12 Popular ERP Features: List of Key Capabilities
The 12 most popular ERP features include:
- Integrations and Third Party Add-Ons
- Workflow Automation
- Data Analysis
- Built-in and Custom Reporting
- Inventory Management
- Order Fulfillment
- Financial Management
- Customer Relationship Management
- Sales and Marketing
- Human Resources Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Manufacturing and Production
What are ERP Features?
ERP features are the specific capabilities integrated within an enterprise resource planning system.
ERP software provides business applications to help your business manage financials, sales, and operations. Breaking down these core 3 areas, you’ll find accounting capabilities such as a general ledger, accounts payable and receivables, and payroll. Within operations, you’ll be able to manage inventory and supply chain management. And finally, sales can include order management and procurement.
In addition to the above, companies can include human resource management (HRMS) and customer relationship management (CRM) for even greater control over their organization.
ERP Feature #1. Integration and Third Party Add-Ons
ERP integration is the process of connecting ERP software with other applications and/or systems to share data across them. Integrations–whether with eCommerce platforms or EDI tools–gives you a single source of truth, improving data accuracy across your company.
For example, syncing ERP with eCommerce platforms like Shopify or Magento expands functionalities, allowing you to maintain multiple online stores from one interface. Sales or purchase orders in Magento will reflect instantly in your ERP with real-time inventory changes. This ensures that your inventory levels are consistent across all sales channels.
ERP systems are highly sought after for their ability to communicate with various apps in the same ecosystem or with third-party business software. Having fully-integrated ERP means you have a cohesive suite of applications designed to work together.
Many businesses seek ERP systems primarily for the integration capabilities. They may be running two disparate systems (such as an accounting software and production scheduling software) and want to unify them. Additionally, integration helps employees communicate across departments, reducing data duplication, repeat orders, and bottlenecks caused by human error.
ERP Feature #2: Workflow Automation
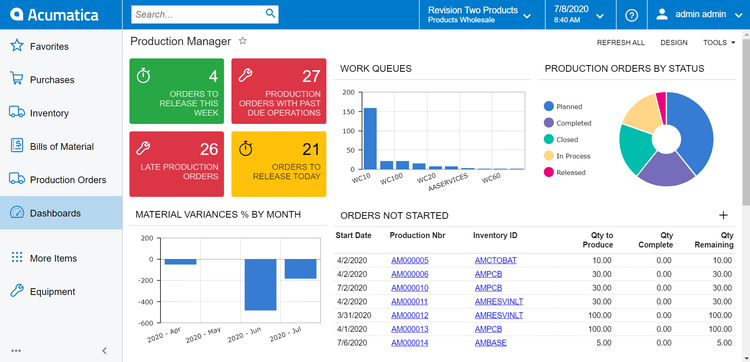
ERP automation can help streamline processes across multiple departments, like finance, sales, and inventory. This will help limit the required manual input and the time it takes to complete tasks. For instance, a manufacturing company could use ERP to automate inventory restocking. When stock levels drop below a certain threshold, the ERP can auto-generate purchase orders without manual input.
Originally designed to connect manufacturing processes, ERP systems enable communication between departments by automating workflows. When your production team complets an order, the ERP instantly notifies the sales department, enabling them to provide delivery timelines to customers. This helps knock down previous barriers organizations used to have when it came to silos.
Before, companies had to wait for other workstations or departments to complete their work before they could complete their own tasks, as they relied on the physical passing of information around. An ERP system automates business operations and stores data in a centralized location. This allows users to make informed decisions quickly, reducing wait times and improving operational efficiency.
ERP Feature #3: Data Analysis
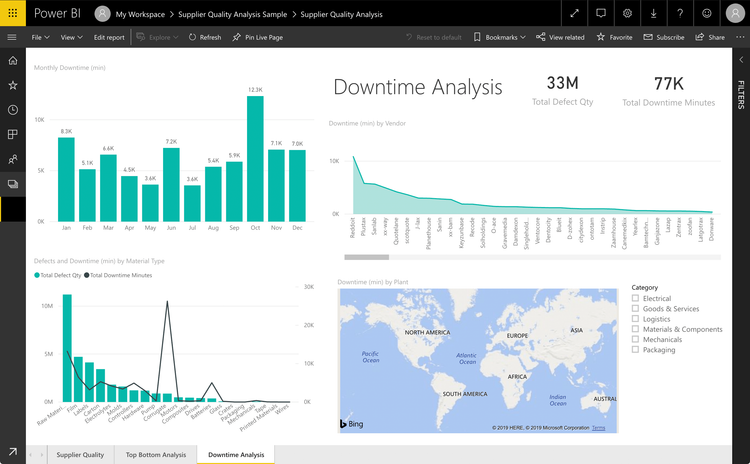
With every area of your business working under a unified ERP software, data on day-to-day operations can be shared across multiple entities and departments. Data broadcasts to multiple streams and allows companies to get real-time feedback for better decision-making.
Anytime a transaction occurs in your organization, whether an operational movement such as inventory control or a financial transaction such as payment for a sale, production, operations, and finance departments can access this data. Companies looking to stay ahead of their competition collect as much data as possible, which can later be displayed in visual and accessible formats.
Here are some key types:
- Dashboards: Customizable dashboards display KPIs like sales performance, inventory levels, and financial health. Generally, users can select which KPIs to track on their personalized dashboards.
- Infographics: Infographics include a mix of visuals, icons, and text to summarize complex ideas, like operational efficiency or annual financial performance.
- Charts: Graphs and charts visualize trends over a period of time, including trends (line charts), distributions (bar charts), or proportions (pie charts).
- Gantt Charts: Gantt charts provide a graphical presentation of project timelines, task assignments, and resource allocation.
- Interactive Visualizations: Dynamic graphics that allow users to manipulate elements like buttons and sliders or drill down into data points for deeper insights.
ERP Feature #4: Built-in and Custom Reporting
Reporting falls into the category of business intelligence tools designed to gather and sort historical data, create engaging visuals, and help analyze and report your findings. Reporting features occur in all types of business software, and reports can be created from nearly every data type. This includes contact management, marketing success levels, sales activity, and lead management.
- Built-in Reports: Many ERP systems come equipped with a suite of pre-configured reports to capture data behind common business processes. These include financial statements, inventory analysis, and sales performance reports. Built-in reports provide immediate insights without extensive setup.
- Customizable Reports: Most ERP platforms allow you to generate customized reports that cater to unique business requirements. You can modify existing reports or create new ones from scratch by incorporating specific data fields. This allows you to adapt your reporting processes as your company evolves and its needs shift.
The main goal is to offer intuitive reporting interfaces and visual data display capabilities. Business intelligence tools help companies base key decisions on information derived from financial and non-financial key performance indicators. Better reporting can empower both executives and stakeholders to make more informed business decisions, such as enhancing how businesses run and identifying problems before they occur.
ERP Feature #5: Inventory Management
Inventory management helps track stock across multiple locations, maintain optimal levels, and avoid overstock or stockout situations. ERP systems automate monitoring items as they move throughout the supply chain, from raw materials to finished products. The software supports this functionality through serial number tracking, barcode scanning, and automated replenishment.
Some ERPs support automated reordering, where purchase orders are automatically generated if your stock dips below certain thresholds. More advanced software will utilize demand forecasting built on historical sales data, current operational activities, and projected trends like seasonality. Overall, inventory management helps reduce holding costs and ensure the right products are always in stock.
ERP Feature #6: Order Fulfillment
ERP systems also help optimize the entire fulfillment process, from receipt of customer orders to shipment of finished products. This feature streamlines operations like order processing, packing, and delivery. Generally, ERP-driven fulfillment allows businesses to manage orders from multiple sales channels and integrate with shipping carriers for live order tracking.
Additionally, this functionality makes it easier to monitor order status and manage returns. It usually includes analytics and reporting tools to track metrics like shipping times and order accuracy. Order fulfillment is a popular tool because it helps meet customer expectations and reduce costs associated with re-shipping.
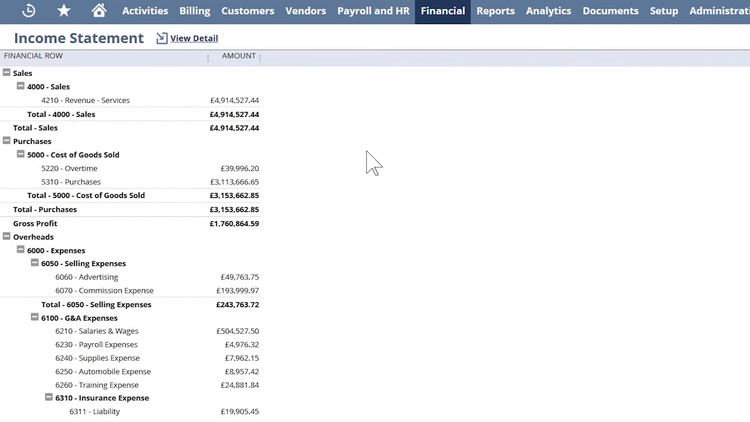
ERP Feature #7: Financial Management
Financial management helps businesses track income and expenses and plan for growth. Commonly referred to as accounting, financial management modules are designed to help businesses make better spending decisions, create accurate financial reports, and manage assets. Because of this, accounting can be thought of as a subset of ERP software.
Key features include:
- Budgeting and forecasting
- Cash flow management
- Payment and expense tracking
- Integration with banking services
- Audit trails
- Tax management
While many differences between ERP and accounting software exist, accounting tends to only provide features such as accounts payables, accounts receivables, general ledger accounts with reporting, and sometimes payroll. Meanwhile, ERP software provides all of the above as well as applications for supply chain management, inventory control, human resources, and eCommerce.
ERP Feature #8: Customer Relationship Management
CRM features provide an integrated toolset for managing client data and tracking interactions. CRM software complexity varies between programs, as it may include some combination of dedicated lead management, service tracking, order management, and marketing functionality.
CRM capabilities help give an integrated view of your customers and prospects, allowing you to get the most out of marketing, sales, and customer service efforts. The use of CRM features within an ERP software can help identify new prospects, assist with upselling, and reduce the time and labor costs involved with managing client data.
Additionally, lead scoring and segmentation help prioritize prospects based on engagement levels, letting your sales team focus on high-potential customers. CRM modules may also provide customer service tools for managing service tickets. Finally, integration with third-party apps like Mailchimp and Hootsuite enables improved interaction tracking across email, chat, and social media platforms.
ERP Feature #9: Sales and Marketing Tools
Sales forecasting and providing quotes are important parts of your overall sales management and marketing efforts. Forecasting applications utilize historical data and sales funnel status tracking to create better projections. Sales quotes allow you to create, share, and track customer-facing sales quotation documents.
Sales and marketing features within ERP software can also include point of sale (POS) capabilities to facilitate in-person or register-based customer payments, order entry to create sales orders, and eCommerce capabilities to help host online product catalogs and shopping carts.
In addition, you can create and manage marketing campaigns directly within your ERP, including social media promotions, targeted ads, and email marketing efforts. Classify customers based on demographics, preferences, and purchasing behavior to improve targeting. Then connect with popular marketing automation apps like HubSpot to enhance outreach.
ERP Feature #10: Human Resources Management
While more commonly found as a standalone solution, most ERP software will include some level of human resource capabilities. These capabilities store employee information and automate tasks involving the people in your organization, such as employee scheduling, recruitment, and boosting productivity. HR features in an ERP software help your organization achieve its goals by allowing managers to better allocate employee time and resources to become a more productive and profitable business.
Human resources also encompass payroll capabilities, which offer functionality for all payment tasks, including calculation of periodic wages, application of deductions, payment processing (check writing or direct deposit), and generation of payroll forms. Tying in with payroll is time tracking, which is useful for recording employee time both for payroll, as well as human resource management purposes.
You can simplify benefits administration, including health insurance and retirement plans, through automated enrollment. Provide career development resources and learning modules to promote professional development. Finally, HR tools can include compliance tracking and reporting tools to ensure your company is compliant with labor laws and regulations.
ERP Feature #11: Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) features within ERP software help manufacturers, logistics providers, distributors, suppliers, and retailers manage the flow of goods and services between locations. This provides assistance from the acquisition of raw materials to the delivery of a finished product to a customer.
SCM features can handle everything from beginning to end, including the demand planning, control, and execution of supply chain processes. Most importantly, it maximizes cost reduction opportunities in getting products provisioned from the vendor to the customer.
Core applications within supply chain management features include requisition and approvals management, purchase orders, vendor and supplier management, sales forecasting, warehouse management, and inventory control.
ERP Feature #12: Manufacturing and Production
Manufacturing ERP features prevent machine downtime and improve the quality and efficiency of the products created by your shop employees. More commonly known as MRP software, most manufacturing software tracks your purchased materials as well as current stock levels to ensure you always have what you need on hand and don’t have to wait for materials to come in to start a new order.
The history of ERP itself stems from the world of manufacturing, as MRP (materials requirements planning) is known as the predecessor to ERP software—created by manufacturers to better plan raw material requirements. The right manufacturing features in your ERP will give your shop a competitive edge by increasing operational efficiency, shortening order cycles, and making it easier to open new revenue streams.
Additionally, manufacturing features may include:
- Bill of materials (BOM) management: Generate and manage BOMs detailing raw materials, components, and subassemblies needed for production.
- Maintenance Management: Schedule predictive and preventive maintenance; monitor equipment performance to minimize downtime.
- Cost Tracking: Monitor direct and indirect production costs for each job, like labor costs, machine operating costs, overhead expenses, and indirect labor.
- Quality Control: Implement quality assurance tools to identify defects and adhere to regulatory standards.
- Production Scheduling: Visualize production timelines and resources with scheduling tools that adjust in real time based on resource availability and market shifts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The ongoing expansion of the ERP market makes it difficult for business leaders to answer some basic questions:
- How likely are you to find the features you need in mainstream ERP products?
- How does the feature breadth of your current ERP software stack up?
- Which features may require a third party add-on module?
- Will you require an industry-specific ERP solution?
To answer these questions, we studied a representative sample of mainstream ERP packages oriented for the SMB market. As a result, we were able to assign percentages to the likelihood of ERP products providing different features your company may require.
To make the data more digestible, we grouped features into 5 basic categories: accounting, operations, sales, human resources, and non-departmental.
Here’s what we found:
Mainstream ERP Software
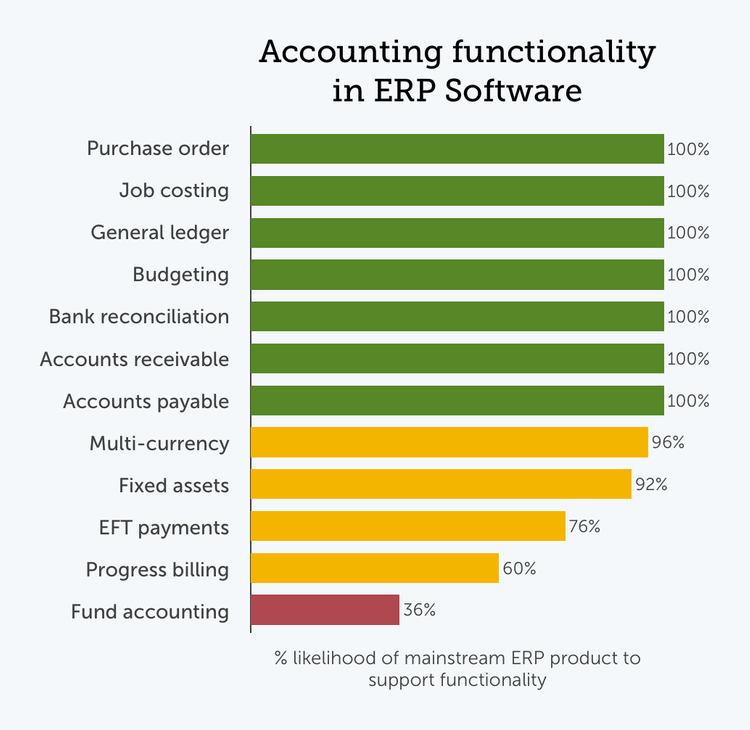
Mainstream ERP products reliably include a core set of accounting and financial management features. The consistent inclusion of ledgers like accounts payable, accounts receivable, and general ledger in ERP products is unsurprising. Strong financial management capability is a cornerstone of any ERP solution.
However, the breadth and sophistication of financial modules can vary. For instance, while electronic funds transfer (EFT) features provide a more advanced payment alternative to traditional check-writing, some mainstream ERP products lack the tool. Fund accounting and progress billing features appear even less frequently—a consequence of their relevance only for certain industries (non-profit/government and service/construction firms, respectively).
Operational ERP Software
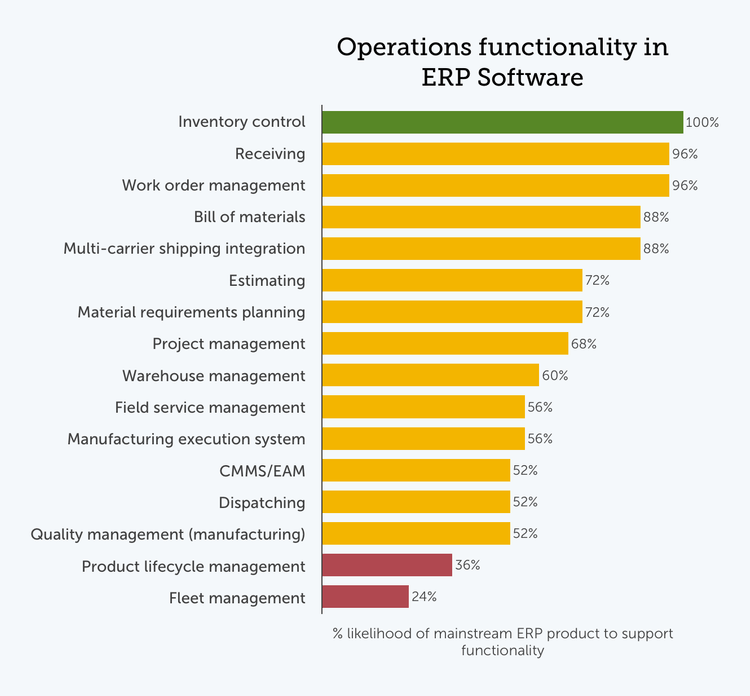
The ambition of ERP software developers is to comprehensively address both financial and operational management requirements. The reason it’s a challenging goal because while many accounting tasks are consistent between industries, operational needs vary substantially. However, there are some mainstream ERP programs that include features diverse enough to meet the needs of manufacturers, distributors, contractors, retailers, and service firms alike.
ERP originated in the manufacturing sector, so it is reasonable to expect a fairly strong representation of manufacturing-oriented functionality. Bill of materials and material requirements planning modules appear in a solid majority of mainstream ERP programs. However, nearly half of ERP products oriented toward the SMB market lack quality management and manufacturing execution system (MES) functions.
Features that deal with standard product tracking tasks such as shipping, receiving, and inventory control are more common. These functionalities apply to a broader audience. While they represent fundamental needs for manufacturers, they are also required by distributors, retailers, and many service-based companies.
Project and service-oriented businesses have distinct requirements for communicating project and job work instructions. Nearly all mainstream ERP products support work orders, and roughly two-thirds of ERP solutions include more in-depth project management features.
Service companies that perform their work off-site, though, may find it more difficult to locate the right solution to support their needs. Field service management and dispatching modules appear in only about half of SMB-oriented ERP systems. Fleet management modules are even rarer, with more than three-quarters of solutions not supporting this functionality.
Sales ERP Software
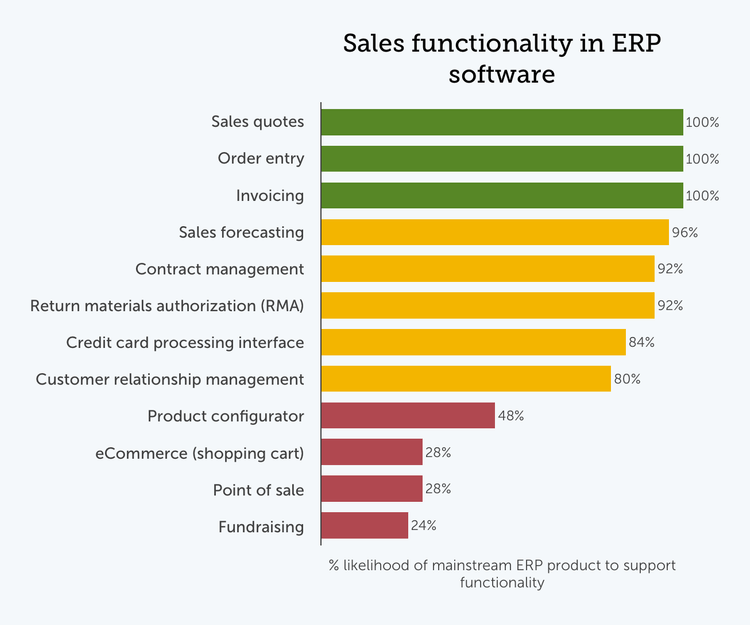
Support for sales-oriented tasks is another hallmark of ERP software. But differences in both sales channels and the nature of what is being sold lead to differences in the software required to support sales processes.
Standard invoicing and order entry appeared in each of the mainstream ERP solutions we surveyed. But support for more specialized sales channels such as direct and online retail is less common. In fact, based on our data, only about a quarter of SMB-oriented ERP products include native point-of-sale or eCommerce platforms.
Many ERP solutions provide functionality designed to enable other sales-related processes. A strong majority of ERP solutions now offer CRM features. Additional sales process tools such as contract management, RMA, and forecasting functionalities are also common.
HR and Payroll ERP Software
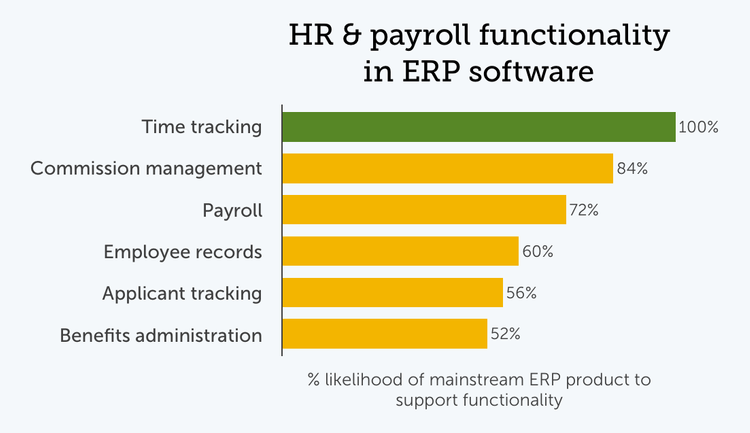
Payment-related functionalities are the most frequently represented human resources features in ERP software. Payroll and commission applications appear in all but a small percentage of mainstream ERP products. Time tracking features, which facilitate not only payroll but other employee management processes, are also consistently found in SMB-oriented ERP programs.
Modules for managing other human resources tasks, such as applicant tracking, benefits administration, and maintaining employee records, each appear in about half of the ERP products designed for the SMB market.
Non-Departmental ERP Software
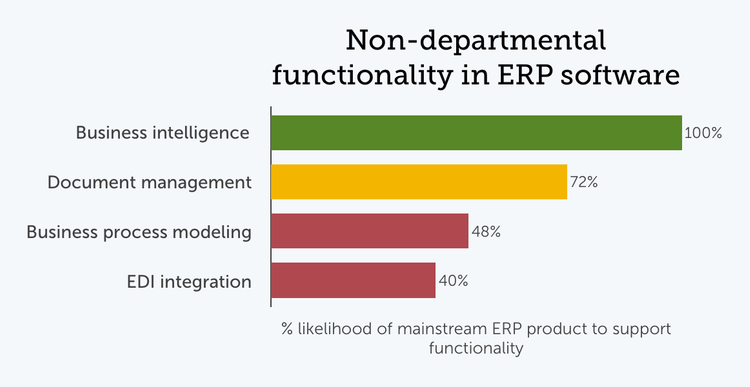
ERP features very often serve cross-departmental needs—but most map to a primary business function. There are a handful of ERP features that flexibly serve a wide variety of management or administrative requirements.
Most ERP features provide some management reporting capabilities but are too complex to be called business intelligence tools. BI software has a more specific meaning when applied to flexible reporting modules that offer advanced functionality, such as visual display dashboards. Even with this more restrictive business intelligence definition, BI modules can be consistently found in mainstream ERP products.
Similarly, many ERP modules offer application-specific document management capabilities. However, an application-neutral document management system can be useful for consistently managing a variety of business documents, and a majority of ERP products offer this functionality in some form.
Sources
For the representative sample, we selected 25 specific SMB-oriented ERP products based on three main factors:
- Product popularity,
- Solution applicability to multiple business types within the SMB market, and
- The clarity of product information provided by the software developers.
When calculating feature inclusion, we did not include features that would need to be provided by sister products from the developer or 3rd party add-ons.
Here is a comprehensive list of the 25 products studied:
- Acumatica ERP
- Deltek Vantagepoint
- Dynamics AX
- Dynamics GP
- Dynamics NAV
- Dynamics SL
- Epicor
- Exact Macola
- Certinia ERP
- IFS Cloud
- Infor VISUAL
- Intacct
- Netsuite
- Odoo
- Plex Cloud ERP
- Ramco ERP Suite
- Sage 100 ERP
- Sage 300 ERP
- Sage ERP X3
- SAP Business One
- SAP Business ByDesign
- SYSPRO
- Aptean Industrial Manufacturing ERP Traverse Edition
- Unit4 ERP
