The Best Logistics Software
In this article, we review software designed for 3PLs, freight forwarders, and trucking companies. We based our assessments on core features like real-time shipment tracking and route optimization to help you address rising costs and improve efficiency.
- User-friendly interface
- Customization options
- Excellent customer support
- Comprehensive range of features
- Heavy customization options
- Integration with shipping carriers
- Real-time tracking and analytics
- Fully automated support for pricing based on fixed rates and tariffs
- Customizable user interface
We’ve evaluated the best logistics software on the market, including GoFreight, Magaya, and Soloplan. After researching and comparing 20+ options, here are our top picks.
- GoFreight: Best Overall
- Magaya: Best for Freight Forwarding
- Soloplan: Best for Route Planning and Dispatching
- Linbis: Best Quote Management Tool
- Fishbowl Inventory: Best for Inventory Control
- Rose Rocket: Best for Trucking
- Extensiv 3PL Warehouse Manager: Best WMS for 3PLs
- Zoho Inventory: Great Dropshipping Management
- Elite EXTRA: Best for Last Mile Delivery
- Descartes Logistics: Modular Architecture
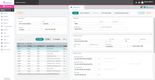
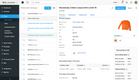
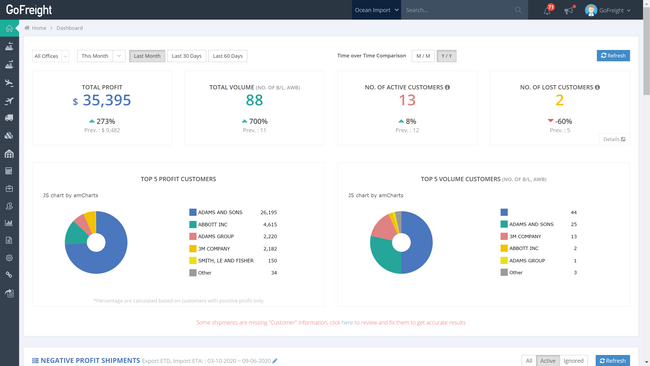
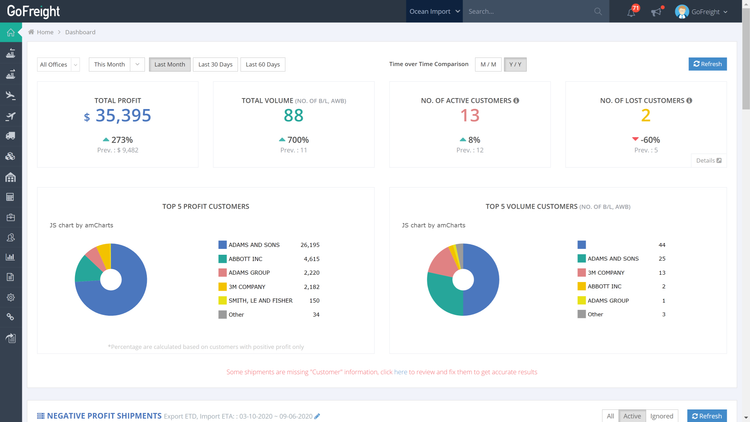
GoFreight - Best Overall
GoFreight offers a range of logistics features, such as freight forwarding, warehouse management, accounting, and customer relationship management.
The software integrates with various shipping carriers, enabling users to manage all their shipments in one place. It also offers customization options, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific business needs, such as:
- Branding: Users can customize the software’s branding with their own logo, colors, and themes to reinforce brand identity and make the software feel more personalized.
- Customizable documents: Users can customize documents such as invoices, bills of lading, and packing lists to match their branding and create a more professional image for customers.
GoFreight provides excellent customer support, with a dedicated team of experts available to assist users with any issues they may encounter.
The software is also constantly updated with new features and improvements based on user feedback. And in recent news, GoFreight has raised $28 million in a Series B funding round led by BOND, to become the “Shopify of freight forwarding” by further developing GoFreight’s platform with a focus on Europe and Southeast Asia.
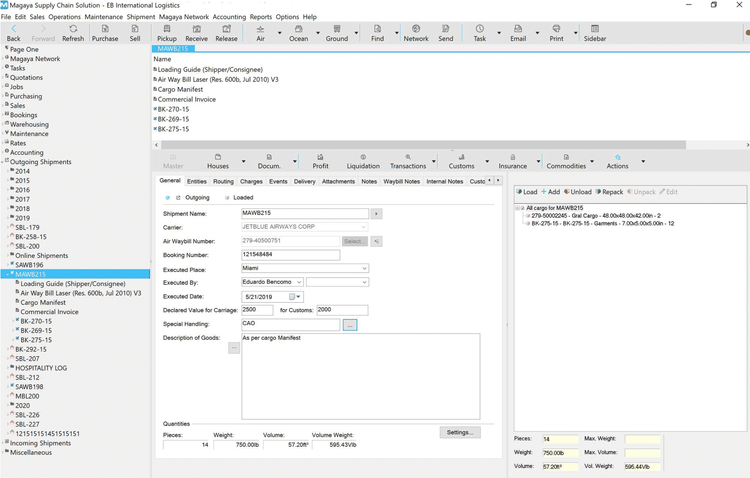
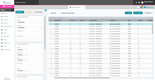
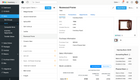
Magaya - Best for Freight Forwarding
Magaya Supply Chain handles freight forwarding, warehouse management, accounting, and customer relationship management.
The software also integrates with various shipping carriers and accounting systems, enabling users to manage all their shipments and financial data in one place.
Magaya Supply Chain is a top logistics software because it offers customization options on:
- Workflows: Automate specific tasks or processes to streamline operations and save time by reducing manual effort.
- User interfaces: Makes it easier to navigate and use the software.
- Reports: Helps businesses gain insights into their operations and make data-driven decisions.
- Data fields: Capture additional information not included in the standard fields to track specific data points relevant to their operations.
- Integrations: Enables data sharing and streamlining operations.
Additionally, Magaya Supply Chain provides excellent customer support, with a dedicated team of experts available to assist users with any issues they may encounter. The software is also constantly updated with new features and improvements based on user feedback.
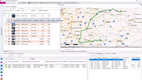
Soloplan - Best for Route Planning and Dispatching
Soloplan supports freight management, route planning, dispatching, and billing. It also provides real-time tracking and analytics, enabling businesses to optimize their operations and make data-driven decisions.
The software is targeted towards forwarders, transport companies, and others in the shipping industry. Usually, the size of the preferred client is mid-sized to global groups.
Customizable user interfaces let users tailor the software so that they can use the features most frequently used and not have to perform needless tasks to get there. By lowering the learning curve for new users, businesses can improve productivity and minimize errors. The software also offers training and support resources to all new companies during onboarding.
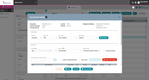
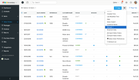
Linbis - Best Quote Management Tool
Linbis’s quote management tool brings speed and accuracy to your quoting process. We appreciate its user-friendly interface, with a clean layout that clearly separates different sections. As you input information, the software dynamically updates key metrics like weight, volume, income, and profit as you input information. Plus, a progress bar at the top helps you understand where you are in the workflow:
- Requested: Start by creating a new quote. Specify the service type, transportation mode, and quote dates. Enter your customer’s name and carrier or broker details, then choose payment terms.
- Pricing: Input shipment details, like origin, destination, and departure dates, then define pickup and delivery locations. Add items like vehicles, containers, and packages, then include charges manually or by configuring auto charges linked to your customer’s account.
- Revision: Review your quote summary and determine if any additional charges are needed.
- Sent: Send the completed quote via email to your customer or internal team.
- Approved: Receive an email notification confirming the recipient approved the quote. You also have the option to print the quotation for your records.
User-friendly with customizable charge configurations, Linbis makes billing more accurate and transparent for third-party logistics providers. Pricing starts at around $79 per month for one user. If multiple employees need access to this software, you’ll need to upgrade to the Premium plan at $299 per month for three users.
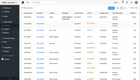
Fishbowl Inventory - Best for Inventory Control
Fishbowl Inventory is an inventory management software particularly suited for small and midsize businesses, Fishbowl stands out from other logistics solutions for its competitive pricing structure, making it an affordable option for those with budget constraints.
Seamless integration with QuickBooks is a significant advantage for users who rely on this accounting software, allowing for streamlined operations and efficient management of inventory.
What makes Fishbowl particularly appealing is its suitability for manufacturers with FDA or USDA audit requirements, emphasizing traceability and compliance.
5 Rose Rocket - Best for Trucking
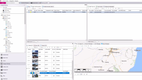
Rose Rocket is a transportation management system that can be used for overall logistics, especially within the modern trucking industry.
What really sets Rose Rocket apart is the Network TMS, which automates every aspect of the freight process, ensuring orders are efficiently dispatched and tracked for on-time deliveries. The software’s driver mobile app, customer portals, and partner portals enhance communication and visibility at every step.
Rose Rocket’s feature set, modern aesthetic, and regular updates make it a compelling choice for trucking companies looking to optimize operations, save time, and improve the shipping experience. Its integration with Google and the emphasis on creating a network of users and partners add to its value proposition in the logistics industry.
Extensiv 3PL Warehouse Manager - Best WMS for 3PLs
Extensiv 3PL Warehouse Manager is an all-in-one system for 3PLs to control everything from order fulfillment to shipment and the final invoice. Specifically, the mobile smart scanning tool is a great way for warehouses to optimize their workflows. The on-screen prompts and real-time accuracy help pickers and packers easily handle on-the-fly changes. And with the handheld scanners, your team can pick products fast and boost productivity.
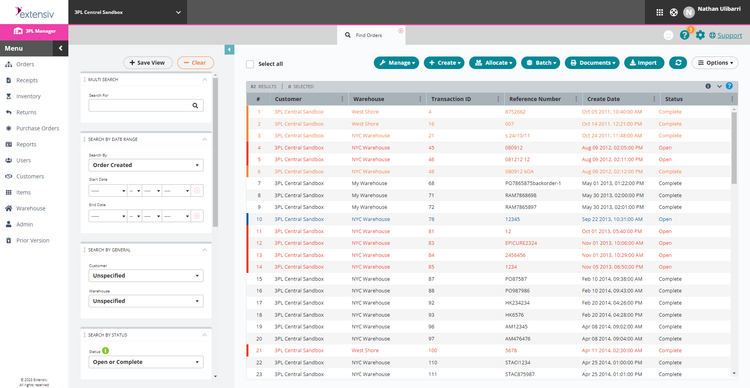
Additionally, you can receive against ASNs to ensure that incoming shipments have the correct items. That way, you don’t have to manually check labels or wait for your system to update. Once received, the orders go directly to the mobile scanner, which optimizes routing based on your preferred method, whether it’s multi-order or pick-to-bin. Not only does it make your warehouse more efficient, but it is also more accurate, leading to fewer incorrect shipments and returns.
Extensiv 3PL Warehouse Manager is best suited for small to mid-sized 3PLs that need greater inventory visibility and faster order fulfillment. Pricing starts at $599/month, but you will need a custom quote based on your company size, user count, and desired features.
Zoho Inventory - Great Dropshipping Management
Zoho Inventory streamlines and manages the dropshipping process. The platform allows businesses to create specific sales orders marked as “Dropship”. This indicates that the items in the order are to be procured from a vendor and shipped directly to the customer.
In addition, you can associate specific vendors with each product you intend to dropship, streamlining the purchase order creation process.
As with regular sales orders, dropship orders in Zoho Inventory are trackable. You can view the status of the order, whether the vendor has acknowledged it, whether the product has been shipped, and other relevant updates.
Elite EXTRA - Best for Last Mile Delivery
Elite EXTRA is a transportation logistics software that provides a third-party delivery network to help you outsource. This is useful for meeting increasing demand without expanding your fleet through established providers. It integrates with your eCommerce, POS, or ERP software to display your orders. Once they’re ready for dispatch, choose between several different carriers like Doordash, Rodie, and GoLocal. The system displays their respective cost and speed to ensure value for your business and on-time delivery for your customers.
You and your client will receive real-time updates regardless of which carrier you choose. This gives you transparency while your packages are in transit, so you have an accurate record of events, including proof of delivery and optional eSignatures for sensitive packages. Plus, the text notifications inform your customers of their order’s status to boost their experience.
Elite EXTRA lets you choose in-house or third-party delivery, allowing you to easily manage a hybrid system. Unfortunately, to receive pricing information, you must contact the developers directly for a custom quote. That said, the delivery network feature can be purchased independently or with its routing and dispatch system, giving you flexibility.
Descartes Logistics - Modular Architecture
Descartes Logistics offers a modular and interoperable logistics platform. The modular design means that businesses can select and implement only the specific components they need.
Descartes’ modules span across transportation management, streamlining contract negotiations, optimizing cargo loads, and ensuring regulatory compliance in customs.
The routing, mobile, and telematics module features sophisticated route planning tools, using advanced algorithms to factor in delivery windows and driver schedules. It also ensures real-time execution monitoring.
Descartes offers specialized modules for those in the brokerage and forwarding sectors. Tailor-made tools boost forwarding companies’ back-office operations, and brokers find everything they need for customs clearance and declarations.
What is Logistics Management Software?
Logistics software manages the supply chain of products from the point of origin to the point of consumption via transportation, inventory, warehousing, material handling, and packaging features. Also known as logistics management software (LMS), these solutions help businesses streamline shipping, track vehicle maintenance, optimize routes, and provide warehouse management capabilities for quick and efficient workflows.
Whether your business is inbound or outbound, web-based logistics software providers can help you streamline real-time operations.
Key Features
- Order Management: Capture, track, and fulfill orders across multiple sales channels. Manage invoicing, manage recurring orders, integrate with shipping carriers, clone orders, detect errors, handle back orders, manage returns, and reconcile with purchase orders.
- Inventory Management: Keep track of all items your company builds, buys, stores or sells. Measure stock levels, how quickly documents are submitted, the accuracy of shipments, and double-check product quantity and quality.
- Warehouse Management (WMS): Manage and coordinate inventory and actions throughout a warehouse or distribution center. Optimize picking and shipping to ensure higher order fulfillment accuracy, faster delivery times, efficient labor management, and increased real-time visibility of an order’s status.
- Transportation Management: Coordinate with shippers and vehicles to Plan, execute, and optimize the physical movement of goods, creating a complete transportation logistics software. Use route optimization to find fuel- and time-efficient routes. Consolidate shipments into the most efficient loads possible.
- Forecasting: Use real-time visibility to better anticipate customer demand, arrange resources, and plan production accordingly. Collect historical data on order volumes and inventory to continually update forecasts from sales.
Additionally, the best end-to-end logistics software should integrate with various shipping carriers, enabling users to manage all shipments in one place. The correct carrier is chosen based on the type of freight, the shipping services offered, and the overall costs.
How to Choose Software
Step 1: Define Your Business Needs
Begin by listing down the specific needs and goals of your logistics business. Are you looking for a solution to manage your fleet, streamline warehouse operations, or improve last-mile deliveries?
Step 2: Consider Pricing Structures
- Fixed Licensing vs. Subscription: Some software solutions might require a one-time purchase fee, while others operate on a subscription model. Determine which better suits your cash flow structure.
- Volume-based Pricing: Since logistics operations may have fluctuating volumes, some software providers offer pricing based on usage or volume. This can be economical for businesses with variable shipment volumes.
- Customization Costs: Customized features tailored to specific needs might carry additional costs. However, investing in such features can often lead to long-term cost savings by improving operational efficiencies.
Step 3: Evaluate Key Features
- Real-time Tracking: This allows businesses to monitor shipments in real-time, ensuring timely deliveries and efficient route planning.
- Inventory Management: A comprehensive system for monitoring inventory levels, predicting stock-outs, and planning restocks can improve warehouse operations.
- Fleet Management: Oversee vehicle maintenance, track fuel consumption, and manage driver performance to enhance overall fleet productivity.
- Automated Reporting: Automated reports on performance metrics, expenses, and revenues can support informed decision-making.
- User Interface: An intuitive, easy-to-use interface is vital for smooth daily operations and user adoption.
Step 4: Explore Integrations
- Accounting Software: Integration with software such as QuickBooks or Xero can streamline financial operations.
- CRM Software: Connecting to CRMs like Salesforce or HubSpot can enhance customer relationship management by aligning sales and delivery processes.
- eCommerce Software: For businesses involved in e-commerce logistics, integrations with platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, or Magento can streamline order processing and fulfillment.
- Communication Tools: Linking to communication platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams can foster better internal communication and coordination.
Step 5: Request a Demo or Trial Period
Before making a commitment, ask the software vendor for a demo or a trial period. This hands-on experience will help you better understand the software’s functionalities, ease of use, and suitability for your operations.
Step 6: Rank and Make a Decision
Based on the gathered information, rank the software options. Compare different solutions based on pricing, features, integrations, user reviews, and support.
Benefits
When utilizing a logistics management system, you can enjoy the following benefits:
More On-Time Shipments
Logistics software can refine your transportation methods by managing your data correctly. Shippers can reduce expected delivery timelines by using automation software to schedule shipments in a convenient, predictable path for your employee’s existing workloads.
Automation within your logistics process can also help make your business more predictable. This predictability can lead to improved data on your freight management, allowing you to make real-time adjustments as needed. Quality logistics software will let you run reports and make more informed decisions based on your trends and history.
Reduce Costs with Real-Time Freight Rates
Logistics software can help combat rising transportation costs and save money by comparing different shipping services, delivery agents, and shipping methods to find the most cost-effective option possible. Implementing online logistics software can provide real-time rates of various carriers, which can let you select your preferred carrier based on a number of factors, including cost.
Using software, your company may also find logistics service providers offering expedited shipping. This can improve the planning of your shipments and lead to higher customer satisfaction, benefits that should help make you a more profitable organization over time.
Anytime Access Via Cloud-Based Software
Cloud-based Software-as-a-Service, or SaaS, has been on the rise in nearly every industry. In the logistics industry, cloud-based software can help give a more visible and transparent view of your operations. And user-friendly mobile apps provide you with continual, real-time visibility into your logistics no matter where you are. Companies implementing SaaS logistics options to be more flexible, robust, and affordable.
Cloud technology is always connected to your resources and integrated with all departments. Important data such as carrier rates, party screening data, and your vendor list can be updated frequently with the most up-to-date information. This is particularly useful for eCommerce companies that need constant online visibility.
Cloud software gives your employees access from any location and provides a more affordable way of paying for it. The most cost-effective logistics management software products are billed on a subscription-based pricing model, meaning your organization only pays on an annual or monthly basis.
Pricing
The cost of logistics software can vary widely. The final price depends on several factors, including the size of your shipping operations, the number of shipments you handle, the number of users needing access, and whether the package includes support and hosting services. Here’s a general guide on what to expect based on your company size:
Low-Tier
- Company Size: 1-25 employees
- Average Yearly Cost: $5,000-15,000 per year
- Examples: Onfleet, Route4Me, TruckingOffice
Mid-Tier
- Company Size: 25-150 employees
- Average Yearly Cost: $15,000-100,000 per year
- Examples: Rose Rocket, FreightPath, Kuebix TMS
High-Tier
- Company Size: 150-500 employees
- Average Yearly Cost: $100,000-250k per year
- Examples: MercuryGate, 3Gtms, Blue Yonder TMS
Enterprise
- Company Size: 500+ employees
- Average Yearly Cost: $250,000+ per year
- Examples: SAP TM, Oracle Transportation Management, Manhattan Associates TMS
Software Types
Freight Forwarders
Freight forwarding logistics software helps freight companies manage cargo receipt, storage, and delivery. It also creates documents needed to move shipments, such as air waybills and bills of lading through quotations, bookings, and pickup orders. Freight forwarding works with air, ocean, and ground shipments. These solutions give step-by-step guides on how to handle your cargo and freight forwarding operations on a daily basis.
Logistics software for freight forwarders gives real-time access to information throughout the entire shipment process. Whether the logistics process is still in the order entry and purchasing stage, through bookings, customs processing, and security, or at the final shipment and delivery stage, freight forwarding logistics software will streamline the documenting of the shipping and transportation process. The software combines all areas of the logistics process to create a unified effort between procurement, inventory management, vendors, and carriers.
Trucking Software
Also known as trucking dispatch software, this subset of logistics software is made for trucking companies to automate the route optimization and scheduling processes for drivers. It includes tools for monitoring orders, trucks, trailers, and drivers from a centralized program. These solutions are designed to reduce the overall cost of running your fleet and improve productivity.
Some fleet management companies may rely on trucking software. Fleet management businesses will focus more on local transportation rather than long-haul. Usually, these businesses deal with shorter driving distances, so efficient route planning is a must. They also have strong asset management features that cover preventive maintenance on their vehicle fleet.
Dispatching and Scheduling
Dedicated dispatching software and tools within logistics software can ensure orders and deliveries are fulfilled in a specified time slot. Dispatchers can monitor trucks’ locations via GPS tracking capabilities. This shows how far along routes drivers are from nearing their destination, which helps detail the big picture of whether your business is operating on schedule or not.
Scheduling and dispatching tend to go hand in hand. When one driver completes an order, they can instantly be scheduled into an available slot, depending on their location and whether they are the most optimal person to handle the delivery.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Software
Third-party logistics software (3PL) is the use of a third-party business to outsource distribution, warehousing, and fulfillment services. Many 3PL businesses need their own logistics software to manage their clients and the variety of outsourced logistics services they are providing them.
3PL software allows these fulfillment operations to complete orders, manage their warehouses, coordinate their shipping, track what is in their inventory, and establish billing. 3PL software and logistics management software are almost identical in functionality, but 3PL software will provide more of a focus for third-party logistics operations.
Some of the top benefits of 3PL software include improved warehouse management and inventory control, labor management, efficient workflows, finding cheaper and reliable shipping, accurate billing, and document management.
Some logistics solutions are further categorized as standalone software:
- Demand forecasting and planning software
- Distribution enterprise resource planning (ERP)
- Inventory management
- Supply chain management
- Transportation management systems (TMS)
All of the software solutions on this list improve business processes by letting logistics companies manage the operations related to warehousing and shipping goods via trucks, airplanes, boats, trains, and more. However, logistics management offers end-to-end control of your supply chain.