company can benefit from ERP software. You may notice business picking up or your customer base expanding, which leads to increased work volume, hiring more people, and developing a broader range of products. This complexity may overwhelm an unprepared organization, meaning you’ll need to be pragmatic in rolling out your ERP system.
ERP solutions can be customized based on the industry you’re in or on the primary features necessary to improve your business performance. Some software is developed with a specific industry or set of functionalities in mind. Others are more generic and require an ERP vendor who has experience inserting the solution into your environment.
Accounting
Financial management capabilities are at the forefront of ERP implementation. Modules such as accounts payable, accounts receivable, and a general ledger will help track revenue and expenses. This may also include payroll for your organization.
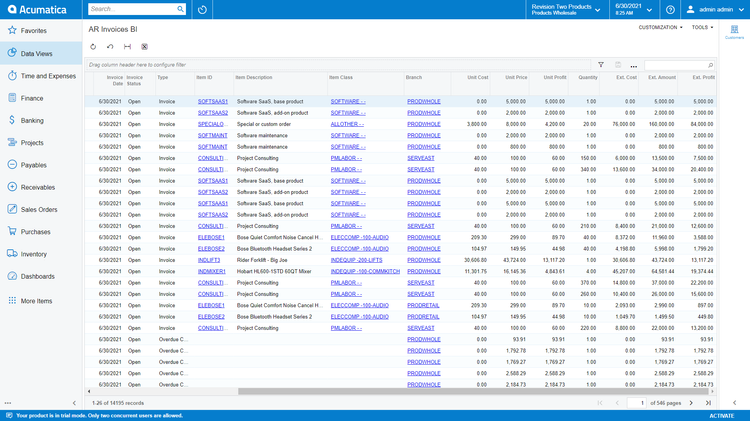
Inventory Management
An inventory management module within an ERP system will help track all information about the items that your company builds, buys, stores, or sells. Inventory management software simplifies pricing products and helps maintain the most effective stock levels. Integrating inventory with other ERP applications will reduce stock level requirements and lower warehousing costs based on a better understanding of your stock movement.
Customer Relationship Management
CRM software is often sold separately, but ERP software can offer many capabilities to aid in customer relations. These key applications support the sales and marketing staff and address the needs for contact management, tracking conversation history, managing leads, reviewing order histories, and creating quotes.
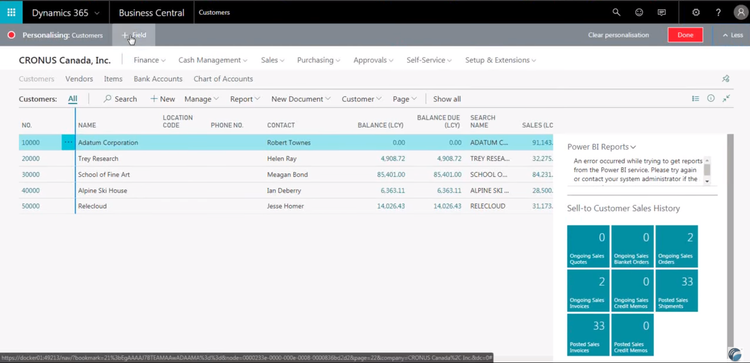
Human Resources
An enterprise resource planning system can monitor your organization’s workforce via human capital management features. HR modules aid in the hiring process and maintain positive relationships with your existing staff. These tools cover employee onboarding, time and attendance tracking, and benefits management.
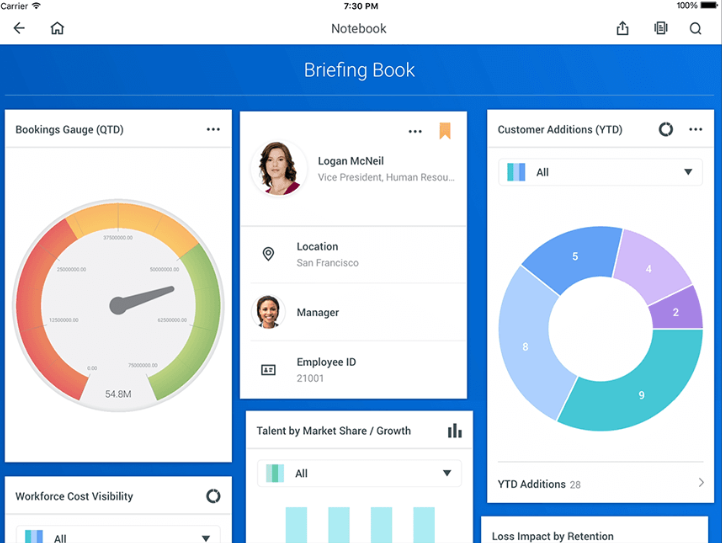
Supply Chain Management
Manufacturers and distributors are some of the most prominent businesses that use ERP software daily. This can be attributed to the need to improve the logistics involved with acquiring raw materials and delivering a finished product to a customer. A supply chain management software suite will manage the flow of goods and services between locations as efficiently and cost-effectively as possible.
How Could an ERP System Help Small Business Become Efficient?
Small-business ERP systems are tailored for affordability, simplicity, and scalability, setting them apart from traditional enterprise ERP solutions. They offer essential modules to streamline operations without the complexity and cost of larger systems.
These ERPs are customizable to a small business’s needs and allow for an ‘a la carte’ feature selection, making them cost-effective. As the business grows, the system can easily scale to include more functionalities. This targeted, flexible approach makes small-business ERP systems a smart investment for companies needing streamlined management without enterprise-level overhead.
How Can an ERP System Improve Accounting Efficiency?
Consolidation of Financial Data
ERP systems centralize financial transactions, reducing the risk of duplicate entries and inconsistencies. An accounting firm, for example, could easily reconcile client accounts across different departments using a centralized financial data system.
Faster Closing Cycles
ERP systems enable quicker month-end and year-end closing by streamlining the financial reporting process. Automated reconciliation and built-in compliance checks speed up these cycles, ensuring that financial statements are generated promptly and accurately.
Compliance and Auditing
ERP systems feature built-in compliance mechanisms and audit trails, simplifying the often complex and time-consuming process of meeting regulatory standards. These features offer ease of compliance and a framework for accountability, reducing the risks associated with financial audits.
Benefits of an ERP System
If you’re looking to implement an ERP or upgrade your existing system, it’s important to understand the benefits of ERP first and foremost. This can give you real-time visibility into what your business needs, what you can afford, and what you can realistically implement into your environment.
- Improve productivity: Eliminate redundant or repetitive tasks through automation.
- Lower operational costs: By automating and optimizing processes, you can minimize labor costs.
- Provide better customer service: Increase the speed at which you can access customer information and history with your company
- Become a more mobile business: Access data remotely with cloud ERP software that can work in a web browser or via a mobile device like an iPad.
- Streamline processes and gain visibility into workflows: Monitor your internal mechanisms to make better business decisions. Provide transparency to your employees, vendors, customers, or even shareholders.
- Improve data security: Set security permissions to ensure key company data is not compromised.
Summary
ERP systems streamline workflows by bringing your business processes into one place. When all of your real-time data is available in a single platform, you’ll eliminate the need to use separate unconnected programs or document sharing with Excel spreadsheets. Housing your data in one place also improves collaboration between various departments, leading to better communication during critical projects.
ERP software also offers better financial reporting by allowing analytics to review both historical and real-time financial data. This will aid in informed decision-making and help break down your business by region, location, profit center, or even employee.
Rather than having your company’s financials and sales data split across multiple systems, a unified single system will also improve data security and accessibility. A centralized repository will let you monitor day-to-day processes for continuous improvement. This will lead to improved communication between multiple departments that may rely on each other to complete orders.
Examples of Top ERP Software
Before you proceed with an ERP implementation, you’ll want to determine your business’s needs and what you care most about, such as an on-premise or cloud-based ERP. The following is a brief collection of ERP solutions we’ve helped visitors review over the years.