Best Manufacturing ERP Software
Manufacturing ERP systems perform differently depending on whether you’re in discrete, process, or mixed-mode production. We’ve tested and reviewed various software for everyone, from chemical producers to automakers and job shops.
- Offers resource management workbench tool
- Supports indented BOMs with multiple components
- Great for discrete manufacturing
- Dynamic adjustment function for tweaking formulas
- Formula management integrates with costing capabilities
- Includes quality control and compliance features
- Supports up to 15 levels of assemblies
- Integration with AI, MI, and IoT
- Offers hybrid, on-prem, and cloud deployment
In this guide, we’ve ranked the top systems based on how well they support different manufacturing models. Whether you operate in a discrete, process, engineer-to-order (ETO), or mixed-mode environment, these ERP solutions offer diverse strengths to meet the demands of your manufacturing business.
- Infor CloudSuite Industrial: Best for Make-to-Stock
- Epicor Kinetic: Best for Make-to-Order
- SAP S/4HANA: Best for Engineer-to-Order
- BatchMaster ERP: Best for Process Manufacturing
- Datacor ERP: Best for Pharmaceuticals
- SYSPRO: Best for Hybrid Manufacturing
- Deacom ERP: Best for Food and Beverage
- QAD Adaptive ERP: Best for Medical Devices
- Acumatica: Best for Building Materials
- xTuple: Most Affordable Option
- DELMIAWorks: Best for Industrial Manufacturing
- Dynamics 365: Best for Additive Manufacturing
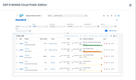
Infor CloudSuite Industrial - Best for Make-to-Stock
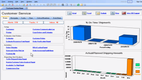
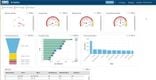
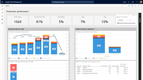
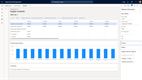
Infor CloudSuite Industrial helps you predict demand with its advanced planning and scheduling (APS) module. It keeps everything in sync, so you can avoid overproduction and stockouts.
This manufacturing software system creates demand forecasts by combining historical data, customer orders, and supply chain inputs. Here’s how it works:
- Historical Data Analysis: Uses past sales data to predict demand patterns and customer behavior.
- Real-Time Data Integration: Syncs live inventory, orders, and schedules to keep forecasts up-to-date.
- Forecast Adjustments: Updates demand forecasts as customer orders come in, balancing supply with demand.
- Scenario Planning: Lets you test “what-if” scenarios, which helps you simulate changes in demand.
Because Infor CloudSuite syncs production schedules with demand signals, APS helps MTS manufacturers avoid overstocking finished goods or missing orders during a spike. This means less warehouse carrying costs and better on-time delivery performance.
Additionally, this industrial manufacturing software even factors in supplier lead times and raw material availability; that way, your production plans reflect what you can realistically deliver. Rather than forecasting in a vacuum, you’ll get a supply-chain-aware plan that connects consumer demand with procurement and capacity.
While CloudSuite Industrial excels in demand forecasting, users say its quality management system (QMS) module could be more robust. That’s because its corrective action/preventative action (CAPA) capabilities are pretty basic and tailored more for straightforward quality issues. We recommend something like QAD ERP O³ for complex manufacturing environments.
Read our full Infor CloudSuite Industrial review.
Epicor Kinetic - Best for Make-to-Order
Epicor Kinetic has one of the stronger product configurators we’ve seen on the market. The configurator is visually engaging, allowing you to customize products with options like length, width, size, and finishes—all represented by clear, modern icons. It even updates total pricing in real time and auto-adjusts part numbers based on your selections.
The dynamics list feature is another plus. It sets up dependencies between configuration options based on what you’ve chosen, so you only pick valid combinations. Once you’ve finalized your configurations and created a production order, Kinetic auto-generates custom bills of materials (BOMs), operations lists, and routings for you.
Compared to systems like NetSuite, Kinetic doesn’t require multiple add-ons for complex manufacturing. However, with extensive capabilities comes a heftier price tag. Pricing is not public; you’ll need to call for a quote. Beyond the subscription license, there’s a $175/user/month fee. For startups or smaller manufacturers, we recommend more affordable options like JobBOSS² or xTuple.
Manufacturers with over 50 employees will likely find Kinetic’s pricing and capabilities a good match. Epicor also has retail and distribution programs for those selling directly to consumers. While Kinetic requires an initial investment of time and money, it’s a strong option if you’re ready to scale operations.
Read our full review of Epicor Kinetic.
SAP S/4HANA - Best for Engineer-to-Order
SAP S/4HANA is best for sectors like industrial machinery, heavy equipment, aerospace, and defense. It offers strong support for ETO projects that involve complex work breakdown structures (WBS). Its project planning app simplifies the creation and management of WBS, so you can stay on top of every project detail.
Setting start and end dates for each WBS element is straightforward. You can link tasks to dependencies, such as ensuring that design work is completed before moving on to prototype development. This helps you create a clear project timeline. The system also lets you define key phases like design, prototype creation, manufacturing, and delivery. Each phase can be further broken down into specific tasks for a more structured approach that helps you ensure every component is accounted for.
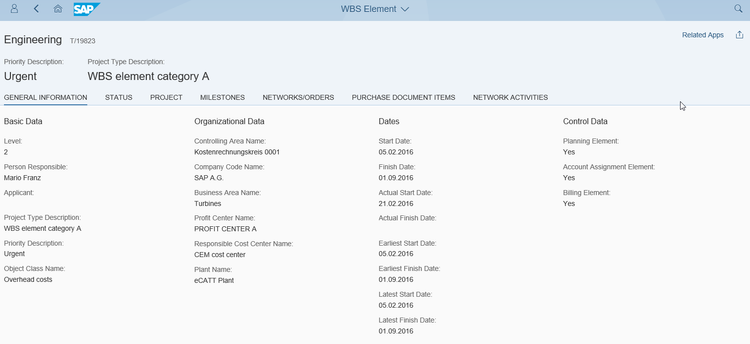
You can allocate costs to each WBS element, whether it’s engineering hours, materials, or manufacturing costs. You can also track and document any changes requested by clients. If a change in specs arises, just update the design element and adjust tasks and resources. The system will even show you how these changes impact your project timeline and budget.
Keep in mind though, SAP S/4HANA is a premium solution best suited for large corporations. If you’re a small or mid-sized company, you’ll likely find it too costly and complex for your needs. You’re better off with a solution for smaller enterprises at a lower price point, like SYSPRO or Total ETO.
Learn more about SAP S/4HANA in our full review.
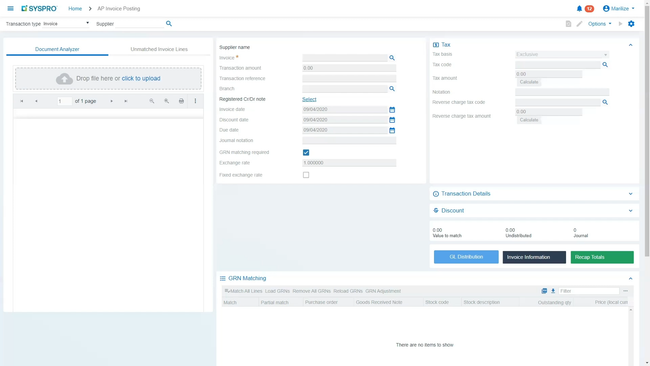
BatchMaster ERP - Best for Process Manufacturing
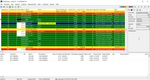
BatchMaster ERP offers formula management tools for sectors like chemicals, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. It has a dynamic adjustment function for tweaking formulas during development and production. You can easily scale batch sizes up or down while keeping proportions just right and even switch out ingredients based on cost and availability. This flexibility helps you fine-tune your formulas for different production needs.
In addition, formula management integrates with BatchMaster’s costing capabilities. You can roll up existing and theoretical product expenses, covering fixed, tiered, and scalable costs. Plus, you can apply fees to intermediates, recipes, and finished goods. The system even lets you run what-if cost scenarios during development, giving you a clearer picture of how changes might impact your expenses.
Formula management works hand-in-hand with the QMS module to set up quality control specs directly within your formulas. Your plant can auto-generate QC test plans based on formula settings. You can also make real-time changes to formulas based on test results and maintain traceability for each lot for consistent quality and compliance.
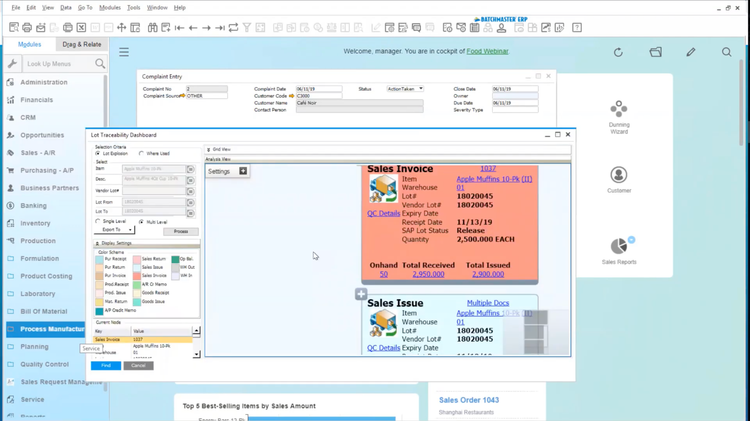
The UI isn’t the most user-friendly, which could be a hurdle for new users. The module and menu layouts can feel somewhat clunky, and the software’s design–developed using Microsoft’s .NET framework–looks a bit old-school with its traditional buttons, color schemes, and navigational panes.
However, if your company already uses Microsoft products like Outlook, Excel, or Dynamics 365 CRM, you’ll find that BatchMaster ERP integrates well with these tools. So, even if the interface seems a bit dated, the trade-off is a platform that provides precise control over recipes, batch sizes, and compliance without shaking up your current setup.
Read our full review on BatchMaster ERP.
Datacor ERP - Best for Pharmaceuticals
Datacor’s production history feature is especially useful for drug manufacturers. This ERP keeps a full record of every batch and formula used, capturing details from initial formulation to the finished product. It also enables precise adjustments through multi-level formula capabilities and what-if analysis tools.
Additionally, Datacor helps your company meet industry-specific regulatory requirements:
- FDA Validation Toolkit: Ensures adherence to GMP and FDA Title 21 CFR Part 11 requirements, covering data integrity and electronic records.
- Cradle-to-Grave Lot Tracking: Offers end-to-end traceability, vital for swift recall processes and batch issue resolution. Helps comply with regulations like the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA).
- Automated Documentation: Generates detailed records of ingredient changes and batch specifics, aiding regulatory compliance.
Although Datacor has a strong feature set, users report that customization options are somewhat limited. While you can personalize dashboards and configure workflows, more complex customizations require working directly with Datacor’s developers, which could incur extra costs.
Learn more in our Datacor review.
SYSPRO - Best for Hybrid Manufacturing
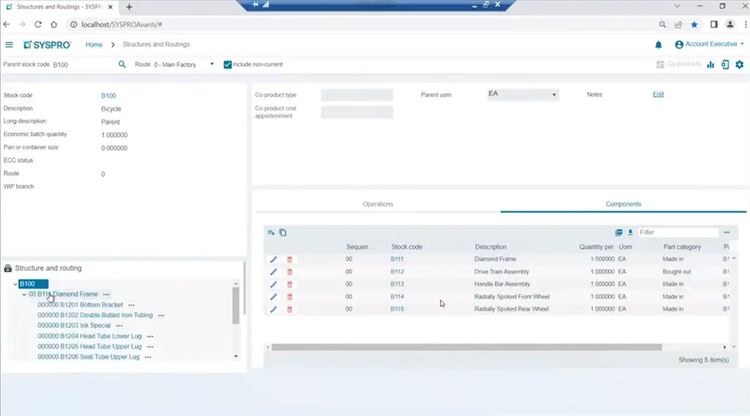
SYSPRO’s BOM module supports multiple production modes, from job shop and production line to batch production and mixed-mode environments. This ERP also makes switching between methods easy, which is helpful when you’re producing both standard products and custom orders.
Hybrid manufacturing environments often have complex product structures. SYSPRO’s BOM module supports up to 15 levels of assemblies and sub-assemblies for intricate product hierarchies. It also gives you a detailed breakdown of each component’s sub-components to manage products with multiple layers.
To help meet varying production requirements, SYSPRO offers multiple structure sequencing options. You can define the order in which components are used during production. For example, you can use a simple numeric sequence for linear production paths or alphanumeric sequencing for complex operations, like those with A-series vs. B-series components.
SYSPRO offers considerable flexibility, but some user reviews mention that its built-in reporting is relatively basic and not user-friendly, with limited parameter options. However, users with expertise in tools like Crystal Reports can create more advanced, customized reports.
Read our full SYSPRO review to learn more.
Deacom ERP - Best for Food and Beverage
ECI’s Deacom has specialized tools for food safety, such as configurable quality control checkpoints. These span the entire production lifecycle, so you can set specific quality standards and place holds to prevent shipping non-compliant goods. You can even adjust formulations in real time based on QC test results.
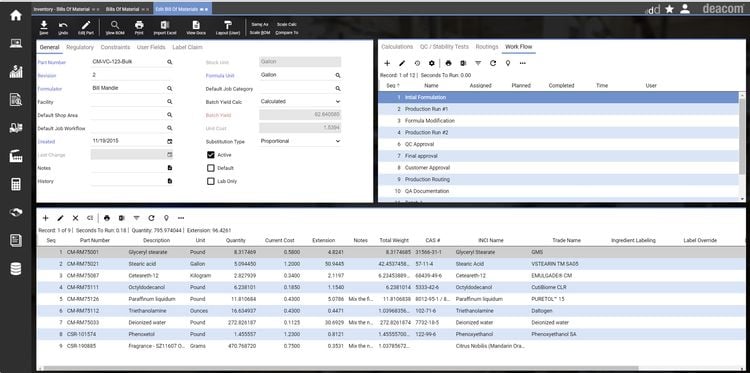
Deacom also assists with documentation, auto-generating Certificates of Analysis, nutrition fact labels, and safety data sheets. With its full lot traceability, you can track materials across your supply chain and manage any recalls.
While Deacom is a solid platform, its single-system design limits how much you can customize it. You can tweak certain features, but the core ERP isn’t set up for major changes to fit unique workflows.
That said, Deacom has made strides recently, switching to a more modular design. You can now pick and choose the modules that fit your needs, which gives it more flexibility. They’ve also introduced Deacom Essentials, a version designed for smaller companies with over ten employees and $5 million in revenue.
Read our full review of Deacom.
QAD Adaptive ERP - Best for Medical Devices
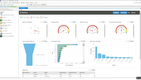
QAD Adaptive ERP offers complete control over inventory and production, helping you optimize processes like lot control and serialization. You can easily track materials moving through production and storage for smoother operations. Serialization adds an extra layer of traceability, making it simple to follow individual items and their packaging – whether it’s for warranties or regulatory reporting.
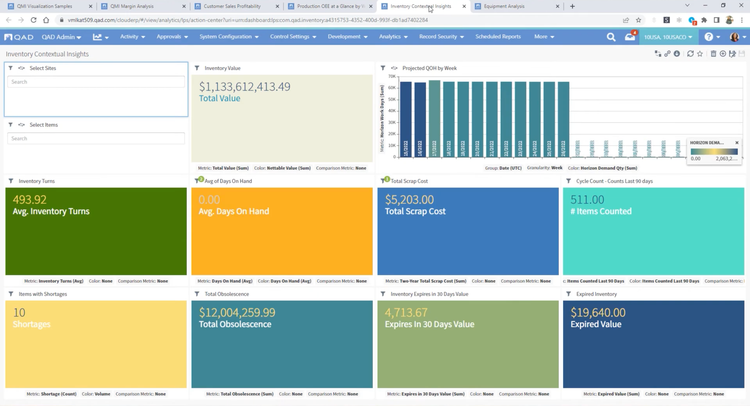
This ERP works hand-in-hand with QAD’s EQMS, a quality management tool. It functions by helping you meet FDA requirements and ISO 13485, a framework for medical device design, production, and servicing. If a quality issue pops up, the system automatically captures this data and starts the necessary workflows to investigate and resolve it.
With built-in CAPA processes, you can monitor corrective actions from start to finish. QAD Adaptive ERP also stores critical data like test results, inspection records, and certificates of compliance for real-time access across teams.
QAD has a long-standing reputation in the medical device industry and is trusted by many leading manufacturers. However, its strong focus on compliance and quality management makes it overly complex and costly for smaller companies. We recommend QAD Adaptive ERP for medium to large organizations in healthcare and pharmaceuticals.
Acumatica - Best for Building Materials
Acumatica’s manufacturing edition can handle multiple-level BOMs, making it easy to configure complex items like doors or windows with many sub-components. Plus, it maintains a complete revision history, which is helpful for managing specification changes over time.
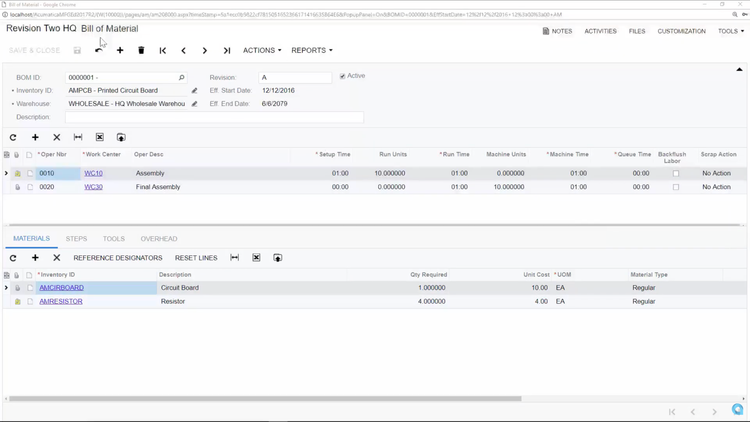
The BOM module connects with MRP systems to ensure raw materials are ready on time, helping avoid delays when supplying materials for construction projects. We also appreciate the flexible cost roll-up tools, which allow you to calculate the total cost of finished goods. This feature supports accurate pricing and financial planning, with options for actual, average, and standard costing methods.
Acumatica is praised for its planning and costing features, but many users find it expensive for small businesses. Its pricing is based on resource use (such as users and transactions), leading to high initial setup costs. Additionally, implementing Acumatica often involves complex customization, increasing both time and expenses.
Learn more in our full review of Acumatica.
xTuple - Most Affordable Option
xTuple is a budget-friendly option for smaller discrete manufacturers. Despite its low cost, it packs a surprising range of features, including inventory control, production scheduling, and MRP functionalities.
This ERP ensures you have the right amount of raw materials and subassemblies available, reducing delays. The system’s MRP tool gives you real-time insight into your purchasing, sales, and production activities so you utilize resources more effectively. It even auto-generates work orders directly from sales orders, factoring in current inventory levels to keep your operations running smoothly.
With xTuple, you can fine-tune MRP by using planner codes. These codes let you set specific handling rules for your materials–such as reorder points, lead times, and lot sizes–so the system knows exactly how to manage inventory for each item. You can also group items for production based on these codes, which makes planning for complex orders easier. For added efficiency, you can use the add-on module xTuple Connect to schedule MRP runs automatically, saving you time and keeping everything in sync.
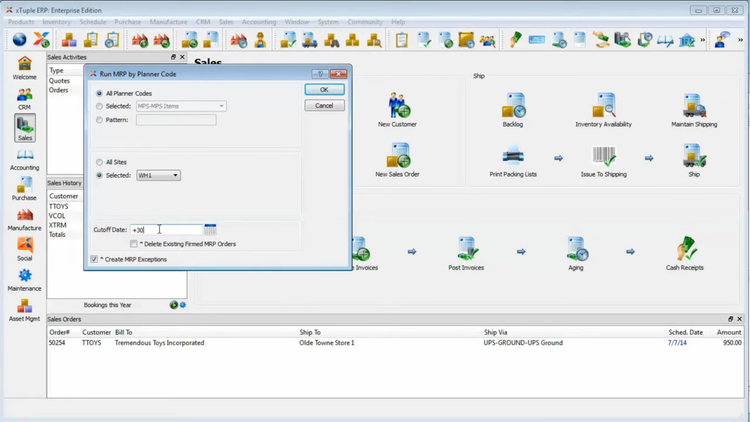
But while xTuple excels in production scheduling and affordability, it’s not the best fit for apparel manufacturers. That’s because it lacks product matrices for managing variations like size, color, or style. Instead, xTuple is more geared toward make-to-stock and mixed-mode production environments.
Read our full review of xTuple.
DELMIAWorks - Best for Industrial Manufacturing
DELMIAWorks, formerly IQMS, includes a built-in MRP module that makes high-volume industrial production environments more cost-efficient. The module uses a time-phased planning window for production and purchasing, considering factors like current demand, lead times, and schedules. You can also configure automated raw material ordering and hard or soft allocation to ensure production keeps up with demand. And when schedules or available inventory change, the system updates in real time, so you’re always looking at current data—no more waiting for manual syncs or batch runs.
Additionally, the MRP system accounts for all areas of the production process on one dashboard. For example, the system measures labor capacity by calculating working hours against the required production hours. It also considers machine availability with smart rescheduling if the demand is too high. Through this advanced planning, your processes can become leaner, and you can better adapt to schedule changes or an influx of orders. It’s especially crucial in the industrial space, where production is capital-intensive and dynamic.
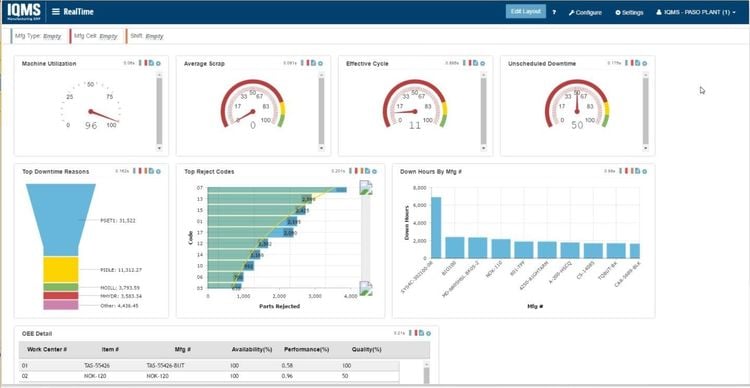
Beyond the MRP functionality, DELMIAWorks also offers add-ons for CAD, Engineering, PLM, MES, and even QMS. These are integrated directly into the ERP system, creating a truly all-in-one manufacturing system. That way, you don’t have to purchase third-party systems and undergo lengthy integration processes. Unfortunately, DELMIAWorks does not publicly disclose pricing, so you’ll need a custom quote.
Learn more on our DELMIAWorks product page.
Dynamics 365 - Best for Additive Manufacturing
Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management offers advanced inventory tools for additive manufacturers. It tracks yields from past production runs, making it easy to optimize resources like powders or filaments. The system then auto-updates orders and inventory, helping you avoid over- or underusing these often costly materials.
Additionally, the ERP supports lot and batch tracking, giving you insights into material lifecycles. This helps you reduce the risk of expired or wasted materials, ensuring you get the most out of your stocks.
With CAD integration, Dynamics 365 SCM integrates product designs directly into workflows. The system supports STL and other CAD files and automatically updates BOMs and production processes as these designs change.
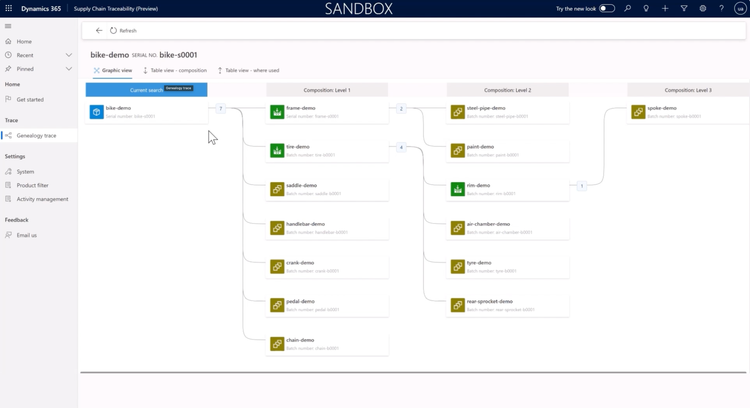
However, it’s worth noting that Dynamics 365 SCM has a higher price tag and a more involved setup than other ERPs. Also, while it integrates smoothly with Microsoft products, you may need additional tools for non-Microsoft applications, so consider your tech stack when deciding.
Other Systems We Like
JobBOSS² is a good option for job shops, offering a scheduling tool with both a planning board and a whiteboard scheduler. It allows you to easily adjust customer due dates and job schedules on the fly, which is useful in fast-paced environments.
Techno ERP is another solid system for small manufacturers with annual revenue under $10M. It offers a strong MRP tool that helps you optimize production and inventory management, which is great for small businesses to boost job profitability.
Systems We Don’t Recommend
Oracle NetSuite can work well for some limited discrete product workflows. However, we don’t recommend it for complex manufacturers. NetSuite generally works best for wholesale, distribution, or service-based companies.
What is Manufacturing ERP?
Manufacturing ERP systems sync and streamline operations such as supply chain processes, inventory control, and production planning. They’re designed to be modular, so you can choose the specific features that best fit your needs and customize your setup as you grow.
These systems go beyond simple order management or finance tracking found in general ERP software. They’re designed to cover end-to-end manufacturing processes, from procurement to production. These platforms may include the capabilities below in their core programs, or they might integrate with other tools to expand functionality:
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): Connects production data directly to inventory and procurement by monitoring real-time activities on the factory floor.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software: Helps manage customer data, sales orders, and post-sales support.
- Human Resource Software: Manages employee data, time tracking, labor resources, and payroll.
- Project Management Software: Provides oversight on deadlines, budgets, and resource constraints – particularly for ETO manufacturers.
- eCommerce Software: Connects online sales channels to manufacturing operations, for manufacturers involved in direct-to-consumer sales.
- Warehouse Management Systems: Manages the storage, movement, and tracking of raw materials and finished products in the warehouse.
Common Challenges
Here are the most common hurdles that manufacturing ERP systems can help you tackle:
- Rising costs for raw materials: Prices for raw materials can fluctuate due to market demand, geopolitical events, or supply issues, impacting your overall manufacturing costs.
- Excess stock or stockouts: Finding the right balance for inventory can be tricky. Running out of stock can interrupt production or sales, while too much stock ties up your capital.
- Supply chain disruptions: Problems with transportation, delays, or supplier reliability can affect the flow of your raw materials and any other components.
- Quality control: Product defects can increase production costs, higher return rates, and unhappy customers.
- Product development: Managing costs while innovating and ensuring new products meet consumer expectations are both critical challenges.
- Demand forecasting: Accurate forecasting helps you align production with market needs while avoiding overproduction or shortages.
- Regulatory compliance: Adhering to industry regulations and standards is vital for ensuring quality and avoiding fines.
- Workforce management: Scheduling and managing your workforce helps you meet your production goals while keeping your team motivated and productive.
- Inefficient scheduling: Poor production scheduling can lead to increased lead times, underutilized resources, and bottlenecks on the factory floor.
Important Features and Benefits for Manufacturers
The main goal of manufacturing ERP is to increase efficiencies and improve reporting and visibility. On a high level, most systems will include features like:
- Production planning: Coordinates production scheduling with labor and raw materials.
- Inventory management: Controls stock levels and tracks inventory movements; usually includes dynamic reordering.
- Material resource planning (MRP): Manages the procurement, planning, and scheduling of components and raw materials to meet production demands.
- Financial management: Integrates financial planning tools like cost tracking and budgeting.
- Supply chain management: Includes procurement, warehousing, and logistics tools.
- Shop floor management: Provides current data on shop floor activities, labor, material usage, and production metrics.
- BOMs management: Manages bills of material to define components required for product assembly.
- Yield management: Includes tools to maximize product output from raw materials.
- Demand forecasting: Helps predict demand to optimize inventory levels and production schedules.
- Maintenance management: Enables maintenance scheduling and asset management.
Software specialized for certain manufacturing styles will include different features. For example, process manufacturing ERP systems will generally include:
- Recipe and formula management: Manages and adjusts recipes or formulas for batch production for more consistent quality.
- Lot control and batch tracking: Tracks product batches throughout production for traceability and compliance.
On the other hand, discrete manufacturing software would provide:
- Engineering change management: Tracks product design changes and their impact on production.
- Product data management (PDM): Manages product data and documentation, including drawings, specs, and other critical information needed for assembly.
Types of Manufacturing
Different types of manufacturing environments require specialized software. Manufacturing ERP can be further divided into specialized subtypes with feature sets unique to specific operations:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Additive manufacturing software | Supports the creation of objects through additive processes, commonly referred to as 3D printing. |
| Apparel ERP | Designed for the fashion industry, with inventory management for textiles and order tracking for custom garments. |
| Aerospace manufacturing software | Assists in advanced materials management, supply chain tracking, and compliance with standards like AS9100 and AS9145. |
| Chemical manufacturing software | Helps track and report compliance with regulatory agencies, including the FDA, EPA, DEA, ATF, and FSIS. Features recipe management, quality assurance, inventory storage planning, expiration tracking, and recall management. |
| Cosmetic manufacturing software | Includes features for quality control, ingredient tracking, formula management, and compliance with regulations like the FDCA. |
| Discrete manufacturing software | Manages the production and assembly of distinct, countable products. |
| Food manufacturing ERP | Provides tools for batch production tracking, inventory control, recipe management, and food safety compliance. |
| Furniture manufacturing software | Manages resource allocation, production planning, and BOM management for furniture assembly. |
| Jewelry manufacturing software | Specializes in jewelry production, including sales order management, production planning, design integration, and casting management. |
| Machine and job shop software | Helps with job costing, quoting, and work order management for custom and small-batch production processes. |
| Medical device manufacturing software | Streamlines the production process and ensures regulatory compliance for healthcare devices, including adherence to ISO 13485 standards. |
| Pharmaceutical manufacturing software | Provides recipe management, batch tracking, quality control, and expiration management for drug manufacturers. |
| Process manufacturing software | Focuses on optimizing the production of items that are typically not countable, such as liquids, powders, or chemicals. |
Each industry has its unique requirements. For example, medical device distributors need to comply with ISO 13485 standards, so they’ll benefit from software that ensures regulatory compliance and product traceability. On the other hand, apparel manufacturers might prioritize product matrices for size and color variations.
Manufacturing ERP Trends
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
ERP systems are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and utilizing machine learning to enhance decision-making, automate routine tasks, and provide predictive insights. While true AI is still in its infancy stage, many of the larger providers are working to incorporate features like demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, and intelligent scheduling.
For example, Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP has introduced “AI-powered tools” that analyze historical data to forecast demand and optimize inventory levels, reducing inventory stockouts and overstocking.
IoT-Connected Shop Floors
Over the last few years, manufacturing ERPs have introduced features beyond basic inventory and production tracking by fully integrating with shop floor machines and IoT (Internet of Things) devices. These new tools allow companies to monitor machine performance, material flows, inventory levels, and production output in real time, enabling faster response to production issues and overall better equipment effectiveness.
For example, SAP S/4HANA integrates machine data directly into its ERP, allowing manufacturers to track machine health, energy consumption, and material usage live. Similarly, DELMIAWorks connects ERP scheduling and production planning with smart sensors and any robotics on the factory floor, providing real-time visibility into each production cycle.
Flexible & Usage-Based Pricing
Some ERP vendors are rethinking how software is priced and sold. Traditional systems like per-user or fixed license pricing are being replaced by flexible, consumption-based models, especially for cloud ERPs. This means pricing is aligned with actual business activity, such as transaction volume, API usage, and data usage, rather than how many employees need access to the platform. This shift benefits manufacturers with seasonal or fluctuating production schedules, allowing them to scale their ERP investment up or down without overpaying during the slow season.
One of the leaders in this space is Acumatica, which offers resource-based pricing based on system consumption rather than per-seat licensing.
If you’re interested in learning more about the structure of ERP pricing, explore our post on How Much Does an ERP Cost?
How to Choose the Right ERP for Your Manufacturing Type
Different types of manufacturing each have their unique requirements. By identifying these needs, you can choose an ERP solution that aligns with your production goals.
| Manufacturer Type | Recommended Systems | Est. U.S. Market Cap | Key Features | Product Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discrete Manufacturers | Epicor Kinetic, SAP S/4HANA | $1.8 trillion | BOM management, production scheduling | Automobiles, electronics, appliances |
| Process Manufacturers | Deacom, BatchMaster ERP, Datacor | $1.4 trillion | Recipe management, batch tracking, compliance | Chemicals, food & beverage, pharmaceuticals |
| Mixed-Mode Manufacturers | SYSPRO, Aptean Industrial Manufacturing Workwise Edition | $700 billion | Flexibility, multi-mode support | Packaged foods, cosmetics, electronics |
| Make-to-Stock (MTS) | Acumatica, Infor CloudSuite Industrial | $1.1 trillion | Inventory optimization, forecasting, supplier collaboration | Consumer goods, apparel, household appliances |
| Make-to-Order (MTO) | Epicor Kinetic, JobBOSS² | $900 billion | Inventory management, lead time optimization, demand planning | Custom furniture, specialized electronics, metal parts |
| Engineer-to-Order (ETO) | SAP S/4HANA, Epicor Kinetic | $500 billion | Project management, customization, cost estimation | Custom machinery, industrial equipment |
Cloud vs. On-Premise Deployment
Deciding whether to deploy your system in the cloud or on-premise ERP is a crucial decision for manufacturers. They each offer unique advantages and disadvantages:
| Consideration | Cloud ERP | On-Premise ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Cloud-based systems have a lower initial investment due to their monthly or yearly subscription pricing model but higher long-term price. | High upfront costs due to hardware and infrastructure investment, but can be advantageous for a long-term investment. |
| Accessibility | You can access the software anywhere with an internet connection, making it great for multi-site data consolidation. | Limited to on-site access unless additional systems for remote access are implemented. |
| Customization | Limited customization options compared to on-premise systems with a more out-of-the-box feel. | High degree of customization tailored to specific manufacturing workflows. |
| Maintenance | The vendor automatically updates the SaaS systems, so you always use the most current version and reduce IT load. | Requires a larger IT infrastructure for updates, troubleshooting, and hardware maintenance. |
| Updates | Automatic updates ensure the latest features and security patches are always available. | Manual updates must be managed by internal teams, increasing complexity. |
| Data Security | Data is stored offsite, raising concerns about sensitive information for some manufacturers. | Data is stored locally, offering full control but also increased responsibility for security. |
| Internet Dependency | Requires a stable internet connection for optimal performance. | Operates without internet dependency, ensuring reliability in offline scenarios. |
| Deployment Time | Faster deployment compared to on-premise systems. | Longer implementation timelines due to infrastructure setup and customization. |
Pricing
Pricing for manufacturing ERP varies, from small business software like JobBOSS², which starts at $3,000/year, to products like xTuple, which starts at $175/user/month. For growing businesses, Acumatica’s small business packages can range from $1,800 to $2,800/month, based on resource usage rather than per-user licensing.
Most of the time, you’ll need to contact the ERP developer for a pricing quote. Quotes will vary greatly depending on your needed functionalities, business size, and industry. Key factors that directly affect price include:
- Additional modules
- Training requirements
- Initial implementation
- Total user count
- Ongoing support and maintenance
On-premise software (locally installed):
This option generally involves a significant initial investment for product licensing, implementation and customization, training costs, and potentially new hardware if your existing IT infrastructure is insufficient.
- Licensing: $10,000 to $500,000+
- Implementation & Training: $20,000 to $50,000
- Annual Support: $2,000 to $25,000+
Cloud-based options (SaaS):
Cloud solutions usually come with lower upfront costs since you pay for the software over time. However, most systems still involve implementation costs for customization, data migration, and training.
- Implementation & Setup: $5,000 to $50,000+ (dependent on project scope)
- License Subscription: $5,000 to $200,000+ per year
- Additional Costs: $2,000 to $10,000+ per year for advanced modules, premium support, and storage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is manufacturing ERP different from MRP software?
When some businesses talk about manufacturing ERP software, they’re actually referring to a manufacturing or material resource planning solution, shortened to MRP software. While MRP focuses on tasks like purchase planning, shop floor control, and demand forecasting, manufacturing ERP goes further. It handles these functions and integrates applications for accounting, HR, and payroll. The range of tools can vary based on your manufacturing needs.
Over time, the term “MRP” has become a catch-all for various manufacturing software, making distinguishing between general manufacturing software and a full ERP system confusing.
Do ERP systems work directly with manufacturing machines?
Is QuickBooks a manufacturing software?
Smaller manufacturers and wholesalers may use QuickBooks Desktop Enterprise as an alternative to ERP software. However, it lacks tools like production planning found in dedicated manufacturing software. As businesses grow, they might find they need additional features like:
- Advanced material requirements planning
- Quality control
- Production management
- Bill of materials