What is a Manufacturing Execution System (MES)?
What is an MES?
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) streamlines the manufacturing process, providing real-time data collection, monitoring, and control of production resources. These systems are pivotal components in today’s manufacturing landscape, bridging the gap between enterprise-level planning and shop floor operations.
By integrating seamlessly with other systems and equipment, MES enhances visibility, enforces quality, and ensures maximum efficiency across all aspects of the manufacturing journey, from raw materials to finished products. A company that uses MES wisely will optimize its manufacturing operations and improve overall production performance.
How Does an MES Work?
MES uses computers and software to monitor raw materials in real time as they are purchased, gathered, transported, stored, and produced. The goal of MES is to provide manufacturers with a clear overview of how materials, ranging from consumables to equipment, are used on a plant floor through every step of production. MES also ensures procedures follow international regulations such as the ISA-95 standard*.
These standards include:
- Product definitions
- Resource management
- Scheduling of production processes
- Production order dispatching and execution
- Production data collection
- Performance analysis
- Track and trace of production
A comprehensive MES can connect information from multiple manufacturing plants with vendor and supplier updates. Decision makers can then access performance metrics in real time to better adjust production based on factors such as scrap and rework.
Further, you can get details on labor and equipment used within your manufacturing facility. An MES solution can show which machines are most reliable or which workers have the necessary labor skills for certain processing tasks, all of which are vital information for making more informed decisions on the factory floor.
*/ Set by the International Society of Automation, ANSI/ISA-95 is the result of merging MESA-11 with the Purdue Reference Model.
Top MES Benefits
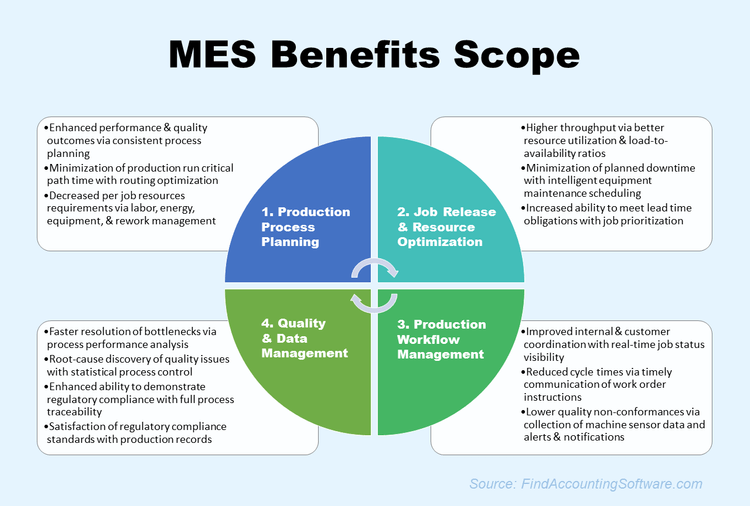
MES offers many benefits to manufacturers, including:
- Maximized resource utilization
- Streamlined manufacturing cycle times (reduced downtime, increased uptime)
- Reduction of scrap and/or rework
- Increased production quality and control
- Mobile inventory
- Improved regulatory compliance standards
- Real-time material and product traceability
Together, these benefits improve business performance from the initial acquisition of materials to the final customer interaction. With a single MES controlling the shop floor, you can make instant adjustments in the face of unexpected downtime or changing delivery dates.
MES Core Features
In order to provide these benefits, the key functionality of MES systems can be categorized into the key areas of data collection, forecasting, and traceability. However, the Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Association (MESA) International has 11 core functionalities. The main manufacturing process modules used for each are:
Data Collection
- Paperless document management: Store and retrieve operational documents such as SOPs, CAD drawings, production specifications, and other file types
- OEE analysis: Measure overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) based on collected performance, loading, and availability data
- Labor management: Track the time and attendance of workers and correlate it to their respective job assignment data
- Waste tracking: Document raw material waste and production scrap to find ways to reduce waste
Process Forecasting
- Order management: Optimize order processing by tracking orders across multiple sales channels by connecting inventory and sales order data
- Production scheduling: Prioritize work in progress based on deadlines or priority orders based on sales predictions or vendor demand
- Inventory management: Track information on all products your company builds, buys, stores or sells
- Change management: Coordination for order changes, including alterations to material, equipment, processes, or routing
- Downtime management: Scheduling and tracking of machine downtime based on connections with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or via manual input
Product Traceability
- Electronic traceability: Utilize barcodes, SKU numbers, or RFID to perform part, batch, or lot tracking and pinpoint order/material position in production flow without manual data input
- Job tracking: Gain real-time data visibility into order status as the job progresses through the factory
- Line log book: Digital record of shift events, including set-up conditions, tool changes, material changes, and process adjustments
- Quality management: Analyze risks, set quality objectives, implement workflows to meet quality control standards, and prepare for audits
- Inspection management: Coordinate workflow controls in accordance with local, federal, or internal standards for your industry to remain compliant in the event of inspections or audits
- Supply chain management: Create control systems for materials at every stage of the supply chain, whether on the shop floor or warehouse storage
- Labor skills validation: Documentation of employee competencies and certifications for management of adherence to ISO and other quality standards
What Industries Use an MES?
MESs are used across several industries to help their production processes. While the core functionalities stay consistent, each industry has specific functionalities and applications. These industries include:
- Automotive: MES is important for manufacturers managing complex assembly lines and processes. It helps track parts through assemblies, manage product recalls, and monitor component availability while maintaining industry standards.
- Food and Beverage: MES helps food and beverage manufacturers comply with FDA and HCCP laws with real time monitoring and control. Other industry features include batch and recipe management and lot traceability.
- Pharmaceutical: Similar to the food and beverage industry, pharmaceutical manufacturers rely on an MES to stay compliant with strict requirements like good manufacturing practices (GMP) and serialization.
- Metal and Mining: MESs are used in the metal and mining industry to prevent workplace accidents through environmental monitoring. It also optimizes resources for greater efficiency.
MES Integration Options
Sometimes known as manufacturing operations management (MOM), MES can be integrated via software APIs or as part of a larger software system, particularly product lifecycle management (PLM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. And that’s certainly not all:
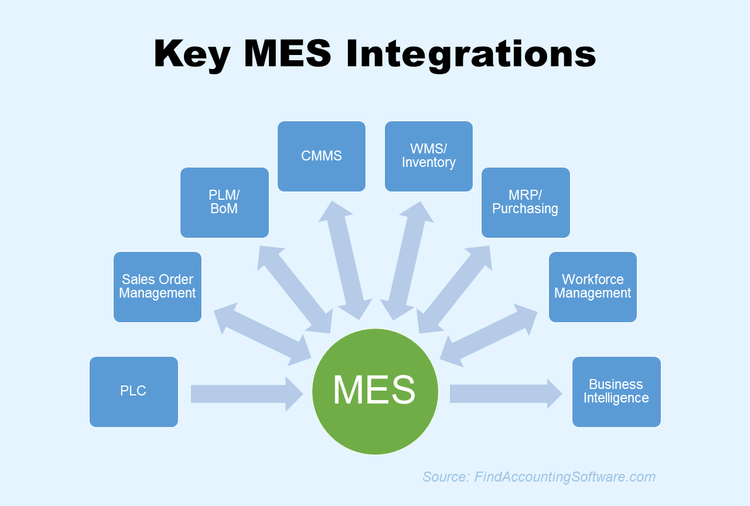
Some standalone MES are dependent on other types of manufacturing software to function effectively. Along with ERP and PLM, the main applications which can be connected to manufacturing execution systems include:
- Warehouse management (WMS) tools
- Inventory management solutions
- Order management tools
- Manufacturing resource planning (MRP) solutions
The question is whether buyers are better suited to purchase an ERP that includes MES as one component of a larger suite of business management modules or whether MES should be purchased as a separate program and connected to existing systems.
Whether you purchase MES as a standalone software will largely depend on what legacy systems you have and what additional functionality your business needs. For instance, not all ERP systems are suited for industry-specific manufacturing, which can make them inadequate for your business.
What is an MES Platform?
An MES platform simply refers to the full-scale software that streamlines raw material production processes for a company through a central hub. Data can be shared between multiple users and locations in real time through a Cloud-based platform as part of a smart manufacturing system.
In some circumstances, an MES platform may combine compatible manufacturing software and factory floor hardware, which may also refer to a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system (SCADA).
Looking for MES software for your production facility? Start your search today.
